当前位置:网站首页>Use yolov5 to train your own data set; Installation and use of yolov5; Interpretation of yolov5 source code
Use yolov5 to train your own data set; Installation and use of yolov5; Interpretation of yolov5 source code
2022-06-22 03:36:00 【m0_ sixty-seven million four hundred and one thousand six hundr】
* disclaimer :
1 This method is for reference only
2 The operation methods of other bloggers have been copied , To paste the path .
3*
Scene one :Anconda Environment basic operation
Scene two :yolov5 Use
Scene three :yolo v5 Train your own dataset
Scene 4 :yolov5 Source code interpretation
…
Scene one :Anconda Environment basic operation
1: Basic commands
see Anaconda Version information for conda -V
see python Version information python
open Jupyter Notebook command jupyter notebook perhaps ipython notebook
sign out python Input environment : ctrl+z
The command line terminates a running program command : ctrl + c
see opencv Version information :
2: Create and use your own virtual environment
Generate a file called jiance Environment , Used for identification tasks :conda create -n jiance python=3.7
Enter this environment , That is to activate the environment source activate jiance windows Next : activate jiance
The next step is In this environment, you can download the packages you need pip insatll numpy Or is it conda install numpy=1.10
Get out of this environment :source deactivate
See what environments have been created :conda info --envs
View the created package :conda list
Quit this jiance Environmental Science : linux Next source deactivate windows Next deactivate
3: Delete package 、 Delete environment Or update the package
Delete numpy package :conda remove numpy Or designate conda remove numpy=1.10
to update numpy package : conda update numpy
to update jiance All the bags inside : conda update - -all
Search for numpy package : conda search numpy
Delete jiance The command of this environment : conda env remove -n jiance
4: Shared environment
For example, my present jiance I downloaded a lot of packages in this environment , Equipped with a recognized environment , Others want to use my environment or I want to quickly migrate projects from my computer to other computers :
First enter my environment : activate jiance Execute this statement conda env export > name .yaml
for example conda env export > environment.yaml
The first part of the command conda env export Used to output the names of all packages in the environment
Through the second half environment.yaml Save it to and name it “environment.yaml”

What others need to do is get this yaml file : conda env create -f environment.yaml
Scene two :yolov5 Use
1: install pytorch (windows nothing GPU) Environmental Science
Switch to the above jiance In the environment of
conda install pytorch==1.8.0 torchvision==0.9.0 torchaudio==0.8.0 cpuonly
2: download yolo v5
3: Unzip the downloaded project , use pycharm open , Then associate the project with us in Anconda Create a good virtual environment in 
4. Download dependency
Mode one : stay pycharm Execution in terminal pip install -r requirements.txt

Mode two : Enter... At the top of the project folder cmd You can go to windows Open the terminal to the project folder , Switch to virtual environment activate jiance And then type the command pip install -r requirements.txt
5: Download the weight file
test
The path in the command It can be changed flexibly ,yolo v5 The version of now has 6 A version update , The directory structure of each version may be different , for example bus.jpg stay v1 The version is inference Under the folder , stay v6 Version is in data Under the folder , The following command is v6 Version of ( It's just that the path is different )

The test image
python detect.py --source=data/images/bus.jpg
python detect.py --source=data/images/people.jpg --weights=weights/yolov5s.pt
The confidence level exceeds 0.4 Show it
python detect.py --source=data/images/people.jpg --weights=weights/yolov5s.pt --conf 0.4


Test video
python detect.py --source=data/images/1.mp4 --weights=weights/yolov5s.pt
camera
python detect.py --source 0
python detect.py --source 0 --weights=weights/yolov5s.pt
Model integration detection
python detect.py --source=data/images/people.jpg --weights=weights/yolov5s.pt yolov5l.pt
Change the test save path 
…
Scene three :yolo v5 Train your own dataset


1.1 Training skills
object detection YOLOv5 anchor Set up
yolov5 anchors Setup details
【Python】 Calculation VOC Format XML File the target area and aspect ratio and generate histogram 

Remember to put it in jyputer It is convenient to save and view the results
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Jan 10 21:48:48 2021
@author: YaoYee
"""
import os
import xml.etree.cElementTree as et
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdm
import cv2
path = ".......................Annotations" # Your path
files = os.listdir(path)
area_list = []
ratio_list = []
def file_extension(path):
return os.path.splitext(path)[1]
for xmlFile in tqdm(files, desc='Processing'):
if not os.path.isdir(xmlFile):
if file_extension(xmlFile) == '.xml':
tree = et.parse(os.path.join(path, xmlFile))
root = tree.getroot()
filename = root.find('filename').text
# print("--Filename is", xmlFile)
for Object in root.findall('object'):
bndbox = Object.find('bndbox')
xmin = bndbox.find('xmin').text
ymin = bndbox.find('ymin').text
xmax = bndbox.find('xmax').text
ymax = bndbox.find('ymax').text
area = (int(ymax) - int(ymin)) * (int(xmax) - int(xmin))
area_list.append(area)
# print("Area is", area)
ratio = (int(ymax) - int(ymin)) / (int(xmax) - int(xmin))
ratio_list.append(ratio)
# print("Ratio is", round(ratio,2))
square_array = np.array(area_list)
square_max = np.max(square_array)
square_min = np.min(square_array)
square_mean = np.mean(square_array)
square_var = np.var(square_array)
plt.figure(1)
plt.hist(square_array, 20)
plt.xlabel('Area in pixel')
plt.ylabel('Frequency of area')
plt.title('Area
'
+ 'max=' + str(square_max) + ', min=' + str(square_min) + '
'
+ 'mean=' + str(int(square_mean)) + ', var=' + str(int(square_var))
)
plt.savefig('aabb1.jpg')
ratio_array = np.array(ratio_list)
ratio_max = np.max(ratio_array)
ratio_min = np.min(ratio_array)
ratio_mean = np.mean(ratio_array)
ratio_var = np.var(ratio_array)
plt.figure(2)
plt.hist(ratio_array, 20)
plt.xlabel('Ratio of length / width')
plt.ylabel('Frequency of ratio')
plt.title('Ratio
'
+ 'max=' + str(round(ratio_max, 2)) + ', min=' + str(round(ratio_min, 2)) + '
'
+ 'mean=' + str(round(ratio_mean, 2)) + ', var=' + str(round(ratio_var, 2))
)
plt.savefig('aabb.jpg')
First, calculate the aspect ratio , And then in yolov5 Create a new... In the program python file test.py, Calculate the anchor box manually :
import utils.autoanchor as autoAC
# Recalculate dataset anchors
new_anchors = autoAC.kmean_anchors('./data/mydata.yaml', 9, 640, 5.0, 1000, True)
print(new_anchors)
Output 9 The new anchor box is calculated based on its own data set , You can replace it with the configuration file you are using in order *.yaml in ( such as yolov5s.yaml) , You can train again .



Hyperparametric evolution Hyperparameter Evolution
python train.py --resume
During the training , If the size of your picture is 320x256, You want the input of the model to be the same 320x256. Then you just need to add
--img 320 --rect
1.2 Train your own dataset
First step : Use labelImg Label your own dataset
Don't have a Chinese path
B Station teaching video —>LabelImg Instructions for using the labeling tool
Training ideas : yolov5 Two training methods are supported : The first method is to write the path of the training file directly to txt File in . The second method is to directly transfer in the folder where the training files are located . Training v1.0 Code for ( The other versions are the same , It's just v1.0 Code may be more prone to problems )
The second step : Divide the training set / Test set
We follow the second way :
.
Create the following folders , stay yolov5 Create mydata Folder , And then in mydata Under the folder.
all_images Put pictures in the folder
all_xml Put in the folder xml file
make_txt.py Files are used to partition data sets
train_val.py Folders are used to convert labels
Pay attention to two py The document should be built in mydata Under the folder

make_txt.py
import os
import random
# Nothing needs to be changed , Just change the division ratio below
trainval_percent = 0.1
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'all_images'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv) # From all list Back in tv A number of items
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
if not os.path.exists('ImageSets/'):
os.makedirs('ImageSets/')
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '
'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()

The third step : Next, prepare labels, Also is to voc Format conversion to yolo Format
function train_val.py, On the one hand, the document will all_xml in xml The file to txt File in all_labels In the folder , On the other hand, generate the data storage architecture required for training .( Here, if your data is directly txt If you want to change the label, you can comment out the function of label conversion ) The code is as follows :

train_val.py
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
import shutil
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
sets = ['train', 'trainval']
# Change here ...............
classes = ['dog' , 'cat']
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('all_xml/%s.xml' % (image_id))
out_file = open('all_labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '
')
wd = getcwd()
print(wd)
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('all_labels/'):
os.makedirs('all_labels/')
image_ids = open('ImageSets/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
image_list_file = open('images_%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
labels_list_file=open('labels_%s.txt'%(image_set),'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
image_list_file.write('%s.jpg
' % (image_id))
labels_list_file.write('%s.txt
'%(image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id) # If the tag is already txt Format , Comment out this line , be-all txt Store in all_labels Folder .
image_list_file.close()
labels_list_file.close()
def copy_file(new_path,path_txt,search_path):# Parameters 1: Where to store the new file Parameters 2: Set up for the previous step train,val Path of training data txt file Parameters 3: File location for search
if not os.path.exists(new_path):
os.makedirs(new_path)
with open(path_txt, 'r') as lines:
filenames_to_copy = set(line.rstrip() for line in lines)
# print('filenames_to_copy:',filenames_to_copy)
# print(len(filenames_to_copy))
for root, _, filenames in os.walk(search_path):
# print('root',root)
# print(_)
# print(filenames)
for filename in filenames:
if filename in filenames_to_copy:
shutil.copy(os.path.join(root, filename), new_path)
# Search the target according to the path of the divided training file , And copy it to yolo New path in format
copy_file('./images/train/','./images_train.txt','./all_images')
copy_file('./images/val/','./images_trainval.txt','./all_images')
copy_file('./labels/train/','./labels_train.txt','./all_labels')
copy_file('./labels/val/','./labels_trainval.txt','./all_labels')

