当前位置:网站首页>Information System Project Manager - Chapter VII project cost management
Information System Project Manager - Chapter VII project cost management
2022-06-27 06:06:00 【lufei0920】
Information system project manager — Chapter vii. Project cost management
The process of project cost management
Through project cost management, try to control the actual cost of the project within the budget range . Ensure that projects are completed within a comparable budget .


One 、 Planning cost management
Planning cost management : The project cost structure has been formulated 、 Estimate 、 Standards of budget and control .

1、 Type of cost
• Variable cost : With production 、 The cost that varies with workload or time is variable cost . Variable cost is also called variable cost .
• fixed cost : Not with production 、 Non recurring costs that change due to changes in workload or time are fixed costs .
• Direct cost : The cost directly attributable to the project work is the direct cost . Such as project team travel expenses 、 Wages 、 Fees for materials and equipment used in the project .
• Indirect costs : Expenses allocated to the project from the general management expense account or the project cost shared by several projects , It forms the indirect cost of the project , Such as tax 、 Additional benefits and security costs, etc .
• Opportunity cost : Is the use of a certain time or resources to produce a commodity , The lost opportunity to use these resources to produce other best alternatives is the opportunity cost , It generally refers to one of the biggest losses after making a choice .
• Sunk cost : It refers to what has happened due to past decisions , And costs that cannot be changed by any decision now or in the future . Sunk cost is a kind of historical cost , It's an uncontrollable cost to an existing decision , Will greatly affect people's behavior and decision-making , The interference of sunk cost should be eliminated in investment decision-making .
2、 Example cost management plan

Two 、 Estimated cost
cost estimation : The process of preparing an approximate estimate of the funds required to complete the project activities .

1、 There are three main steps in project cost estimation
1) Identify and analyze component accounts of project cost , That is, the category of resources or services included in the project cost , for example : Labor cost 、 Material cost 、 Consulting fee, etc .
2) Accounts are formed according to the identified project cost , Estimate the cost size of each cost account .
3) Analyze the cost estimation results , Find various alternative costs , Coordinate the proportional relationship between various costs .
2、 Tool technology for cost estimation
2.1 Analogical estimation
Analogy estimation method is also called “ Top down estimation ”.
The basic operation steps of this method are :
First , The upper management personnel collect historical information about similar projects ;
secondly , Work with relevant cost experts to estimate the total cost of the current project ;
Again , Transfer the estimation results to the adjacent next level management personnel according to the hierarchy of the project work breakdown structure diagram , On this basis , They estimate the cost of their work and activities ;
Last , Continue to pass on their estimates to the next level of Management , Until the grass-roots personnel of the project .
Scope of application : Previous projects for analogy are very similar in form and substance ; When the project information is difficult to obtain ( Little mastery of project details ).
advantage : It's easy , Less time-consuming 、 Low cost .
shortcoming ( limitations ): Due to the uniqueness of the project , The estimation accuracy of this method may be low .
2.2 Parameter estimation method
Parameter estimation is the use of historical data and other variables ( For example, the square meter cost during construction , Number of coding lines in software programming , Required man hours , Function point method in software project estimation, etc ) The statistical relationship between ,
An estimation technique to calculate the cost of activity resources . The accuracy of this technical estimation depends on the complexity of the model and the amount of resources and cost data involved .
2.3 Reserve analysis
Emergency reserve
Emergency reserve : Many cost estimation experts are used to adding provisions or contingency reserves to the cost estimation of planned activities . Emergency reserve is the estimated cost freely used by the project manager , Used to deal with expected but uncertain events , These events are called “ Known unknown events ”, Is part of the project scope and cost baseline .
Manage reserves
Manage reserves : Planned for the future , But the budget reserved for possible cost changes . Not part of the cost benchmark , Used for processing “ Unknown unknown events ”.
The difference is shown in the table below 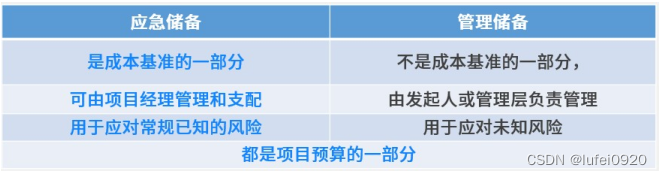
2.4 Bottom-up estimating
Bottom-up estimating : It is also called Bill of quantities . First, the cost of a single work package or activity is specified 、 Careful estimation ; Then report to the higher levels .
advantage : detailed 、 accuracy .
shortcoming : Time consuming 、 The cost of estimating itself is high .
2.5 quality cost
quality cost : Quality cost considerations and assumptions .
The cost of prevention : Prevent non conformance ( train );
Evaluate costs : The cost of evaluating to ensure compliance ;
rework ( Failure ) cost : Rework and repair 、 guarantee .
The first two items are consistency costs .
2.6 Seller's bid analysis
Seller's bid analysis : According to the bidding situation of the qualified seller , Analyze project cost .
3、 Estimated cost output

3、 ... and 、 Budget making
Cost budget : Aggregate estimated costs for all individual activities or work packages , To establish a cost benchmark .

