当前位置:网站首页>Sword finger offer (medium level)
Sword finger offer (medium level)
2022-06-25 08:05:00 【Ruizxzx】
()(1) Search in a two-dimensional array
(2) Reconstruction of binary tree
utilize Arrays.copyOfRange(n,from,to) Perform array interception , Easier to implement .
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] vin) {
int pren = pre.length;
int vinn = vin.length;
if(pren==0 || vinn==0)
return null;
int node = pre[0];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(node);
for(int i = 0;i<vin.length;i++)
if(vin[i]==node){
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,1,i+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(vin,0,i));
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,i+1,pren),Arrays.copyOfRange(vin,i+1,vinn));
break;
}
return root;
}(3) The next node of a binary tree
(4) Path in matrix
Simpler code :
1、 Change the matrix path to ‘.’, Return to the original value after use . Instead of flag Matrix notation 1
2、 About i,j The judgment of whether to exceed the session is put at the beginning if of use , Super session is direct false;
3、 It's easy to get wrong , To index The last match is directly given to true
public boolean hasPath (char[][] matrix, String word) {
for(int i=0;i<matrix.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<matrix[0].length;j++){
if(deepPath(matrix,i,j,word,0))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean deepPath(char[][] m,int i,int j,String word,int index){
// There is no need for m[i][j]=='.' Set up false The judgment of the , Because only with word Only when the median value matches, will it pass , It has been included in m[i][j]!=word.charAt(index) In judgment
if(i<0||i>=m.length||j<0||j>=m[0].length||m[i][j]!=word.charAt(index))
return false;
if(index==word.length()-1)
return true;
char t = m[i][j];
m[i][j] = '.';
boolean res = deepPath(m,i-1,j,word,index+1)||
deepPath(m,i+1,j,word,index+1)||
deepPath(m,i,j-1,word,index+1)||
deepPath(m,i,j+1,word,index+1);
m[i][j]=t;
return res;
}(5) Cut the rope
The idea of dynamic programming is to start from the smallest problem , Then the results of its subproblems can be applied to larger problems .
If the sub problem occurs many times , Just one calculation .
1、 This topic n=2 and n=3 And cut into 2 and 3 The value is different. .
because n=2 and n=3 It must be cut, so it corresponds to 1,2. But in the cut paragraph 2 and 3 It is not necessary to continue cutting. The maximum is 2,3.
Others can be conveniently or in turn ( It is not necessary to exclude that the cutting length is 1 Section of , Because it is certainly not as big as other values )
public int cutRope (int n) {
// write code here
if(n==2)
return 1;
if(n==3)
return 2;
int[] max = new int[n+1];
max[1] = 1;
max[2] = 2;
max[3] = 3;
for(int i = 4;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<i;j++){
max[i] = Math.max(max[i],max[j]*max[i-j]);
}
}
return max[n];
}Note that when the index is negative
(7) Adjust the array order so that the odd Numbers precede the even Numbers ( One )
Note that this question is to keep the relative position inside the odd and even numbers after adjustment
(8) The entry node of a link in a list
The neglected problem here is ,slow Take a step ,fast Take two steps slow=pHead.next,fast=pHead.next.next;
error 1:slow=pHead,fast=pHead.next.next; This is equivalent to slow Not a step
error 2: Walk together c Step by step , from pHead Start
(9) The substructure of a tree
Let's focus on the recursive part . Easy to ignore , If at first root1==null It must be false
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1==null||root2==null)
return false;
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack();
stack1.push(root1);
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack1.pop();
if(isSame(node,root2)){
return true;
}
if(node.left!=null)
stack1.push(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
stack1.push(node.right);
}
return false;
}
public boolean isSame(TreeNode node,TreeNode root2){
if(node==null&&root2!=null)
return false;
if(root2==null)
return true;
if(node.val!=root2.val)
return false;
return isSame(node.left,root2.left)&&isSame(node.right,root2.right);
}(10) Pressure into the stack 、 Pop-up sequence
Space complexity is small : Consistent with the idea of using stack to assist , However, the part of the array that has been put on the stack is used as the stack .
top Point to the top of the stack ,pushIndex Point to the next number to operate on
public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA,int [] popA) {
if(pushA.length==0)
return true;
int pushIndex = 0,top=-1,popIndex=0;
while(popIndex<popA.length){
if(top>=0&&popA[popIndex]==pushA[top]){
top--;
popIndex++;
}
else{
if(pushIndex>=pushA.length)
return false;
else{
pushA[++top]=pushA[pushIndex];
pushIndex++;
}
}
}
return true;
}(11) The post order traversal sequence of binary search tree
For the use of stack Implementation of the recursive method , incomprehension
(12) The path of a value in a binary tree ( Two )
The recursion of this problem is consistent with the complexity of using queue time control , And non recursive implementation is troublesome , So I only practiced recursion .