Step four : Create your own yaml file , Sure copy once yolov5 in data Under the coco128.yaml
train: ./mydata/images/train/
val: ./mydata/images/val/
nc: 2
names: ['dog' ,'cat']
Step five : Modify the configuration file of the network model , modify models/yolov5s.yaml The content of , Select one according to the parameters of your actual running model .yaml Make changes , I chose yolov5s.yaml.
Mainly modify the number of categories nc Value Of course, you can also modify your network structure .
Step six : Training
The training skills are above , Of course, you can go to train.py Modify the default value of the corresponding attribute in .
python train.py --data coco.yaml( Data and information , Generally, we also designate ourselves ) --cfg yolov5s.yaml ( Network structure information , have access to yolov5s Of , You can also use your own ) --weights '' ( there weights Is to specify whether or not to train on the basis of others ) --batch-size 64
Training v1 The problem is :
TypeError: can't convert cuda:0 device type tensor to numpy. Use Tensor.cpu() to copy the tensor to host memory first.Click the error prompt file directlyThe second question is : No corresponding label
No labels found in D:.B_yolov5_weeksyolov5_1.0mydataImages.
.
In fact, this problem is because we make labels The problem of , That is, you go mydata Under folder lables There are... In the folder train and val Folder to put the corresponding label, But mine is empty .
.
In fact, we have generated the corresponding lables, stay mydata There will be superfluous lables Folder ,
This labels Under folder train and val Folder is not empty , Replace mydata In a folder labels Folder
1.3 Performance evaluation

Validate the model
python val.py --data data/coco128.yaml --weights weighs/myyolo.pt --batch-size 6
Visualization of training process :
tensorboard --logdir ./runs
And then enter... On the browser side http://localhsot:6006/#scalars It depends on what the above command returns
…
Scene 4 :yolov5 Source code interpretation

Supporting documents
1: export.py —> The model is converted to onnx file

# netron Yes pt File compatibility is poor , The purpose of this document is to put pt The weight file of is converted to onnx Format , Convenient in netron And other tools
# Back -i The website is added to get from Tsinghua mirror , faster
# command pip install onnx>=1.7.0 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
# pip install coremltools==4.0 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
# Change orders : python export.py --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --img 640 --batch 1
netron github Check online
fast open 
2.yolov5s.yaml—> Network structure file






3. Model building code activations.py–> Activate function definition file
Activate function definition code

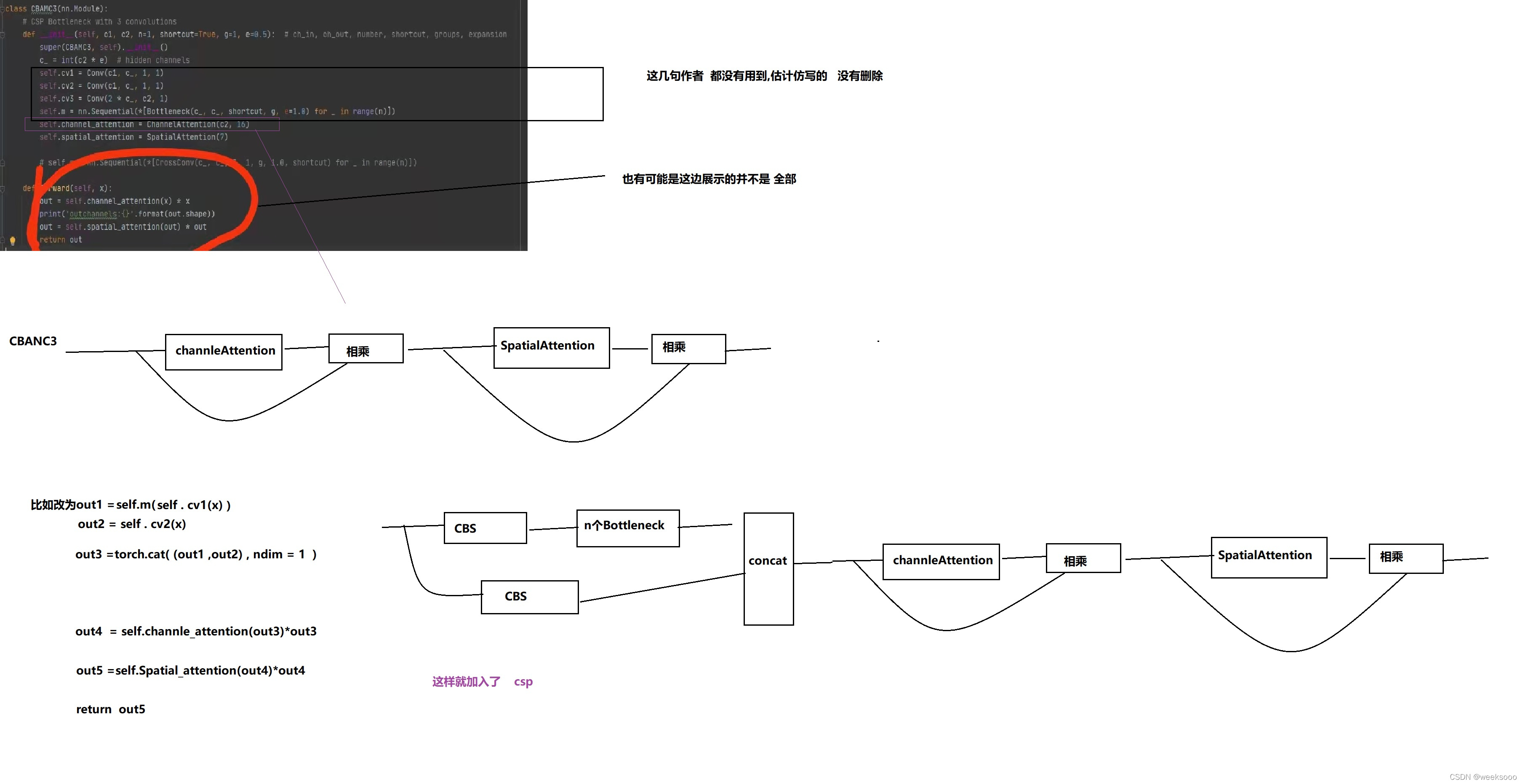
4 Model building code common.py—> Network component code
This file defines the implementation of many network components , Some are as follows .







5: Data set preprocessing to load code parsing —>Augmentations.py And Datasets.py