1、 Comparison between cost estimate and cost budget

2、 Budget making — Tool technology
2.1 Cost summary

explain : The cost base includes contingency reserves but does not include management reserves ; The project budget includes management reserves .
2.2 Historical relations
Historical relations : There may be some historical relationships between relevant variables that can be used for parameter estimation or analogy estimation . Based on these historical relationships , Use project features ( Parameters ) To build a mathematical model , Forecast the total cost of the project .
2.3 Capital limit balance
Capital limit balance : Should be based on any restrictions on project funding , To balance capital expenditure . If you find a difference between the capital limit and the planned expenditure , The work schedule may need to be adjusted , To balance the level of capital expenditure . This can be achieved by adding mandatory dates to the project schedule .
3、 Output — Cost basis
Cost baseline ( Also called cost benchmark ) It is a time phased budget used to measure and monitor project cost performance . Usually, the S Curve form display . When to plan how much to spend , It is the scale of cost in time .
A project ( Especially big projects ) There can be multiple cost benchmarks , To measure all aspects of project cost performance . For example, expenditure plan or cash flow forecast is the cost benchmark for measuring expenditure ; In large projects , Management may require the project manager to monitor internal costs separately ( artificial ) And external costs ( Contractor's cost ) wait , Multiple baselines can be set .
3.1 Project cost budget table ( Cost basis )


explain : Total project budget = Cost basis + Manage reserves
Total capital requirements = Cost basis + Manage reserves
The project budget and fund demand amount are equal , The former is S curve , The latter is ladder like .
Four 、 cost control
cost control : Monitor project status , To update project costs : The process of managing cost baseline changes .