(12) Binary search tree and double linked list
1、 Adopt the idea of middle order traversal , The convenient end is orderly
2、 utilize head Record the first node , use pre Record the previous node of the traversal sequence . Pay attention when it is necessary to pre When updating ,pre by null, At this time, the first node of the traversal sequence is marked as head;
3、 Don't fall into the trap of recording the next node , Can't do . Flexibility means pre.right Point to the present , current left Point to pre.
Recursive method implementation :
private TreeNode head = null;
private TreeNode pre = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null)
return null;
convert(pRootOfTree);
return head;
}
public void convert(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)
return ;
convert(root.left);
if(pre == null){
head = root;
}
else{
pre.right = root;
root.left = pre;
}
pre = root;
convert(root.right);
}Non recursive methods : You can also see the sequence traversal in the implementation of the action stack
1、 When the pointer is not null , Or if the stack is not empty, continue the operation
2、 utilize while Stack the left child node of the currently pointed node , Until there are no more left subtrees
This pointer is null , Or into the stack until there is no left subtree . Out of stack ( At this point, the operation on the outbound node is consistent with recursion )
3、 Point the pointer to the right child of the current stack node ,
At this time, the left child of this node must have operated , The next thing to do is the right child
That is, each time you traverse the leftmost node , Operation is completed , Point to the right child of the current node , cycle .
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null)
return null;
TreeNode head = null;
TreeNode pre = null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
while(pRootOfTree!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(pRootOfTree!=null){
stack.push(pRootOfTree);
pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.left;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(pre==null)
head = node;
else{
pre.right = node;
node.left = pre;
}
pre = node;
pRootOfTree = node.right;
}
return head;
}A simpler way , Use the substring of the string to obtain and splice .
Recursively transfer to the current new string , The remaining letters ,ArrayList<String>
Note here ,ArrayList Passing in a function is a copy of the address , Not just a copy of the parameters
public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList();
if(str==null||str.length()==0)
return null;
newString(str,"",result);
return result;
}
public void newString(String str,String newstr,ArrayList<String> result){
if(str.length()==0){
if(!result.contains(newstr.toString()))
result.add(newstr.toString());
return ;
}
for(int i = 0;i<str.length();i++){
newString(str.substring(0,i)+str.substring(1+i,str.length()),newstr+str.charAt(i),result);
}
}This question can be realized in three ways : Heap sort , Controlled quick platoon , Bubbling
For the idea of heap sorting : Use a big push , Because the value of the heap top is easy to obtain , Every time we have to see if it is before 4 Small , It depends on whether it is smaller than the current maximum , Therefore, a large top pile shall be used .
/*
The idea of priority queue is adopted here ( Big pile top )
Maintain a large top pile , If it is redundant after adding elements each time k Delete the largest
After all of them are added once, there's nothing left k The smallest .
PriorityQueue Usage of
Big pile top new PriorityQueue<Integer>((o1,o2)->(o2-o1));
Small cap pile new PriorityQueue< >();
Customize Queue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
});
*/
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList();
if(input.length==0||k==0)
return res;
Queue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((o1,o2)->(o2-o1));
for(int i=0;i<input.length;i++){
if(queue.isEmpty()||queue.size()<k)
queue.add(input[i]);
else{
if(input[i]<queue.peek()){
queue.poll();
queue.add(input[i]);
}
}
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
res.add(queue.poll());
}
return res;
}The purpose of the proposal is clearly understood
ArrayList Of add You can add... At the corresponding position ( Insert the element )
private ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList();
public void Insert(Integer num) {
int index = 0;
if(res.isEmpty())
res.add(num);
else{
while(index<res.size()){
if(num<=res.get(index)){
// If you add... Here , When you want to access the end, you cannot insert , Because it won't enter if
//res.add(i,num);
break;
}
index++;
}
res.add(index,num);
}
}
public Double GetMedian() {
if(res.size()%2==0){
int index1 = res.size()/2;
int index2 = index1-1;
return (res.get(index1)*1.0+res.get(index2))/2;
}
else{
return (double)res.get(res.size()/2) ;
}
}(16) In integers 1 Number of occurrences ( from 1 To n In integers 1 Number of occurrences )
Calculate each bit 1 Count the number of occurrences
In two parts , Suppose this digit 12345, Calculate hundreds of digits base=100
1、 The top 100 is 12 Then there are 12 individual 100~199 There are 12*100 One .(n/(base*10))*base
2、 After the hundreds, the hundreds are 345(n%(base*10)), That is, the calculation includes 100~199 How many numbers between .
so n%(base*10)<base 0 individual
base<= n%(base*10) <base*2 Yes n%(base*10)-base+1 eg:123 Yes 23+1 individual 100~123
n%(base*10) >= base*2 It includes 100~199 Yes base individual
public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int sum = 0;
int index = 1, flag = 10;
while(n/index!=0){
sum+=n/flag*index;
if(n%flag>=index&&n%flag<index*2)
sum+= n%flag - index +1;
else if(n%flag>=index*2)
sum+=index;
index*=10;
flag*=10;
}
return sum;
}(17) Make the array the smallest number
Time complexity :O(nlog2n), You can use the self-contained fast platoon
thought : Sort the array ; The sorting rules here , That is, whoever puts the smallest in front of it , It's not as small as putting it in front .