6: Index related codes and losses Loss Code —>metrics.py And Loss.py

7: autoanchor.py And torch_utils.py And general.py

8: detect.py



9: val.py

10: train.py


11: yolov5 - v6 edition detect.py Comment code
# YOLOv5 ?? by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Test script
"""
Run inference on images, videos, directories, streams, etc.
Usage:
$ python path/to/detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source 0 # webcam
img.jpg # image
vid.mp4 # video
path/ # directory
path/*.jpg # glob
'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc' # YouTube
'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4' # RTSP, RTMP, HTTP stream
"""
import argparse
import os
import sys
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
ROOT = FILE.parents[0] # YOLOv5 root directory
if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(str(ROOT)) # add ROOT to PATH
ROOT = Path(os.path.relpath(ROOT, Path.cwd())) # relative
from models.common import DetectMultiBackend
from utils.datasets import IMG_FORMATS, VID_FORMATS, LoadImages, LoadStreams
from utils.general import (LOGGER, check_file, check_img_size, check_imshow, check_requirements, colorstr,
increment_path, non_max_suppression, print_args, scale_coords, strip_optimizer, xyxy2xywh)
from utils.plots import Annotator, colors, save_one_box
from utils.torch_utils import select_device, time_sync
@torch.no_grad()
def run(weights=ROOT / 'yolov5s.pt', # model.pt path(s)
source=ROOT / 'data/images', # file/dir/URL/glob, 0 for webcam
imgsz=(640, 640), # inference size (height, width)
conf_thres=0.25, # confidence threshold
iou_thres=0.45, # NMS IOU threshold
max_det=1000, # maximum detections per image
device='', # cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu
view_img=False, # show results
save_txt=False, # save results to *.txt
save_conf=False, # save confidences in --save-txt labels
save_crop=False, # save cropped prediction boxes
nosave=False, # do not save images/videos
classes=None, # filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3
agnostic_nms=False, # class-agnostic NMS
augment=False, # augmented inference
visualize=False, # visualize features
update=False, # update all models
project=ROOT / 'runs/detect', # save results to project/name
name='exp', # save results to project/name
exist_ok=False, # existing project/name ok, do not increment
line_thickness=3, # bounding box thickness (pixels)
hide_labels=False, # hide labels
hide_conf=False, # hide confidences
half=False, # use FP16 half-precision inference
dnn=False, # use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference
):
source = str(source)
# If you have parameters --nosave Just don't save , not nosave Namely preservation , That is to say We No settings Parameters nosave When ,nosave The value is False
save_img = not nosave and not source.endswith('.txt') # save images , Here, you can save without receiving the parameter command
# Determine whether the file we have passed in is a file , namely source Tested It's pictures and videos still Open camera
is_file = Path(source).suffix[1:] in (IMG_FORMATS + VID_FORMATS)
# have a look source Is it specified rtsp:// ,rtmp:// The form such as , If it is It shows that we use camera
is_url = source.lower().startswith(('rtsp://', 'rtmp://', 'http://', 'https://'))
# See if it's true Using a camera
webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.txt') or (is_url and not is_file)
if is_url and is_file:
# Judge source Whether there is , Download if it doesn't exist
source = check_file(source) # download
# Directories If you enter a command line with --exist_ok , Then the above parameter attributes exist_ok The value of is true
# project In the previous parameter definitions , The default is ROOT / 'runs/detect' name The default is exp , So the function of parameters Under your project Create a Catalog runs / detect / exp
save_dir = increment_path(Path(project) / name, exist_ok=exist_ok)
# If it is an incoming parameter --save-txt , That is to say, the coordinates of the detected frame are expressed in txt Save up , Will be in save_dir namely runs / detect / exp/ Next create a labels Folder
# If No input , Namely Default yes false , Will not create
(save_dir / 'labels' if save_txt else save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
# Load model, Use torch_utils in select_device() function According to device Value Make device selection
device = select_device(device)
# Load model
model = DetectMultiBackend(weights, device=device, dnn=dnn)
stride, names, pt, jit, onnx, engine = model.stride, model.names, model.pt, model.jit, model.onnx, model.engine
# Check if the image size is s( The default is 32) Integer multiple , If not Just adjust it to 32 Integer multiple
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride) # check image size
# Half If the device is cpu , Just use Float 16 , If it is Gpu Just use float32
half &= (pt or jit or engine) and device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported by PyTorch on CUDA
if pt or jit:
model.model.half() if half else model.model.float()
# Dataloader Different data loading methods can be set through different input sources
if webcam:
# Check whether the environment supports Picture shows
view_img = check_imshow() # Support True
cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference
dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)
bs = len(dataset) # batch_size
else:
# Load pictures or videos ,dataset become LoadImages An instantiated object of this class
dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)
bs = 1 # batch_size
vid_path, vid_writer = [None] * bs, [None] * bs
# wramup yes common.py in DetectMultiBackend Class One way , Warm up training The effect of this method is that the learning rate is very small , Slowly increase to the value we set
# Run inference
model.warmup(imgsz=(1, 3, *imgsz), half=half) # warmup
dt, seen = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 0
'''
path picture / video route
im Conduct resize +pad In the following picture , Such as (3, 640 ,512 ) The format is (c, h ,w)
img0s primary size picture for example ( 1080 , 810 ,3 )
vid_cap The current picture is None , Reading video is For video source
'''
for path, im, im0s, vid_cap, s in dataset:
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
t1 = time_sync()
# hold nparray The format of the array is converted to pytorch Format
im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(device)
# uint8 to fp16/32 If half by true Words , Also, the semi precision , namely 16 Bit accuracy
im = im.half() if half else im.float()
# 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0 hold resize After the im Value of each pixel /255 , Let it be in 0-1 Between , In order to better adapt to the model
im /= 255
# im As we know before shapes yes ( 3, 640 ,512 ) In the form of , therefore shape The length is 3
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim Here is an extension shape The operation of becomes (batch-size , 3 ,640 ,512) In the form of
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
t2 = time_sync()
# dt The previous designation is [ 0.0 , 0.0 , 0.0] dt[0] = dt[0]+ t2 - t1 So it's updated dt First value of
dt[0] += t2 - t1
# Inference visualization , This parameter compares Weirdo , For example, you test bus.jpg , commonly Will be in exp{id} Generated under the folder Check the next picture , If this parameter is brought in
# Then what is generated is no longer The detected image is One Empty folder , Name is bus
visualize = increment_path(save_dir / Path(path).stem, mkdir=True) if visualize else False
# take After processing the The graph is brought into the model for prediction
'''
How many prediction boxes are there , All in all 32 Double down sampling , 16 Double down sampling , 8 Double down sampling
( h/32 * w/32 + h/16 * w/16 + h/8 * w/8 ) * 3
because The previous input is no longer the size of the same width and height specified previously : 416, 640, Instead, it uses The form of adaptive scaling , So it is no longer the same width and height
For example, it can be Input yes (640 , 608 ) , Then it changes ( 640/32 * 608/32 + .... ) =23940
pred Namely model Output result , It's the shape yes ([1, 23940, 85]) That is to say Yes 23940 Boxes , 85 Namely 5+80 , 1 yes batch-size Value
85 On the dimension of
pred[ ..., 0:4 ] To predict coordinate information , The information of the coordinate box is shown in xywh Format
pred[ ... , 4 ] For confidence c
pred[ ... , 5:-1 ] from index 5 - ending yes 80 Category information
'''
pred = model(im, augment=augment, visualize=visualize)
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
t3 = time_sync()
# dt The previous designation is [ dt[0]+ t2 - t1 , 0.0 , 0.0] dt[1] = dt[1] + t3 -t2 So it's updated dt The second value of
dt[1] += t3 - t2
# according to You passed in the detection command --conf-thres --iou-thres , --classes , --agnostic-nms --max-det equivalence
# call general.py in non_max_suppression( ) # Non maximum suppression algorithm , Filter box
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det)
''''
pred : The output of forward propagation , The result model model Output , The format of the box is xywh
conf_thres : Confidence threshold
iou_thres : Carry out nms When calculating iou threshold
classes : Specify whether to keep the specified category
agnostic_nums : Conduct nms Whether to also remove the box between different categories
max_det : The maximum number of detections on a graph
after nms operation Format of prediction box xywh----> x1y1 x2y2 That is, the format of the upper left corner and the lower right corner
'''
# dt The previous designation is [ dt[0]+ t2 - t1 , dt[1] + t3 -t2 , 0.0] dt[2] = dt[2] + time_sync() - t3 So it's updated dt The third value of
dt[2] += time_sync() - t3
'''
So at this time dt Value yes [ dt[0]+ t2 - t1 , dt[1] + t3 -t2 , dt[2] + time_sync() - t3]
, respectively, Represents the Before a picture is sent into the model Picture manipulation One processing time ( Include conversion to torch Format , Pixel point /255, and shape Dimension from 3 To 4 Transformation )
This picture is sent to After the model , After processing Of Time end
And after the model , Send in In the post-processing stage nms Carry out inside Not maximally suppressed Period of time
In this way, we can calculate the
'''
# Second-stage classifier (optional)
# pred = utils.general.apply_classifier(pred, classifier_model, im, im0s)
# Process predictions
# The frame generated on each picture is processed
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # per image i It's framed id , for example nms After filtering, only 7 Boxes ,det Is the information of the box
seen += 1 # The previous setting is 0
if webcam: # batch_size >= 1
p, im0, frame = path[i], im0s[i].copy(), dataset.count
s += f'{i}: '
else:
p, im0, frame = path, im0s.copy(), getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)
p = Path(p) # to Path Get the path of the picture ,
# save_dir We know that the front is runs / detect / exp p.name Namely We specify the name of the test file
# for example people.jpg that save_path refer to runs/detect/exp/people.jpg
# For example 1.mp4 , that Namely runs/detect/exp/1.mp4
save_path = str(save_dir / p.name) # im.jpg
# If it's a picture ,labels Information runs / detect / exp /labels/people.txt
txt_path = str(save_dir / 'labels' / p.stem) + ('' if dataset.mode == 'image' else f'_{frame}') # im.txt
# Set up the shape Print information s , For the following printing , 384 x 640 In the form of
s += '%gx%g ' % im.shape[2:] # print string
gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh Normalized gain whwh
# Suppose we add... To the command line --save-crop , The purpose of this sentence is to retain the trimmed prediction box , That is, if save_crop It's true , We are in img0 Do operations on a copy of , Otherwise, it would be im0 On the operation
imc = im0.copy() if save_crop else im0 # for save_crop
# call plots.py Medium class Annotator Class to instantiate
annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=line_thickness, example=str(names))