1、 cost control — Tool technology
1.1 Earned value management
Earned value management : It is a comprehensive range 、 Time 、 Methods of cost performance measurement . The workload will be planned 、 The actual cost is compared with the income of the actual earned value , Determine whether the cost and schedule are implemented as planned .
2、 Example of earned value calculation
1、 scene
For general planning 10 Tianzhong 100 A tree , The completion budget is 10000 element ;
The specific plan is to plant... Every day 10 star , The budget for each tree is 100 element , Spend every day 1000 element ;
2、 Now it's number one 5 The day is over , Budget and implementation :
According to the plan 50 A tree , Spending budget 5000 element ;
Actually planted 30 A tree , It actually cost 4500 element .
| The term | explain | give an example |
|---|---|---|
| Completion budget BAC | Project completion budget ( Without management reserves ) | Planning use 10 Tianzhong 100 A tree , The completion budget is 10000 element |
| actual cost AC | Actual cost of work done | Actually planted 30 A tree , The actual cost 4500 element |
| Plan value PV | The planned value of the work to be done | The first 5 The day is over , According to the plan 50 A tree , Spending budget 5000 element |
| Earned value EV | The planned value of the work actually done ( Approved budget value of completed work ) | Planted 30 A tree , It is planned to cost =30*100 element =3000 element ( Actually planted 30 A tree , According to the plan, a tree costs 100 element ) |
| Schedule deviation SV | EV-PV: Less than 0, Behind schedule ; Greater than 0 Ahead of schedule | EV3000 element -PV5000 element , Less than 0, Behind schedule |
| Progress performance index SPI | EV/PV: Less than 1, backward ; Greater than 1, advance | 3000/5000, Less than 1, Behind schedule |
| Cost deviation CV | EV-AC: Less than 0, Cost overruns ; Greater than 0, Cost savings | EV3000 element -AC4500 element , Less than 0, Cost overruns |
| Cost performance index CPI | EV/AC: Less than 1, Overspending ; Greater than 1, save | 3000/4500, Less than 1, Cost overruns |
| to complete performance index TCPI | Achieve the efficiency to be maintained according to the plan :TCPI=(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC) The efficiency to be maintained by the current completion estimate : TCPI=(BAC-EV)/(EAC-AC) | Greater than 1 Difficult to accomplish equals 1 Just finished less than 1 It's easy to do |
| ETC( Atypical ) | The completion of the project needs to be estimated ( Atypical / Special circumstances of the original budget , It won't happen again , Just planting trees is not skilled , Not in the future ):ETC=BAC-EV | ETC=10000-3000=7000 |
| ETC ( A typical ) | The completion of the project needs to be estimated ( Typical , Not in special circumstances , There will always be , For example, the ground is hard to open Ken ):ETC=(BAC-EV)/CPI | ETC=(10000-3000)/0.6667≈10499 |
| ETC ( Dual effects ) | SPI and CPI At the same time influence :ETC=(BAC- EV)/(CPI*SPI), It can be set according to actual conditions SPI and CPI The weight of | ETC=(10000-3000)/(0.6667*0.6)≈17499 |
| ETC ( re-calculate ) | ETC, There is something wrong with the estimate , Re estimate | There is a problem with the early estimation , Manual revaluation |
| EAC | Completion estimate :EAC=AC+ETC Or a quick formula for typical cases :{EAC=BAC/CPI} | EAC=4500+7000=11500( According to the atypical situation ) ;EAC=4500+10499=14999( As a typical case ) |
| Total completion time forecast | Supplementary knowledge : Planned total construction period /SPI ( A typical ); Atypical : The actual construction period that has occurred + Planned remaining duration | The original planned construction period 10 Months , at present SPI by 0.5, Then the predicted completion period =10/0.5=20 |
| VAC Deviation from completion | The difference between the completion budget and the new completion estimate :VAC=BAC-EAC | VAC=BAC-EAC |
explain :
The advantages of earned value technology : If you only look at the budget and actual expenses , There seems to be no overspending , because AC4500 It seems less than PV5000, But in terms of scope , Actually, it's overspending : Planted 30 A tree , According to the plan, it should take 3000 element , But it actually took 4500 element (EV<AC ).
Three reference rules for Earned Value Management estimation
There are three ways to estimate the implementation value of a work package (EV) The law of :
0-100: The most conservative . Only when it is completely completed will it be recorded as completed .
100-100: The most aggressive . As long as the work starts, it is recorded as done .
50-50: frequently-used . Remember to finish the work at the beginning 50%, Write it down after the work is finished 50%( Another kind of view : Remember to finish the work at the beginning 50%, Over work 50% Remember to complete ) .
Description of schedule deviation and cost deviation
Less than is not a good thing (SV、CV Less than 0, or API、CPI Less than 1): Behind schedule , Cost overruns
Greater than is a good thing (SV、CV Greater than 0, or API、CPI Greater than 1): Ahead of schedule , Cost savings
Is full of EV start

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

How to check the frequency of memory and the number of memory slots in CPU-Z?

Two position relay xjls-8g/220

Implementation of easyexcel's function of merging cells with the same content and dynamic title
![Navigation [machine learning]](/img/79/8311a409113331e72f650a83351b46.png)
Navigation [machine learning]

多线程基础部分Part3

Kubesphere cluster configuration NFS storage solution - favorite

JVM的垃圾回收机制

C语言练手小项目(巩固加深知识点理解)

竣达技术丨多品牌精密空调集中监控方案

Leetcode298 weekly race record
随机推荐
1317. convert an integer to the sum of two zero free integers
Dev++ environment setting C language keyword display color
How win 10 opens the environment variables window
项目-h5列表跳转详情,实现后退不刷新,修改数据则刷新的功能(记录滚动条)
竣达技术丨多品牌精密空调集中监控方案
Webrtc Series - Network Transport 7 - ice Supplement nominations and ice Modèle
Small program of C language practice (consolidate and deepen the understanding of knowledge points)
Comprehensive application of OpenCV in contour detection and threshold processing
30 SCM common problems and solutions!
Multithreading basic part part 1
[collection] Introduction to basic knowledge of point cloud and functions of point cloud catalyst software
427-二叉树(617.合并二叉树、700.二叉搜索树中的搜索、98. 验证二叉搜索树、530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差)
Logu p4683 [ioi2008] type printer problem solving
资深【软件测试工程师】学习线路和必备知识点
Wholestagecodegen of spark
30个单片机常见问题及解决办法!
Junda technology - centralized monitoring scheme for multi brand precision air conditioners
Implementation of easyexcel's function of merging cells with the same content and dynamic title
Two position relay xjls-8g/220
Functional continuous