Everyone has such control , Then the final combination is the smallest .
public String PrintMinNumber(int [] numbers) {
if(numbers.length==0)
return "";
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList();
String result = "";
for(int i = 0;i < numbers.length;i++){
res.add(Integer.toString(numbers[i]));
}
res.sort(new Comparator<String>(){
public int compare(String s1,String s2){
return (s1+s2).compareTo(s2+s1);
}
});
for(String str:res){
result+=str;
}
return result;
}(18) Translate numbers into strings
See code for ideas :
public int solve (String nums) {
if(nums==null||nums.length()==0||nums.charAt(0)=='0')
return 0;
// First rule out special cases, that is, if there is 30、60, Not for 10,20 Can not be compiled directly . because 0 Must be combined with the previous number
for(int i = 1;i<nums.length();i++){
if(nums.charAt(i)=='0'&&nums.charAt(i-1)!='1'&&nums.charAt(i-1)!='2')
return 0;
}
// Reserved here 0, It is easy to calculate the position of the second character. It is possible to set the position of the second character
int[] kinds = new int[nums.length()+1];
Arrays.fill(kinds,1);
for(int i =2;i<kinds.length;i++){
// because kinds Subscript 1 The corresponding is nums Subscript 0, so i-2,i-1
// If the range after combining with the previous digit is 11~19,21~26
if((nums.charAt(i-2)=='1'&&nums.charAt(i-1)!='0')||(nums.charAt(i-2)=='2'&&nums.charAt(i-1)!='0'&&nums.charAt(i-1)<'7'))
kinds[i] = kinds[i-1]+kinds[i-2];
else// Cannot be combined or combined as 10,20 Is equal to the previous result
kinds[i] = kinds[i-1];
}
return kinds[kinds.length-1];
}(19) The greatest value of gifts
This time is mainly about the time complexity . In order to reduce the time complexity , use sum To record the maximum value of the upper right cell . If this output has a value, it will not recurse downward .
1、 Recursive implementation
public int maxValue (int[][] grid) {
int[][] sum = new int[grid.length][grid[0].length];
sumcount(grid,grid.length-1,grid[0].length-1,sum);
return sum[sum.length-1][sum[0].length-1];
}
public int sumcount(int[][] g ,int i, int j,int[][] sum){
if(i==0&&j==0){
sum[0][0] = g[0][0];
return sum[0][0];
}
if(sum[i][j]==0){
// following i==0 and j==0 Our judgment is to ensure that no cross-border access .
if(i==0)
sum[i][j] = sumcount(g,i,j-1,sum)+g[i][j];
else if(j==0)
sum[i][j] = sumcount(g,i-1,j,sum)+g[i][j];
// non-existent i==0 or j==0 Will not cross the line , Downward recursion is possible
else
sum[i][j] = g[i][j]+Math.max(sumcount(g,i-1,j,sum),sumcount(g,i,j-1,sum));
}
return sum[i][j];
}2、 Non recursive methods : Because every position must be acquired on it , The left is bigger . Make fixed . It can be accumulated and calculated from the beginning of dawn .