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size x1y1 x2y2
# Adjust the coordinates of the prediction box : be based on resize+ pad The coordinates of the picture ----> Based on the original size The coordinates of the picture ,
# Use general Medium scale_coords() function
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results
# Print the detected category information . That is to say det[:, -1]
for c in det[:, -1].unique():
n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class The function is to detect the number of each category
s += f"{n} {names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string
# s front It's defined by 384 X 640 Print format , in other words Here we go + Operation of category information
# s yes string type , If Last yes 3 A dog ,2 A cat
# s The end result is 384x640 3 dog 2 cat
# Write results Save forecast results
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
if save_txt: # Write to file
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
line = (cls, *xywh, conf) if save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label format
# write in
with open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '
')
# Whether to draw a frame on the original drawing , for example If we introduce --view-img, That is, whether to display the following pictures or videos
if save_img or save_crop or view_img: # Add bbox to image
c = int(cls) # integer class
# If the parameter passed in yes --hide_labels Namely hide label Information about , Then take None ,
# If confidence is hidden Then say yes Just show Category information ,names Is based on model Acquired , names[c] Point to category information
# conf Point to the confidence level of this category
label = None if hide_labels else (names[c] if hide_conf else f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}')
annotator.box_label(xyxy, label, color=colors(c, True))
if save_crop:
save_one_box(xyxy, imc, file=save_dir / 'crops' / names[c] / f'{p.stem}.jpg', BGR=True)
# Print time (inference-only)
# therefore The information printed here
# For example, the following console information is printed 416x640 3 persons, Done. (0.255s) 0.255s Is the time of reasoning in the model
LOGGER.info(f'{s}Done. ({t3 - t2:.3f}s)')
# Stream results
im0 = annotator.result()
# If it is --view-img , Show ,
if view_img:
cv2.imshow(str(p), im0) # str(p) Is the path of the above picture
cv2.waitKey(3000) # 1 millisecond
# Save results (image with detections)
# Save the picture / The operation of video
if save_img:
if dataset.mode == 'image':
cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)
else: # 'video' or 'stream'
if vid_path[i] != save_path: # new video
vid_path[i] = save_path
if isinstance(vid_writer[i], cv2.VideoWriter):
vid_writer[i].release() # release previous video writer
if vid_cap: # video
fps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
w = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
else: # stream
fps, w, h = 30, im0.shape[1], im0.shape[0]
save_path += '.mp4'
vid_writer[i] = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v'), fps, (w, h))
vid_writer[i].write(im0)
# Print results
# dt = [ Processing before feeding into the model , Detection in the model , nms Handle ]
t = tuple(x / seen * 1E3 for x in dt) # speeds per image
# such as t It is calculated that t= [ 1.00012 , 236.41212 , 2.00011 ]
# Print... To the console Speed: 1.0 ms pre-process , 236.4 ms inference, 2.0 ms NMS per image at shape (1, 3, 640, 640)
LOGGER.info(f'Speed: %.1f ms pre-process, %.1f ms inference, %.1f ms NMS per image at shape {(1, 3, *imgsz)}' % t)
# Print where the saved results are
if save_txt or save_img:
s = f"
{len(list(save_dir.glob('labels/*.txt')))} labels saved to {save_dir / 'labels'}" if save_txt else ''
LOGGER.info(f"Results saved to {colorstr('bold', save_dir)}{s}")
if update:
strip_optimizer(weights) # update model (to fix SourceChangeWarning)
def parse_opt():
# establish Parameter resolution object parser()
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# add_argument() Is to add One What attribute
# nargs refer to ---> Should read The number of command line parameters for , * Express 0 Or more , + Express 1 Or more
# action -- The command line Action when parameters are encountered , action='store_true' , Indicates that the variable is set to as long as it has a parameter passed during runtime True
parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default=ROOT / 'yolov5s.pt', help='model path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/images', help='file/dir/URL/glob, 0 for webcam')
parser.add_argument('--imgsz', '--img', '--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640], help='inference size h,w')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='NMS IoU threshold')
parser.add_argument('--max-det', type=int, default=1000, help='maximum detections per image')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--view-img', action='store_true', help='show results')
parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-conf', action='store_true', help='save confidences in --save-txt labels')
parser.add_argument('--save-crop', action='store_true', help='save cropped prediction boxes')
parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='do not save images/videos')
parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --classes 0, or --classes 0 2 3')
parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
parser.add_argument('--visualize', action='store_true', help='visualize features')
parser.add_argument('--update', action='store_true', help='update all models')
parser.add_argument('--project', default=ROOT / 'runs/detect', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
parser.add_argument('--line-thickness', default=3, type=int, help='bounding box thickness (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--hide-labels', default=False, action='store_true', help='hide labels')
parser.add_argument('--hide-conf', default=False, action='store_true', help='hide confidences')
parser.add_argument('--half', action='store_true', help='use FP16 half-precision inference')
parser.add_argument('--dnn', action='store_true', help='use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference')
# use parse_args() Function to parse the obtained parameters
# That is to say, this sentence Got We type... From the command line Content and carried out analysis , Other properties are defaulted
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.imgsz *= 2 if len(opt.imgsz) == 1 else 1 # expand
print_args(FILE.stem, opt)
return opt
def main(opt):
# Before the final test , Take a look at it requirements.txt In demand Whether the operating environment is installed , If not, update and download
check_requirements(exclude=('tensorboard', 'thop'))
run(**vars(opt))
if __name__ == "__main__":
opt = parse_opt()
main(opt)
"""
weights : Weight of training
source : Test data : It can be a picture / video route , It can also be 0 , Namely Computer camera , It can also be rtsp Equal video stream
img-size : Network input image size
conf-thresh : Confidence threshold
iou-thresh: do nums Of iou threshold
device: Model of equipment
view-img: Whether to show the following pictures / video , The default is False
save-txt: Whether to change the predicted frame coordinates to txt Save as file , Default False
save-conf: Whether to change the predicted frame coordinates to txt Save as file , Default False
save-dir: Pictures after network prediction / The path to save the video
classes: Set to keep only some categories , Form like 0 ,2 ,3
agnostic-nms: Conduct nms Whether to also remove the box between different categories , The default is False
augment : Reasoning is often done scale , Flip (TTA) Reasoning
update: If True , All the models are strip_optimizer operation , Take out pt Optimizer information in the file , The default is false
"""
12: yolov5 - v6 edition val.py Comment code
# YOLOv5 ?? by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Model validation scripts
"""
Validate a trained YOLOv5 model accuracy on a custom dataset
Usage:
$ python path/to/val.py --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --img 640
"""
import argparse
import json
import os
import sys
from pathlib import Path
from threading import Thread
import numpy as np
import torch
from tqdm import tqdm
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
ROOT = FILE.parents[0] # YOLOv5 root directory
if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(str(ROOT)) # add ROOT to PATH
ROOT = Path(os.path.relpath(ROOT, Path.cwd())) # relative
from models.common import DetectMultiBackend
from utils.callbacks import Callbacks
from utils.datasets import create_dataloader
from utils.general import (LOGGER, box_iou, check_dataset, check_img_size, check_requirements, check_yaml,
coco80_to_coco91_class, colorstr, increment_path, non_max_suppression, print_args,
scale_coords, xywh2xyxy, xyxy2xywh)
from utils.metrics import ConfusionMatrix, ap_per_class
from utils.plots import output_to_target, plot_images, plot_val_study
from utils.torch_utils import select_device, time_sync
def save_one_txt(predn, save_conf, shape, file):
# Save one txt result
gn = torch.tensor(shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh
for *xyxy, conf, cls in predn.tolist():
# take xyxy Format ---->xywh , And normalize it
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
# If we introduce --save-conf Write the confidence in txt In the middle
line = (cls, *xywh, conf) if save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label format
with open(file, 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '
')
def save_one_json(predn, jdict, path, class_map):
# Save one JSON result {"image_id": 42, "category_id": 18, "bbox": [258.15, 41.29, 348.26, 243.78], "score": 0.236}
# Get the id
image_id = int(path.stem) if path.stem.isnumeric() else path.stem
# Get coordinate information , Convert to xywh
box = xyxy2xywh(predn[:, :4]) # xywh
'''
It is worth noting that , What we said before xywh yes Center point coordinates and width and height
x1y1x2y2 It's the upper left corner The coordinates of the lower right corner
and coco Of json The coordinate format of the box in the format is ,x1y1wh , Upper left corner And width and height
'''
# So the coordinate information of the center point is transformed into The information in the upper left corner
box[:, :2] -= box[:, 2:] / 2 # xy center to top-left corner
for p, b in zip(predn.tolist(), box.tolist()):
jdict.append({'image_id': image_id,
'category_id': class_map[int(p[5])],
'bbox': [round(x, 3) for x in b],
'score': round(p[4], 5)})
'''
jdit Namely json Dictionaries , Used to store information
image_id : picture id , That is, which picture the information comes from
category_id : Category information ,coco91 claass() , Mapping from index to index 0-90
therefore : p[5] Get the category information , int After conversion , utilize class_map To get at coco91 Information in
bbox: Coordinates of the frame
scorce : Confidence score
'''
# Return to the correct prediction matrix , Each box is It's using x1y1 x2y2 The format of
def process_batch(detections, labels, iouv):
"""
Return correct predictions matrix. Both sets of boxes are in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
Arguments:
detections (Array[N, 6]), x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, class
labels (Array[M, 5]), class, x1, y1, x2, y2
Returns:
correct (Array[N, 10]), for 10 IoU levels
"""
# Initialize prediction evaluation
correct = torch.zeros(detections.shape[0], iouv.shape[0], dtype=torch.bool, device=iouv.device)
# If the box_iou() Function calculation Two box iou , namely labels yes [ Category ,x1y1x2y2 ] detections x1 ,y1 ,x2,y2 ,conf ,class
iou = box_iou(labels[:, 1:], detections[:, :4])
# choose iou Greater than threshold And Category matching , iouv[0] That is, the initial threshold is set to 0.5
x = torch.where((iou >= iouv[0]) & (labels[:, 0:1] == detections[:, 5])) # IoU above threshold and classes match
if x[0].shape[0]:
matches = torch.cat((torch.stack(x, 1), iou[x[0], x[1]][:, None]), 1).cpu().numpy() # [label, detection, iou]
if x[0].shape[0] > 1:
matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 1], return_index=True)[1]]
# matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 0], return_index=True)[1]]
matches = torch.Tensor(matches).to(iouv.device)
correct[matches[:, 1].long()] = matches[:, 2:3] >= iouv
return correct
@torch.no_grad()
def run(data,
weights=None, # model.pt path(s)
batch_size=32, # batch size
imgsz=640, # inference size (pixels)
conf_thres=0.001, # confidence threshold
iou_thres=0.6, # NMS IoU threshold
task='val', # train, val, test, speed or study
device='', # cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu
workers=8, # max dataloader workers (per RANK in DDP mode)
single_cls=False, # treat as single-class dataset
augment=False, # augmented inference
verbose=False, # verbose output
save_txt=False, # save results to *.txt
save_hybrid=False, # save label+prediction hybrid results to *.txt
save_conf=False, # save confidences in --save-txt labels
save_json=False, # save a COCO-JSON results file
project=ROOT / 'runs/val', # save to project/name
name='exp', # save to project/name
exist_ok=False, # existing project/name ok, do not increment
half=True, # use FP16 half-precision inference
dnn=False, # use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference
model=None,
dataloader=None,
save_dir=Path(''),
plots=True,
callbacks=Callbacks(),
compute_loss=None,
):
# Initialize/load model and set device
# Initialize and load the model , And carry out devices setting up
# Determine if you are training call val , If yes, get the training equipment
training = model is not None # If model There is , It is equivalent to training model , training = true
if training: # called by train.py By train.py summon
device, pt, jit, engine = next(model.parameters()).device, True, False, False # get model device, PyTorch model
half &= device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA
model.half() if half else model.float()
else: # called directly , Otherwise It's our normal Parameters Call passed , That is, the call passed in from our command line
# Use torch_utils in select_device() function According to device Value Make device selection
device = select_device(device, batch_size=batch_size)
# Directories If you enter a command line with --exist_ok , Then the above parameter attributes exist_ok The value of is true
# project In the previous parameter definitions , The default is ROOT / 'runs/detect' name The default is exp , So the function of parameters Under your project Create a Catalog runs /val / exp
save_dir = increment_path(Path(project) / name, exist_ok=exist_ok) # increment run
# If it is an incoming parameter --save-txt , That is to say, the coordinates of the detected frame are expressed in txt Save up , Will be in save_dir namely runs / detect / exp/ Next create a labels Folder
# If No input , Namely Default yes false , Will not create
(save_dir / 'labels' if save_txt else save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
# Load model # Load model , utilize common.py Medium DetectMultiBackend Class to load Model
model = DetectMultiBackend(weights, device=device, dnn=dnn)
stride, pt, jit, engine = model.stride, model.pt, model.jit, model.engine
# stride Is the sample size under the model
# Check if the image size is s( The default is 32) Integer multiple , If not Just adjust it to 32 Integer multiple
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride) # check image size
# If the device is not cpu also gpu The number is 1 , Change the model from float32 To float16, Increase the speed of forward propagation
# half yes Half precision prediction , That is to say float16, Here you can see yes Half precision prediction is only CUDA Support
half &= (pt or jit or engine) and device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported by PyTorch on CUDA
if pt or jit:
# If half really , The model takes half precision prediction , Otherwise, it would be float32 forecast
model.model.half() if half else model.model.float()
elif engine:
batch_size = model.batch_size
else:
half = False
batch_size = 1 # export.py models default to batch-size 1 # The default batch size of the model is 1
device = torch.device('cpu')
LOGGER.info(f'Forcing --batch-size 1 square inference shape(1,3,{imgsz},{imgsz}) for non-PyTorch backends')
# Use general. In translation check_dataset() function , Check the incoming data Whether there is
data = check_dataset(data) # check
# Configure
# eval() when , The frame will automatically BN and Dropout Hold on , Use the trained value , Is not enabled BN and Dropout
model.eval()
# Judge whether it is coco Data sets , That is, whether or not the coco Data set to validate the model
is_coco = isinstance(data.get('val'), str) and data['val'].endswith('coco/val2017.txt') # COCO dataset
# If the parameter passed in is --single-cls , There is only one category in the dataset ,nc Set as 1
nc = 1 if single_cls else int(data['nc']) # number of classes
# Set up IOU threshold , from 0.5 - 0.95 , every other 0.05 Take one
iouv = torch.linspace(0.5, 0.95, 10).to(device) # iou vector for [email protected]:0.95
# niou It's the one above iou Number
niou = iouv.numel()
# Dataloader
if not training:
# If Not being summoned during training , That is to say say This is what we ordered to start
# wramup yes common.py in DetectMultiBackend Class One way , Warm up training The effect of this method is that the learning rate is very small , Slowly increase to the value we set
model.warmup(imgsz=(1, 3, imgsz, imgsz), half=half) # warmup
# If task That is to say The verification method is speed , then pad Set to 0 , That is, no filling , If not , It is normal val ,test ,train or study
pad = 0.0 if task == 'speed' else 0.5
# If it is train ,val ,test A kind of , That's what it is task In itself , If yes study Or is it speed A kind of , Start here Convert to val In the form of
# Point to Picture location , That is to do the operation Path to picture
task = task if task in ('train', 'val', 'test') else 'val' # path to train/val/test images
# call datasets.py Medium create_dataloader() Function to create dataloader
# Notice the rect Parameter is true ,yolov5 Our test evaluation is based on rectangular reasoning
# data[task] Point to the image path
dataloader = create_dataloader(data[task], imgsz, batch_size, stride, single_cls, pad=pad, rect=pt,
workers=workers, prefix=colorstr(f'{task}: '))[0]
# Initialize the number of test pictures
seen = 0
# call metrics.py Of ConfusionMatrix Confusion matrix class Instantiation One Confusion matrix
confusion_matrix = ConfusionMatrix(nc=nc)
# Get the name of the category
names = {k: v for k, v in enumerate(model.names if hasattr(model, 'names') else model.module.names)}
# If it is coco Data sets , Just use general.py Medium coco80_to_coco91_class() , Also is to 80 The categories are changed to paper What happened in 91 Classification length ,
# Create a list[ range(1 ,90)] , If not Namely list(range(1000))
# The function is to get coco Index of the category of the dataset , Input coco The category of the dataset is 80 , Theoretically, the index is 0-79 , But its index belongs to 1-90
class_map = coco80_to_coco91_class() if is_coco else list(range(1000))
# Set up s, That is, like the string displayed on the screen
s = ('%20s' + '%11s' * 6) % ('Class', 'Images', 'Labels', 'P', 'R', '[email protected]', '[email protected]:.95')
# Initialize various evaluation indicators
dt, p, r, f1, mp, mr, map50, map = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
# dt Is still [0.0 , 0.0 , 0.0 ] Used to record running time ,p Namely precision , r It's the recall rate
# initialization Loss of test set
loss = torch.zeros(3, device=device)
# initialization json A dictionary of documents , Statistics ,ap
jdict, stats, ap, ap_class = [], [], [], []
pbar = tqdm(dataloader, desc=s, bar_format='{l_bar}{bar:10}{r_bar}{bar:-10b}') # progress bar
# Yes dataloader Traversal
for batch_i, (im, targets, paths, shapes) in enumerate(pbar):
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
t1 = time_sync()
# The first stage : Preprocess the picture before sending it to the model ................................................................
if pt or jit or engine:
# After loading the picture, put it on the corresponding device for processing
im = im.to(device, non_blocking=True)
targets = targets.to(device)
# uint8 to fp16/32 If half by true Words , Also, the semi precision , namely 16 Bit accuracy
im = im.half() if half else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
# 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0 hold resize After the im Value of each pixel /255 , Let it be in 0-1 Between , In order to better adapt to the model
im /= 255
# Get the processed shape
nb, _, height, width = im.shape # batch size, channels, height, width
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
t2 = time_sync()
dt[0] += t2 - t1 # dt by [ dt[0]+t2-t1 , 0 , 0 ]
# Inference...........................................................................................
# The second stage Send the processed image to the model , You can see if it's training Time call val.py So that is model(im)
# Otherwise, it would be model(im, augment=augment, val=True) , out yes Predicted results ,train_out For training results
# If we adopt Called from the command line val.py , No training , So at this point out That's what makes sense , train_out It makes no sense
out, train_out = model(im) if training else model(im, augment=augment, val=True) # inference, loss outputs
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
dt[1] += time_sync() - t2 # dt by [ dt[0]+t2-t1 , dt[1]+time_sync()-t2 , 0 ]
'''
out Namely model Output result , It's the shape yes ([1, 23940, 85]) That is, if Yes 23940 Boxes , 85 Namely 5+80 , 1 yes batch-size Value
85 On the dimension of
out[ ..., 0:4 ] To predict coordinate information , The information of the coordinate box is shown in xywh Format
out[ ... , 4 ] For confidence c
out[ ... , 5:-1 ] from index 5 - ending yes 80 Category information
'''
# Loss
if compute_loss: # The default is None , in other words Only call during training val.py , Then incoming computer_loss by true
# At this time, it will be mentioned through train_out The result calculates and returns the... Of the test set box-loss , obj-loss And cls-loss
loss += compute_loss([x.float() for x in train_out], targets)[1] # box, obj, cls
# Construct a tensor
targets[:, 2:] *= torch.Tensor([width, height, width, height]).to(device) # to pixels
# If we Incoming --save-hybrid , Will save the tag and forecast Mixed results
# That is to say save_hybird by false Words , That is to say lb = []
lb = [targets[targets[:, 0] == i, 1:] for i in range(nb)] if save_hybrid else [] # for autolabelling
# NMS.................................................................................................................
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
t3 = time_sync()
# according to You passed in the detection command --conf-thres --iou-thres , --classes , --agnostic-nms --max-det equivalence
# call general.py in non_max_suppression( ) # Non maximum suppression algorithm , Filter box
out = non_max_suppression(out, conf_thres, iou_thres, labels=lb, multi_label=True, agnostic=single_cls)
''''
out : The output of forward propagation , The result model model Output , The format of the box is xywh
conf_thres : Confidence threshold
iou_thres : Carry out nms When calculating iou threshold
agnostic_nums : Conduct nms Whether to also remove the box between different categories
after nms operation Format of prediction box xywh----> x1y1 x2y2 That is, the format of the upper left corner and the lower right corner
'''
# torch_utils Inside time_sync() function , Role is Time synchronization ( wait for GPU Operation is completed ) , Return current time
dt[2] += time_sync() - t3
# dt by [ dt[0]+t2-t1 , dt[1]+time_sync()-t2 , dt[2]+time_sync() - t3 ] In this way, the time at each stage can be calculated
# Metrics indicators
# Process the information generated by each picture , Including statistics , Write information to txt Go to the folder , Generate json Document Dictionary , Statistics tp etc. ,
for si, pred in enumerate(out):
# per image si It's framed id , for example nms After filtering, only 7 Boxes ,pred Is the information of the prediction box
# targets[ :, 0] It is the number of the picture to which the label belongs , That is, the last labels You will get the original annotation lables Information
labels = targets[targets[:, 0] == si, 1:]
nl = len(labels) # It means that the original label has n A detection target
# Get the category of the tag , For example, the original picture has 3 individual Dog ,2 A cat , That's the top nl by 5 ,
# Explain that there are objects on the original picture , So the statistics are 5 Categories of objects , The number of categories is 2 , If nl by 0 , Explain that there is no object on the original picture , So the number of categories is 0
tcls = labels[:, 0].tolist() if nl else [] # target class
# Path( paths[i] ) , obtain index by si The path to the picture of , shapes[si][0] Is to get this picture shape
path, shape = Path(paths[si]), shapes[si][0]
# seen Used to count how many pictures
seen += 1
# Judge Whether the forecast box information is empty
if len(pred) == 0:
if nl: # If it's empty , It depends on whether there is no detection target in the original image
stats.append((torch.zeros(0, niou, dtype=torch.bool), torch.Tensor(), torch.Tensor(), tcls))
continue
# Predictions , See if there is any incoming --single-cls pred With 85 Dimensional information , front yes Deal with the later xywhc ,80 Category information
# But after nms , Receivable xywh--> x1y1x2y2 top left corner , The form in the lower right corner , So it is x1 y1 x2 y2 c + 80
if single_cls:
pred[:, 5] = 0
predn = pred.clone()
# call general.py Make the corresponding conversion
scale_coords(im[si].shape[1:], predn[:, :4], shape, shapes[si][1]) # native-space pred
# Evaluate
if nl:
# take Target box Convert to x1y1x2y2 In the form of call general.py Make the corresponding conversion
tbox = xywh2xyxy(labels[:, 1:5]) # target boxes
scale_coords(im[si].shape[1:], tbox, shape, shapes[si][1]) # native-space labels
labelsn = torch.cat((labels[:, 0:1], tbox), 1) # native-space labels, Inherent label
correct = process_batch(predn, labelsn, iouv)
'''
As defined above process_batch() Return to the correct prediction matrix
predn yes (Array[N, 6]), x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, class
labels (Array[M, 5]), class, x1, y1, x2, y2
'''
if plots: # The default is true
confusion_matrix.process_batch(predn, labelsn)
else:
correct = torch.zeros(pred.shape[0], niou, dtype=torch.bool)
# stay stats [] Add The correct prediction matrix for each picture , Degree of confidence Forecast category information , Target category information
stats.append((correct.cpu(), pred[:, 4].cpu(), pred[:, 5].cpu(), tcls)) # (correct, conf, pcls, tcls)
# Save/log
# If you pass in --save-txt , Namely take The information of the prediction box is displayed in txt Save the form of ,
if save_txt:
# Save on it save_one_txt() Function definition directory , namely runs / val / labels/ + .txt
save_one_txt(predn, save_conf, shape, file=save_dir / 'labels' / (path.stem + '.txt'))
# If the incoming is --save-json ; preservation coco Format limit json Document Dictionary
if save_json:
# Call the... Defined above save_one_json()
save_one_json(predn, jdict, path, class_map) # append to COCO-JSON dictionary
callbacks.run('on_val_image_end', pred, predn, path, names, im[si])
# Plot images
# Draw the second 1 ,2 individual batch The picture of ground truth and Forecast box and save
# Save in runs / val / exp / va1-batch1_labels.jpg
if plots and batch_i < 3:
f = save_dir / f'val_batch{batch_i}_labels.jpg' # labels
Thread(target=plot_images, args=(im, targets, paths, f, names), daemon=True).start()
# Save in runs / val / exp / val-batch1_pred.jpg
f = save_dir / f'val_batch{batch_i}_pred.jpg' # predictions
Thread(target=plot_images, args=(im, output_to_target(out), paths, f, names), daemon=True).start()
# Compute metrics, All the pictures have been processed , Start calculating metrics
# take stats The information of the list is spliced together
stats = [np.concatenate(x, 0) for x in zip(*stats)] # to numpy
if len(stats) and stats[0].any():
# call metrics.py The total ap_per_class Calculate the indicators for each category , precision p = tp/tp +fp Recall rate = tp/p , map
tp, fp, p, r, f1, ap, ap_class = ap_per_class(*stats, plot=plots, save_dir=save_dir, names=names)
# therefore ap50 Namely iou The threshold for 0.5 When the ap , For each category ap [ iou>0.5 The accuracy of , iou>0.55 Yes, accuracy , .... ]
ap50, ap = ap[:, 0], ap.mean(1) # [email protected], [email protected]:0.95 ap Equivalent to AP (iou The threshold for 0.5 - 0.95) Average value , This is every category
mp, mr, map50, map = p.mean(), r.mean(), ap50.mean(), ap.mean() # Here are all the category properties
# nt It's a list , Test set How many target boxes are there in each category , That is, how many categories are marked in the test set
nt = np.bincount(stats[3].astype(np.int64), minlength=nc) # number of targets per class
else:
nt = torch.zeros(1)
# Print results, Print the results
pf = '%20s' + '%11i' * 2 + '%11.3g' * 4 # print format
LOGGER.info(pf % ('all', seen, nt.sum(), mp, mr, map50, map))
# Print results per class , Print category information
if (verbose or (nc < 50 and not training)) and nc > 1 and len(stats):
for i, c in enumerate(ap_class):
LOGGER.info(pf % (names[c], seen, nt[c], p[i], r[i], ap50[i], ap[i]))
# Print speeds, Print speed information
t = tuple(x / seen * 1E3 for x in dt) # speeds per image
if not training:
shape = (batch_size, 3, imgsz, imgsz)
# such as t It is calculated that t= [ 1.00012 , 236.41212 , 2.00011 ]
# Print... To the console Speed: 1.0 ms pre-process ( Preprocessing ) , 236.4 ms inference( Reasoning ), 2.0 ms NMS per image at shape (1,3,640, 640)
LOGGER.info(f'Speed: %.1f ms pre-process, %.1f ms inference, %.1f ms NMS per image at shape {shape}' % t)
# Plots
if plots:
confusion_matrix.plot(save_dir=save_dir, names=list(names.values()))
callbacks.run('on_val_end')
# Save JSON
# Use previously saved json Format forecast results , adopt cocoapi Evaluation indicators
# It should be noted that The tab of the test set needs to be converted to coco Of json Format
if save_json and len(jdict):
w = Path(weights[0] if isinstance(weights, list) else weights).stem if weights is not None else '' # weights
anno_json = str(Path(data.get('path', '../coco')) / 'annotations/instances_val2017.json') # annotations json
pred_json = str(save_dir / f"{w}_predictions.json") # predictions json
LOGGER.info(f'
Evaluating pycocotools mAP... saving {pred_json}...')
with open(pred_json, 'w') as f:
json.dump(jdict, f)
try: # https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi/blob/master/PythonAPI/pycocoEvalDemo.ipynb
check_requirements(['pycocotools'])
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval
anno = COCO(anno_json) # init annotations api
pred = anno.loadRes(pred_json) # init predictions api
eval = COCOeval(anno, pred, 'bbox')
if is_coco:
eval.params.imgIds = [int(Path(x).stem) for x in dataloader.dataset.img_files] # image IDs to evaluate
eval.evaluate()
eval.accumulate()
eval.summarize()
map, map50 = eval.stats[:2] # update results ([email protected]:0.95, [email protected])
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.info(f'pycocotools unable to run: {e}')
# Return results , Print the location where the result information is saved
model.float() # for training
if not training:
s = f"
{len(list(save_dir.glob('labels/*.txt')))} labels saved to {save_dir / 'labels'}" if save_txt else ''
LOGGER.info(f"Results saved to {colorstr('bold', save_dir)}{s}")
maps = np.zeros(nc) + map
for i, c in enumerate(ap_class):
maps[c] = ap[i]
return (mp, mr, map50, map, *(loss.cpu() / len(dataloader)).tolist()), maps, t
def parse_opt():
# establish Parameter resolution object parser()
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# add_argument() Is to add One What attribute
# nargs refer to ---> Should read The number of command line parameters for , * Express 0 Or more , + Express 1 Or more
# action -- The command line Action when parameters are encountered , action='store_true' , Indicates that the variable is set to as long as it has a parameter passed during runtime True
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/coco128.yaml', help='dataset.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default=ROOT / 'yolov5s.pt', help='model.pt path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=32, help='batch size')
parser.add_argument('--imgsz', '--img', '--img-size', type=int, default=640, help='inference size (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.001, help='confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.6, help='NMS IoU threshold')
parser.add_argument('--task', default='val', help='train, val, test, speed or study')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--workers', type=int, default=8, help='max dataloader workers (per RANK in DDP mode)')
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='treat as single-class dataset')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
parser.add_argument('--verbose', action='store_true', help='report mAP by class')
parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-hybrid', action='store_true', help='save label+prediction hybrid results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-conf', action='store_true', help='save confidences in --save-txt labels')
parser.add_argument('--save-json', action='store_true', help='save a COCO-JSON results file')
parser.add_argument('--project', default=ROOT / 'runs/val', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
parser.add_argument('--half', action='store_true', help='use FP16 half-precision inference')
parser.add_argument('--dnn', action='store_true', help='use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference')
# use parse_args() Function to parse the obtained parameters
# That is to say, this sentence Got We type... From the command line Content and carried out analysis , Other properties are defaulted
opt = parser.parse_args()
# Use general.py Medium def check_yaml() Function to view the data Whether there is
opt.data = check_yaml(opt.data) # check YAML
opt.save_json |= opt.data.endswith('coco.yaml')
opt.save_txt |= opt.save_hybrid
print_args(FILE.stem, opt) # Print opt Information about
return opt
def main(opt):
# Before the final test , Take a look at it requirements.txt In demand Whether the operating environment is installed , If not, update and download
check_requirements(requirements=ROOT / 'requirements.txt', exclude=('tensorboard', 'thop'))
# If opt Properties of task stay train ,val test in , Verify the set on the normal test , Test set
if opt.task in ('train', 'val', 'test'): # run normally
if opt.conf_thres > 0.001: # https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/1466
# Print information : Warning : Confidence threshold Such as 0.20 Far greater than 0.001 Will result in invalid map value
LOGGER.info(f'WARNING: confidence threshold {opt.conf_thres} >> 0.001 will produce invalid mAP values.')
run(**vars(opt))
else:
# Judge opt.weights yes A list of , If it is A list of Assign a value to weights , If not a list , Perform list conversion
weights = opt.weights if isinstance(opt.weights, list) else [opt.weights]
# half by True Namely Say the accuracy is halved , Convert to float 32
opt.half = True # FP16 for fastest results
# If task The value of is speed , It is equivalent to using the form of fast verification
if opt.task == 'speed': # speed benchmarks
# python val.py --task speed --data coco.yaml --batch 1 --weights yolov5n.pt yolov5s.pt...
# Set related properties
opt.conf_thres, opt.iou_thres, opt.save_json = 0.25, 0.45, False
for opt.weights in weights:
run(**vars(opt), plots=False)
# If the incoming is study In the form of , On Assessment yolov5 Series and yolov3-spp The indicators under each scale are visualized
elif opt.task == 'study': # speed vs mAP benchmarks
# python val.py --task study --data coco.yaml --iou 0.7 --weights yolov5n.pt yolov5s.pt...
for opt.weights in weights:
f = f'study_{Path(opt.data).stem}_{Path(opt.weights).stem}.txt' # filename to save to
x, y = list(range(256, 1536 + 128, 128)), [] # x axis (image sizes), y axis
for opt.imgsz in x: # img-size
LOGGER.info(f'
Running {f} --imgsz {opt.imgsz}...')
r, _, t = run(**vars(opt), plots=False)
y.append(r + t) # results and times
np.savetxt(f, y, fmt='%10.4g') # save
os.system('zip -r study.zip study_*.txt')
plot_val_study(x=x) # plot
if __name__ == "__main__":
opt = parse_opt()
main(opt)
"""
data : Dataset configuration file The default is data/coco128.yaml
weights : Test model weight file The default is yolov5s.pt
batch-size : The batch at the time of forward propagation The default is 32,
imgsz : The size of the image input resolution The default is 640
conf-thres : Confidence threshold when filtering boxes The default is 0.001
iou-thres : Conduct NMS When IOU threshold The default is 0.6,
device : Test equipment cpu Or is it 0 representative GPU
save-txt : Whether or not to txt Save the frame coordinates of model prediction in the form of file The default is False
save-conf : Whether to save the confidence information to the above save—txt In the middle The default is False
save-json : Is it in accordance with coco Of josn Save forecast box in format , And use cocoapi Make an assessment The default is Fasle
single-cls : Whether the dataset has only one category The default is False
augment : Whether to use TTA The default is False
verbose : Whether to print... For each category mAP The default is False
project : The default is ROOT / 'runs/val' That is to say, it will be in runs Create under file val Folder
name : The default is exp That is to say, it will be in val Create under folder exp Folder to store the results
task : The default is val Set the test form
"""
13: yolov5 - v6 edition train.py Comment code
# YOLOv5 ?? by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Model training script
"""
Train a YOLOv5 model on a custom dataset
Usage:
$ python path/to/train.py --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --img 640
"""
import argparse
import math
import os
import random
import sys
import time
from copy import deepcopy
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.nn as nn
import yaml
from torch.cuda import amp
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
from torch.optim import SGD, Adam, lr_scheduler
from tqdm import tqdm
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
ROOT = FILE.parents[0] # YOLOv5 root directory
if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(str(ROOT)) # add ROOT to PATH
ROOT = Path(os.path.relpath(ROOT, Path.cwd())) # relative
import val # for end-of-epoch mAP
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from models.yolo import Model
from utils.autoanchor import check_anchors
from utils.autobatch import check_train_batch_size
from utils.callbacks import Callbacks
from utils.datasets import create_dataloader
from utils.downloads import attempt_download
from utils.general import (LOGGER, check_dataset, check_file, check_git_status, check_img_size, check_requirements,
check_suffix, check_yaml, colorstr, get_latest_run, increment_path, init_seeds,
intersect_dicts, labels_to_class_weights, labels_to_image_weights, methods, one_cycle,
print_args, print_mutation, strip_optimizer)
from utils.loggers import Loggers
from utils.loggers.wandb.wandb_utils import check_wandb_resume
from utils.loss import ComputeLoss
from utils.metrics import fitness
from utils.plots import plot_evolve, plot_labels
from utils.torch_utils import EarlyStopping, ModelEMA, de_parallel, select_device, torch_distributed_zero_first
'''
For example, we are in the environment variable of our computer Got up One is called key Value , If it points to the address of a compiler : home/jdk
os.getenv(key ) The role of Is to get the value of this point : namely home/jdk ;
If there is no indication key The direction of yes A value , that os.getenv(key ) Just go back to one None
If we don't specify key The direction of , os.getenv(Key , 'value does not exist ' ) If it cannot be found, it will return value does not exist
So here Use os.getenv('LOCAL_RANK', -1) , If you can't find it LOCAL_RANK The value of the point , Just Is to return the specified -1, that LOCAL_RANK = int(-1)=-1
So here Use os.getenv('RANK', -1) , If you can't find it RANK The value of the point , Just Is to return the specified -1, that RANK = int(-1)=-1
So here Use os.getenv('WORLD_SIZE', 1) , If you can't find it WORLD_SIZE The value of the point , Just Is to return the specified 1, that RANK = int(1)=1
RANK Number the process
LOCAL_RANK by GPU Number
'''
LOCAL_RANK = int(os.getenv('LOCAL_RANK', -1)) # https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/elastic/run.html
RANK = int(os.getenv('RANK', -1))
WORLD_SIZE = int(os.getenv('WORLD_SIZE', 1))
def train(hyp, # path/to/hyp.yaml or hyp dictionary
opt,
device,
callbacks
):
# obtain opt Properties of
save_dir, epochs, batch_size, weights, single_cls, evolve, data, cfg, resume, noval, nosave, workers, freeze =
Path(opt.save_dir), opt.epochs, opt.batch_size, opt.weights, opt.single_cls, opt.evolve, opt.data, opt.cfg,
opt.resume, opt.noval, opt.nosave, opt.workers, opt.freeze
# ............................................. Set the storage path of the training generated model ....................................
# If no hyperparametric evolution is specified , So the following statement opt.save_dir = str(increment_path(Path(opt.project) / opt.name, exist_ok=opt.exist_ok))
# opt.project ----> runs/tarin opt.name----->exp So it's equivalent to save_dir by runs/train/exp
# If hyperparametric evolution is used , opt.project ----> runs/evolve save_dir Namely runs/evolve /exp 了
# Set the storage location of the training model , That is to say runs / train/exp/weights
w = save_dir / 'weights' # weights dir
# Create the corresponding route
(w.parent if evolve else w).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
# stay weights Create last.pt and best.pt
last, best = w / 'last.pt', w / 'best.pt'
# .......................................... Load the super parameter configuration file ..........................................
# Hyperparameters , Judge hyp Whether it's a string , If it's a string , It shows that the program has not started evolution , Or go down main() In the function , It has become the corresponding dictionary
if isinstance(hyp, str):
# If it's a string , Just call safe_load() Function to load the corresponding hyp The super parameter configuration file is given to hyp, Now hyp For the dictionary
with open(hyp, errors='ignore') as f:
hyp = yaml.safe_load(f) # load hyps dict
# call general.py Medium colorstr( ) function Print It's different Color To modify Hyperparameters , Output : Super parametric Parameters : key = value , Learning rate these
LOGGER.info(colorstr('hyperparameters: ') + ', '.join(f'{k}={v}' for k, v in hyp.items()))
# Save run settings , If there is no hyperparametric evolution , So that is Open by writing runs/train/exp Under the hyp.yaml, Just write it in hyp
if not evolve:
with open(save_dir / 'hyp.yaml', 'w') as f:
yaml.safe_dump(hyp, f, sort_keys=False)
# preservation opt Configuration of , That is, after you input the command and change it opt Information
with open(save_dir / 'opt.yaml', 'w') as f:
yaml.safe_dump(vars(opt), f, sort_keys=False)
# Loggers
data_dict = None
if RANK in [-1, 0]:
loggers = Loggers(save_dir, weights, opt, hyp, LOGGER) # loggers instance
if loggers.wandb:
data_dict = loggers.wandb.data_dict
if resume:
weights, epochs, hyp = opt.weights, opt.epochs, opt.hyp
# Register actions
for k in methods(loggers):
callbacks.register_action(k, callback=getattr(loggers, k))
# Config , Without evolution , plots by true
plots = not evolve # create plots
# Check whether the device is cpu , If it is cpu ,cuda by false , If not cpu , So that is cuda by true , That's it GPU
cuda = device.type != 'cpu'
init_seeds(1 + RANK) # Set random seeds
# ................................................... obtain data Specified training set information ..................................
with torch_distributed_zero_first(LOCAL_RANK):
# call general Medium check_dataset() Function to Check Check the incoming data Whether there is , Back is a dictionary
data_dict = data_dict or check_dataset(data) # check if None
# With Training default Folder data Under the coco128.yaml For example , It's stored inside
'''
path: ../datasets/coco128 Path information
train: images/train2017 Path information of training picture
val: images/train2017 Verify the path information of the picture
test: optional Serious information about the test
nc: 1 Type and quantity information
names: ['person'] Name information of corresponding category
download: https://ultralytics.com/assets/coco128.zip If no download address exists , But we usually specify our training set
'''
# ............................................. Get the path of the training set data set .............................................................
# from data designated In file obtain Training set route train_path , Get the path of the validation set val_path
train_path, val_path = data_dict['train'], data_dict['val']
# If we pass --single_cls , It is equivalent to that we specify that the dataset has only one class , nc by 1 , Otherwise, it will be from data_dict Get in there nc The number of
nc = 1 if single_cls else int(data_dict['nc']) # number of classes
# If The incoming assignment is a single category however stay data designated yaml The category name in the file is not A category , that names=[ 'item' ]
# Otherwise , Namely Page you pass in the specified single category and just yaml The category name in the file is also a , that names= data_dict['names'] , Namely That category name
names = ['item'] if single_cls and len(data_dict['names']) != 1 else data_dict['names'] # class names
# If The number of names does not equal Number of categories specified , Print : 3 A name has been found , But the number of categories in the data is 4
assert len(names) == nc, f'{len(names)} names found for nc={nc} dataset in {data}' # check
# see Verify that the path to the set is str , That is, the validation set path is specified , And if so coco/val2017.txt ending , So that is coco Data sets , Otherwise it's not
is_coco = isinstance(val_path, str) and val_path.endswith('coco/val2017.txt') # COCO dataset
# .................................................... See if you use pre training ...........................................
# Model weights Whether we use others' training model as our pre training , # Check if the document is Ends with the specified suffix Check if the document is Ends with the specified suffix
check_suffix(weights, '.pt') # check weights
pretrained = weights.endswith('.pt') # If we specify --weight '' , Default not specified is yolov5s.pt
if pretrained: # If it is true , That is, pre training
with torch_distributed_zero_first(LOCAL_RANK):
# If the corresponding file is not found locally , Then try downloading , from google Automatically download the model on the cloud disk
# But because of the Internet , Most likely, the download failed , therefore , If you want to use it, you should download it first
weights = attempt_download(weights) # download if not found locally
# Loading model and parameters
ckpt = torch.load(weights, map_location=device) # ckpt Namely checkpoint
# Just call common.py class Model, Instantiate a model , Load model
# Model creation , It can be done by opt.cfg To create , It's fine too adopt ckpt['model'].yaml To create
# The difference is whether it is reusme ,resume Will opt.cfg Set to null , Then according to ckpt['model'].yaml To create a model
model = Model(cfg or ckpt['model'].yaml, ch=3, nc=nc, anchors=hyp.get('anchors')).to(device) # create
exclude = ['anchor'] if (cfg or hyp.get('anchors')) and not resume else [] # exclude keys