public int maxValue (int[][] grid) {
if(grid==null||(grid.length==0&&grid[0].length==0))
return 0;
for(int i = 0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(i==0&&j==0)
continue;
if(i==0)
grid[i][j] += grid[i][j-1];
else if(j==0)
grid[i][j] += grid[i-1][j];
else
grid[i][j] += Math.max(grid[i-1][j],grid[i][j-1]);
}
}
return grid[grid.length-1][grid[0].length-1];
}(20) The longest substring without repeating characters
thought : utilize Hashmap Implement Dictionary
If map This character already exists in , And in f,l Between ( Because at this time l Is the current position, so only judge whether it is greater than or equal to f) Then repeat .f Becomes a duplicate of the current position +1
The right border keeps moving , When the length increases, it will be updated
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) {
// write code here
if(s==null)
return 0;
Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap();
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int f = 0,l = -1;
for(int i = 0;i<s.length();i++){
if(map.get(s.charAt(i))!=null&&map.get(s.charAt(i))>=f){
f = map.get(s.charAt(i))+1;
}
l++;
if(l-f+1>max)
max=l-f+1;
map.put(s.charAt(i),i);
}
return max;
}(21) Ugly number
1、 Non recursive thinking , With minimum heap , Minimum number of POPs per time .( Is the current low i Number of samples ) then min*2、min*3,min*5 The team ( If this number does not exist in the heap , Use one HashMap Auxiliary judgment )
Values added in the middle may appear long The type exceeds int
public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if(index==0)
return 0;
Queue<Long> queue = new PriorityQueue();
Map<Long,Integer> map = new HashMap();
long num=0;
int sum=0;
queue.add(1L);
map.put(1L,1);
while(sum<index){
num = queue.poll();
sum++;
if(!map.containsKey(num*2)){
queue.add(num*2);
map.put(num*2,1);
}
if(!map.containsKey(num*3)){
queue.add(num*3);
map.put(num*3,1);
}
if(!map.containsKey(num*5)){
queue.add(num*5);
map.put(num*5,1);
}
}
return (int)num;
}2、 recursively

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int InversePairs(int [] array) {
if(array.length<=0)
return 0;
return merge(array,0,array.length-1);
}
public int merge(int[] arr,int l, int r ){
if(l>=r)
return 0;
int m = (r+l)/2;
int sum = merge(arr,l,m)+merge(arr,m+1,r);
int[] t = new int[r-l+1];
int lindex = l,rindex=m+1;
for(int k = 0;k<t.length;k++){
// The right side is finished , Then there must be no reverse order pairs
if(rindex>r){
t[k]=arr[lindex++];
}
// Can still enter for Cycle description , There must be one side left and right . namely rindex>m be lindex Must not be greater than l
//arr[lindex]<arr[rindex] Maybe this time rindex Greater than r Therefore, it should be regarded as the second judgment
else if(lindex>m||arr[lindex]<arr[rindex])
t[k] = arr[rindex++];
else{
sum=(sum+(r-rindex+1))%1000000007;
t[k] = arr[lindex++];
}
}
int k = 0;
for(int i = l;i<=r;i++)
arr[i] = t[k++];
return sum;
}
}(23) The second of binary search tree k Nodes
In fact, the idea of middle order traversal is used here , So it is the key to realize the middle order traversal with stack
/*
At present
The pointing node is not null( That is, there is still content to be put into the stack )
Stack is not empty. ( That is, there are still nodes not out of the stack )
Into the loop
Each time, loop to the leftmost node of the current node ( When the pointer becomes empty, the leftmost is completed )
The top of the stack is the current traversal element
Because the left side of the element out of the stack must have been put into the stack ( When you enter, you enter to the left ), So it points to its right
( If the right side is empty , Entering the next loop will not execute the stack , Go straight to the next )
*/
public int KthNode (TreeNode proot, int k) {
if(proot==null||k<=0)
return -1;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode node = proot;
while(node!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(node!=null){
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
k--;
node = stack.pop();
if(k==0)
return node.val;
node = node.right;
}
return -1;
}(24) Two numbers that appear only once in the array
- Time complexity :O(n)
- Spatial complexity :O(1)
- The method of thinking
The XOR operation is full and the XOR of the same number will be cancelled out , Same as 0 Different for 1.a^x^y^z^c^x^y^z^c^b=a^b
(1) Want to get a,b You need to divide the input into two groups . It is known that a And b Different , At least one XOR result must be 1. Therefore, you can use whether this bit is 0 To distinguish between .( Can be obtained from a^b Start looking for , Find the first one for 1 Bit )
(2) This is whether it is 0 The input can be divided into two groups .a^x^y^x^y=a;b^z^c^z^c=b
Then we can get the result of exclusive or for these two groups of contents a and b.
public int[] FindNumsAppearOnce (int[] array) {
// write code here
int ab = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<array.length;i++){
ab^=array[i];
}
int k = 1;
while((ab & k) == 0)
k = k << 1;
int[] num = new int[2];
for(int i = 0;i<array.length;i++){
if((array[i] & k) == 0)
num[0]^=array[i];
else
num[1]^=array[i];
}
if(num[0]>num[1]){
int t = num[0];
num[0] =num[1];
num[1]=t;
}
return num;
}(25) And for S Two numbers of
Methods with less time complexity
Method 1 :
Ideas :sum - a That is, another number corresponding to the current number . If in this array, you can output this pair .
To quickly locate when is no longer available HashMap Storage , This calculation package does not contain faster .
Be careful : May appear [1445]8,[1456]8. So you can't simply store the number in the hash first , Then traverse from the beginning
Otherwise [1456]8 in ,4 Include but be yourself , If you judge whether you are yourself by subscript , be [1445]8 Deposit in key4, Front will cover back .
Therefore, it should be kept at the same time , Compare . Current vs. previous .
If it exists before the matching number, enter the number pair ; If not, deposit hash surface . The above two accidents can be excluded .
public ArrayList<Integer> FindNumbersWithSum(int [] array,int sum) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList();
if(array.length<=1)
return res;
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0;i<array.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(sum-array[i])){
res.add(array[i]);
res.add(sum-array[i]);
return res;
}
else{
map.put(array[i],i);
}
}
return res;
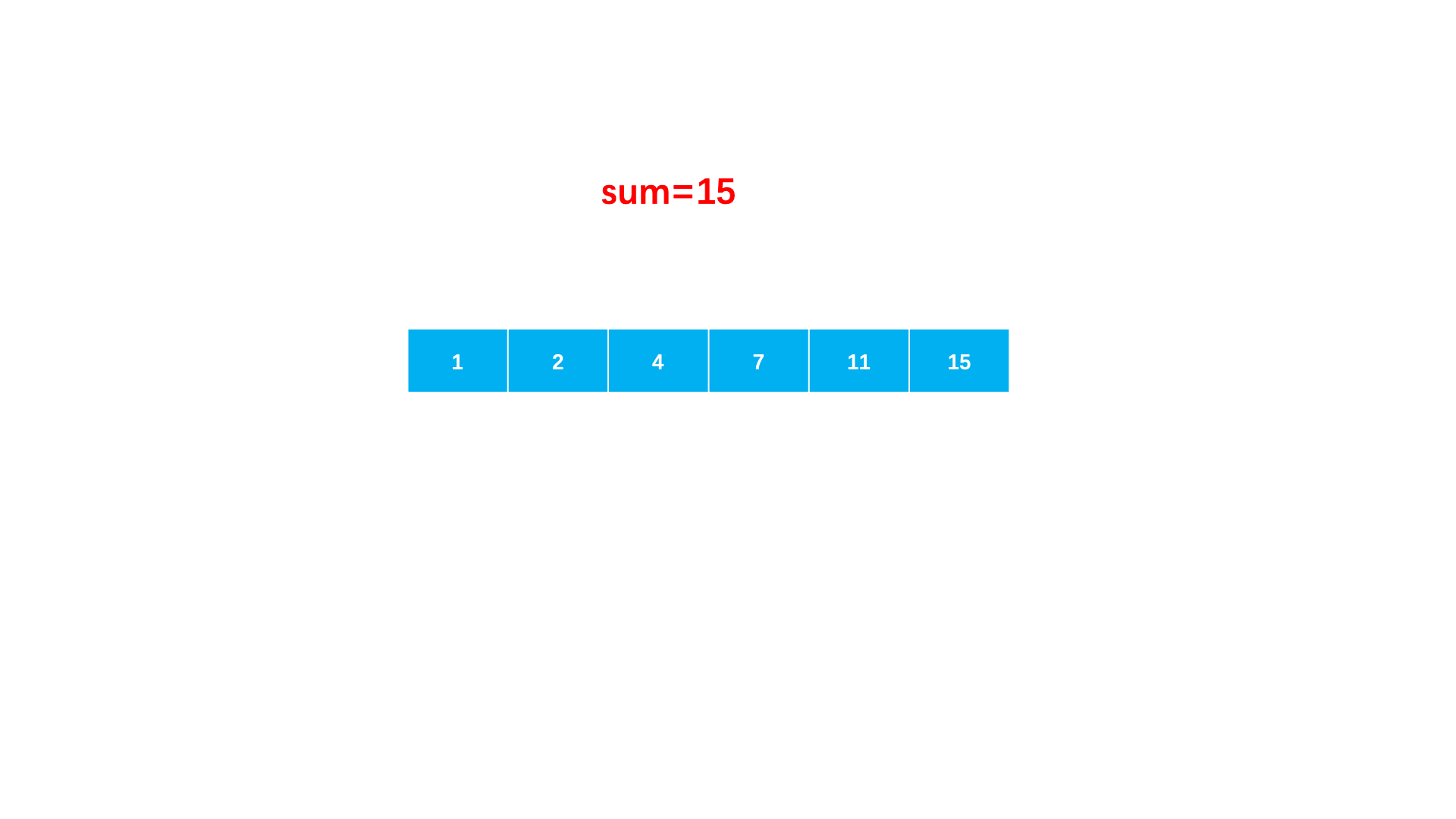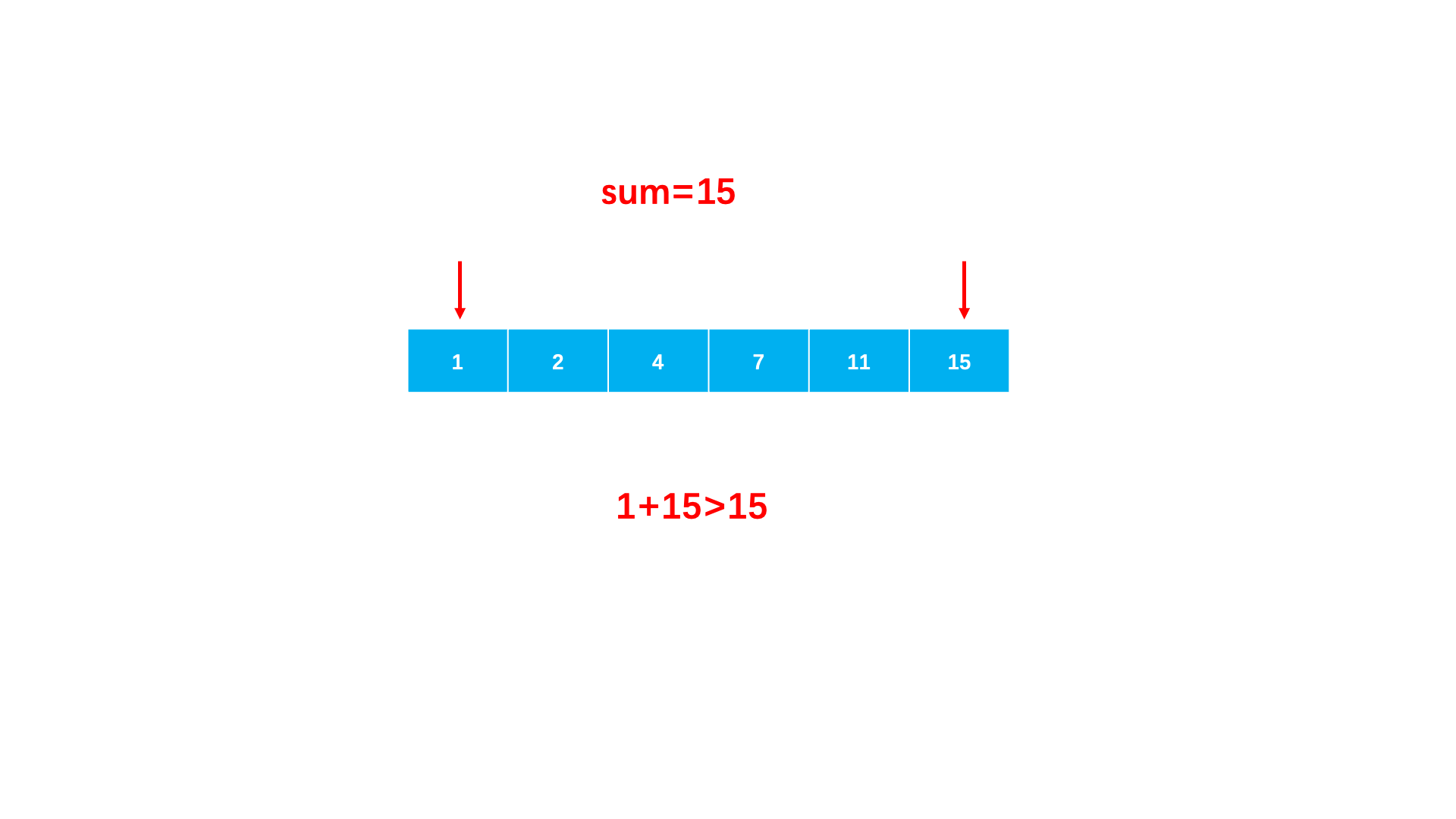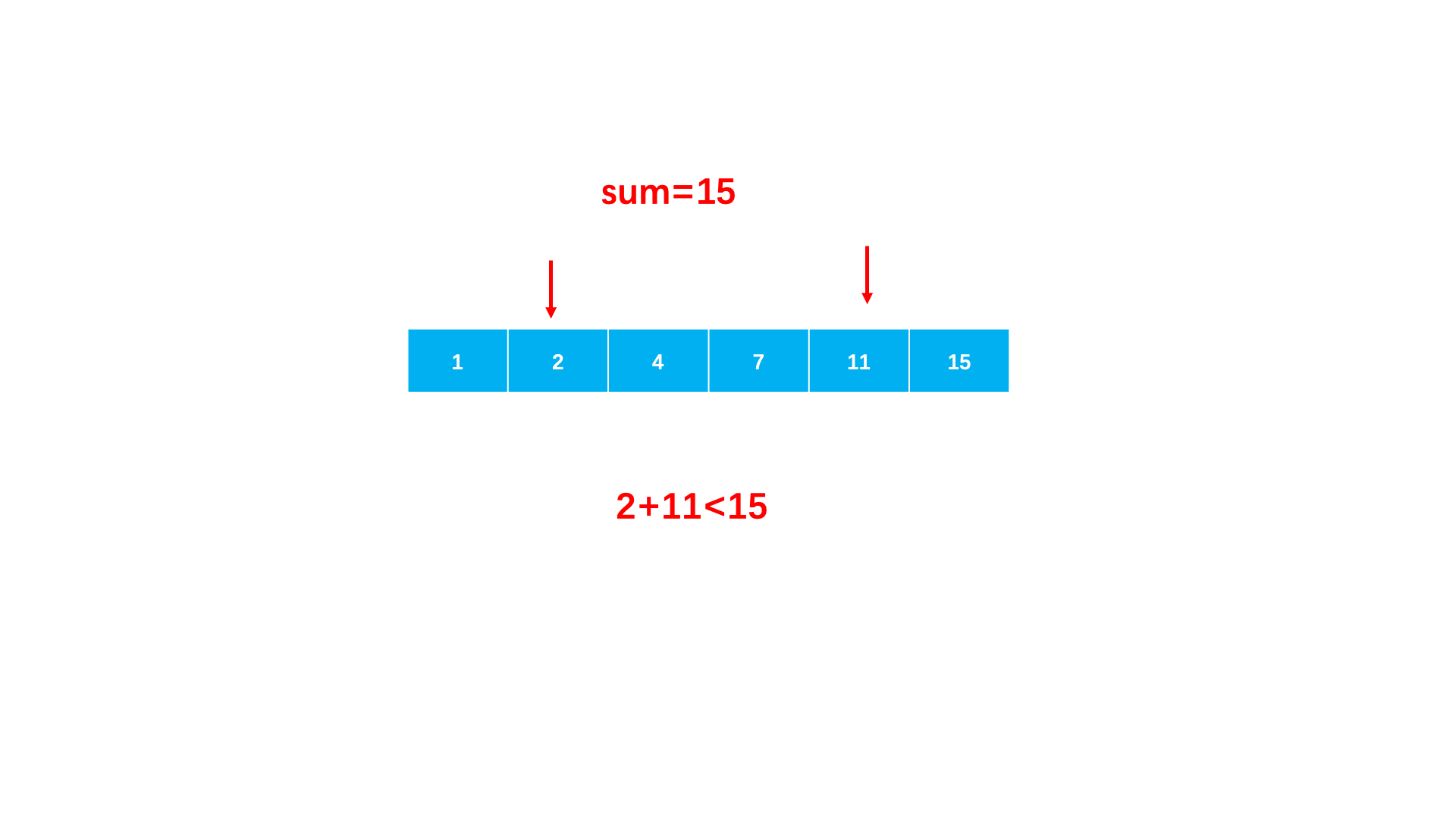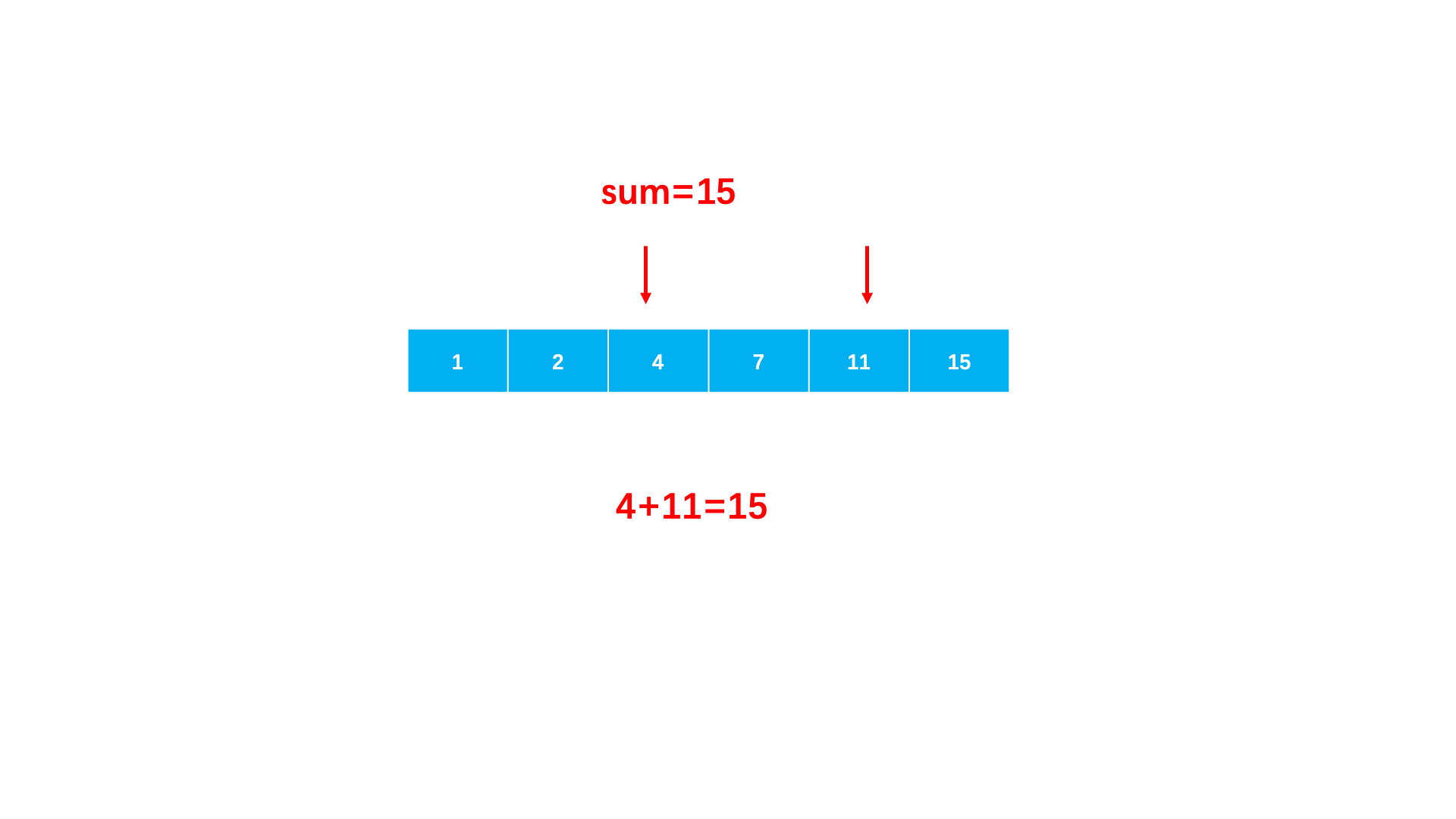
}Method 2 : Make full use of the order of the array . You can start by pointing to the minimum value with a pointer , A pointer to the maximum value ends .
When the sum of two numbers is greater than sum, Explain that you need to point to smaller , So the right pointer moves .
When the sum of two numbers is less than sum, Explain that you need to point to a larger , So the left pointer moves .
public ArrayList<Integer> FindNumbersWithSum(int [] array,int sum) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList();
if(array.length<=1)
return res;
int l = 0, r = array.length-1;
while(l<r){
if(array[l]+array[r]>sum)
r--;
else if(array[l]+array[r]<sum)
l++;
else{
res.add(array[l]);
res.add(array[r]);
return res;
}
}
return res;
}(26) Left rotation string
(27) The path of a value in a binary tree ( Two )
边栏推荐
- Basic use of ActiveMQ in Message Oriented Middleware
- 洛谷P3313 [SDOI2014]旅行(树链+边权转点权)
- ffmpeg+SDL2实现音频播放
- FM信号、调制信号和载波
- 企业全面云化的时代——云数据库的未来
- Analysis and utilization of Microsoft Office Word remote command execution vulnerability (cve-2022-30190)
- Atlas conflict Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (cve-2022-26134 vulnerability analysis and protection
- [Video] ffplay uses MJPEG format to play USB camera
- 洛谷P2839 [国家集训队]middle(二分 + 主席树 + 区间合并)
- Atlas conference vulnerability analysis collection
猜你喜欢

图像超分综述:超长文一网打尽图像超分的前世今生 (附核心代码)
FM信号、调制信号和载波

剑指offer刷题(中等等级)

三台西门子消防主机FC18配套CAN光端机进行光纤冗余环网组网测试

Force buckle 272 Closest binary search tree value II recursion

Electronics: Lesson 012 - Experiment 13: barbecue LED

使用报文和波形记录分析仪RoyalScope的帧统计功能排查CAN总线偶发性故障

Electronics: Lesson 010 - Experiment 9: time and capacitors

Introduction to the main functions of the can & canfd comprehensive test and analysis software lkmaster of the new usbcan card can analyzer

50 pieces of professional knowledge of Product Manager (IV) - from problem to ability improvement: amdgf model tool
随机推荐
【补题】2021牛客暑期多校训练营6-n
现在通过开户经理发的开户链接股票开户安全吗?
Set the textalign property of the label control in C to control the method of text centering
深度学习系列48:DeepFaker
CAN总线工作状况和信号质量“体检”
PH neutralization process modeling
Drawing of clock dial
基于Anaconda的模块安装与注意事项
产品经理专业知识50篇(四)-从问题到能力提升:AMDGF模型工具
C disk drives, folders and file operations
Pychart's wonderful setting: copy immediately after canceling the comment and bring #
Anaconda based module installation and precautions
力扣 272. 最接近的二叉搜索树值 II 递归
TCP MIN_RTO 辩证考
[daily training] 207 Class Schedule Card
C WinForm panel custom picture and text
C control refresh
417-二叉树的层序遍历1(102. 二叉树的层序遍历、107.二叉树的层次遍历 II、199.二叉树的右视图、637.二叉树的层平均值)
电子学:第013课——实验 14:可穿戴的脉冲发光体
How to create a new branch with SVN