# hyp.get('achors') Is to generate several pre selected box super parameters , cfg Is the structure of the model , So exclude=['anchor']
# This also affects whether to remove anchor Of key, That is to say ( No load anchor ) , If resume Do not load anchor
# This is mainly because the saved model will be saved anchors , Sometimes users customize anchor after , Again resume, It is based on coco Data sets anchor Will override your own settings anchor
csd = ckpt['model'].float().state_dict() # checkpoint state_dict as FP32
csd = intersect_dicts(csd, model.state_dict(), exclude=exclude) # intersect
model.load_state_dict(csd, strict=False) # load
# Display the key value pairs for loading pre training weights and creating models
LOGGER.info(f'Transferred {len(csd)}/{len(model.state_dict())} items from {weights}') # report
else:
# That is, we don't use other people's pre training models , Just call common.py Class in Model, Instantiate a model
model = Model(cfg, ch=3, nc=nc, anchors=hyp.get('anchors')).to(device) # create
# ........................................................ Freeze the model layer ..........................................
# Freeze the model layer , Set the name of the frozen layer
# You can see https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/679
# Freeze , That is, whether the demand is frozen , The default is [0] , If you pass in --freeze Is to freeze the requirements of some layers
freeze = [f'model.{x}.' for x in (freeze if len(freeze) > 1 else range(freeze[0]))] # layers to freeze
for k, v in model.named_parameters():
v.requires_grad = True # train all layers
if any(x in k for x in freeze):
LOGGER.info(f'freezing {k}')
v.requires_grad = False # By way of requires_gard Set to false , That is, no gradient calculation
# ..................................... Enter the size setting and batch-size Set up .................................................
# If you add some structure to your network structure , Make the smallest eigenvalue of your output no longer 32 Times down sampling , Remember to change the content here ......................
# Image size , If not 32 Under sampling , for example 128 times , To change Many About the setting of down sampling , For example, the picture should be 128 And so on . ..... ......
gs = max(int(model.stride.max()), 32) # grid size (max stride)
# call general.py In the document check_img_size( ) Function to check whether the image size is s( The default is 32) Integer multiple , If not Just adjust it to 32 Integer multiple
imgsz = check_img_size(opt.imgsz, gs, floor=gs * 2) # verify imgsz is gs-multiple
# Batch size , The default is 16
if RANK == -1 and batch_size == -1: # single-GPU only, estimate best batch size
# call autobatch.py Medium check_train_batch_size , The main check is the training set batch_size Compliance with specifications
batch_size = check_train_batch_size(model, imgsz)
loggers.on_params_update({"batch_size": batch_size})
# Optimizer .................................... Optimizer settings , The default optimizer is SGD..........................................
# nbs Nominal batc_size:
# For example, the above settings are set by default opt.batch_size by 16 , nbs=64
# Then the gradient of the model is accumulated 64/16= 4 (accumulate) After that , Updating the model once , Expansion in disguise batch_size
nbs = 64 # nominal batch size
accumulate = max(round(nbs / batch_size), 1) # accumulate loss before optimizing
# according to accumlate Set the weight attenuation factor , weight_decay stay hyp It is used in 0.00036
# The new attenuation coefficient is = 0.00036 * batch_size * With the above rules (nbs /batch_size ) /nbs
hyp['weight_decay'] *= batch_size * accumulate / nbs # scale weight_decay Weight decay
LOGGER.info(f"Scaled weight_decay = {hyp['weight_decay']}")
g0, g1, g2 = [], [], [] # optimizer parameter groups
# Set optimizer list , That is to divide the model into 3 Group , (weight , bias , All other parameters ) To optimize
for v in model.modules():
if hasattr(v, 'bias') and isinstance(v.bias, nn.Parameter): # bias
g2.append(v.bias)
# bias Load on g2 In the optimization list of
if isinstance(v, nn.BatchNorm2d): # weight (no decay)
g0.append(v.weight) # If it is bn layer , Add weights without attenuation to g0 in , That is to say BN Layers do not have weight attenuation
elif hasattr(v, 'weight') and isinstance(v.weight, nn.Parameter): # weight (with decay attenuation )
g1.append(v.weight) # Add the weight of the attenuated layer to g1 in
# If we pass in a parameter yes --adam , in other words opt.adam by true , therefore We're going to use Adam Optimizer
if opt.adam:
optimizer = Adam(g0, lr=hyp['lr0'], betas=(hyp['momentum'], 0.999)) # adjust beta1 to momentum
# Otherwise, the default is SGD Optimizer
else:
optimizer = SGD(g0, lr=hyp['lr0'], momentum=hyp['momentum'], nesterov=True)
# Set up weight Optimization method
optimizer.add_param_group({'params': g1, 'weight_decay': hyp['weight_decay']}) # Attenuation operation
# Set up biases Optimization method
optimizer.add_param_group({'params': g2}) # add g2 (biases)
# Print information : optimizer : Adam with parameter groups , How many weight The weight has no attenuation , How many weight Weight falloff , How many bias
LOGGER.info(f"{colorstr('optimizer:')} {type(optimizer).__name__} with parameter groups "
f"{len(g0)} weight (no decay), {len(g1)} weight , {len(g2)} bias")
del g0, g1, g2
# ................................................ Set the attenuation of learning rate , Here is the cosine annealing method for attenuation ..............................
# Scheduler Set learning rate attenuation , Here is the cosine annealing method for attenuation
if opt.linear_lr:
lf = lambda x: (1 - x / (epochs - 1)) * (1.0 - hyp['lrf']) + hyp['lrf'] # linear Annealing formula
else:
lf = one_cycle(1, hyp['lrf'], epochs) # cosine 1->hyp['lrf']
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lf) # plot_lr_scheduler(optimizer, scheduler, epochs)
# ...................................................................................................................
# EMA call torch_utils.py In the document ModelEMA class Model EMA , Is to make an index of the parameters in the network model moving average , Smooth the weights , It has better effect on some training
ema = ModelEMA(model) if RANK in [-1, 0] else None
# Resume
# Initialize the start of training epoch And the best results
# best_fitness In order to [ 0.0 , 0.0 , 0.1 , 0.9 ] Is the coefficient multiplied by [ accuracy p , Recall rate , [email protected] , [email protected]:0.95 ] Then sum up and get
# best_fitness To preserve best.pt
start_epoch, best_fitness = 0, 0.0
if pretrained: # pretrained = weights.endswith('.pt') That is, whether to use pre training
# Optimizer
if ckpt['optimizer'] is not None: # If ckpt Medium optimizer There's something , is not None , Namely true
optimizer.load_state_dict(ckpt['optimizer'])
best_fitness = ckpt['best_fitness']
# EMA
# Create... For the model EMA Exponential moving average , If GPU The number of processes is greater than 1 , Do not create
# EMA( Exponentially moving average ): An averaging method that gives higher weight to recent data
# use EMA Methods average the parameters of the model , In order to improve the test indicators and increase the people of the model , Reduce model weight jitter
if ema and ckpt.get('ema'):
ema.ema.load_state_dict(ckpt['ema'].float().state_dict())
ema.updates = ckpt['updates']
# Epochs
start_epoch = ckpt['epoch'] + 1
if resume:
assert start_epoch > 0, f'{weights} training to {epochs} epochs is finished, nothing to resume.'
'''
If the new settings epochs Less than loaded epoch
It will be regarded as the newly set epochs For the number of rounds that need to be retrained instead of the total number of rounds
'''
if epochs < start_epoch:
LOGGER.info(f"{weights} has been trained for {ckpt['epoch']} epochs. Fine-tuning for {epochs} more epochs.")
epochs += ckpt['epoch'] # finetune additional epochs
del ckpt, csd
'''
DP Training : Reference resources https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/679
DataParallel Pattern , Only single machine and multi card are supported
RANK Number the process , If set rank=-1 And there are many pieces GPU , Then use DataParallel Model
rank =-1 And GPU The number of 1 , No distributed training
'''
# DP mode
if cuda and RANK == -1 and torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:
# You have more than one card Warning : Not recommended DP Training , In order to get better distributed multi block GPU Training results , Use torch.distributed.run Method
# see also https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/475 More on gpu The tutorial begins
LOGGER.warning('WARNING: DP not recommended, use torch.distributed.run for best DDP Multi-GPU results.
'
'See Multi-GPU Tutorial at https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/475 to get started.')
model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
# SyncBatchNorm sync_bn Indicates whether to use cross card synchronization
if opt.sync_bn and cuda and RANK != -1:
model = torch.nn.SyncBatchNorm.convert_sync_batchnorm(model).to(device)
LOGGER.info('Using SyncBatchNorm()')
# ................................................ Create a training set based on the training set path train_loader..................................
# Trainloader, Use datasets.py Medium create_datalaoder() Method
train_loader, dataset = create_dataloader(train_path, imgsz, batch_size // WORLD_SIZE, gs, single_cls,
hyp=hyp, augment=True, cache=opt.cache, rect=opt.rect, rank=LOCAL_RANK,
workers=workers, image_weights=opt.image_weights, quad=opt.quad,
prefix=colorstr('train: '), shuffle=True)
# Get the maximum category value in the tag And with the number of categories nc compare
mlc = int(np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0].max()) # max label class , The maximum number of categories of labels
nb = len(train_loader) # number of batches
# mlc If it is greater than nc Print : Number of label categories mlc More than in Defined in the dataset nc value , Of the allowed tags The category value is in 0 -- nc-1 Between
assert mlc < nc, f'Label class {mlc} exceeds nc={nc} in {data}. Possible class labels are 0-{nc - 1}'
# ................................................ To create a training set based on the validation set path val_loader..................................
# Process 0
if RANK in [-1, 0]:
# Use datasets.py Medium create_datalaoder() Method to create a validation set val_loader
val_loader = create_dataloader(val_path, imgsz, batch_size // WORLD_SIZE * 2, gs, single_cls,
hyp=hyp, cache=None if noval else opt.cache, rect=True, rank=-1,
workers=workers, pad=0.5,
prefix=colorstr('val: '))[0]
# .............................. Draw all of them lables1 Type information of , Center point distribution information , And length and width information ..................................
if not resume: # If not Breakpoint training
labels = np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0) # Get dataset The tag value of
# c = torch.tensor(labels[:, 0]) # classes
# cf = torch.bincount(c.long(), minlength=nc) + 1. # frequency
# model._initialize_biases(cf.to(device))
if plots: # plots = not evolve That is to say, if we don't turn on hyperparametric evolution , That is to say plots by true , Then print the relevant information
# call plots.py Medium plot_lables Information , save_dir The path to runs/train/exp/ Next ,
plot_labels(labels, names, save_dir)
# Anchors , If the parameter we pass in is --noautoanchor Then go to true , Is to turn off the automatic calculation of the aiming box ,
# here not ot opt.noautoanchor for flase , Just don't do what's inside sentence , Otherwise, by default , It will start the automatic aiming frame calculation
# ........ .............. ............. Whether to enable auto aiming frame calculation ........................................................
if not opt.noautoanchor:
# By default, auto aiming calculation is enabled , call autoanchor.py Medium check_anchors Turn on Automatically calculate the best aiming frame , That is to calculate the best aiming frame
check_anchors(dataset, model=model, thr=hyp['anchor_t'], imgsz=imgsz)
model.half().float() # pre-reduce anchor precision
# That is to say Breakpoint training Auto frame calculation will not be enabled
callbacks.run('on_pretrain_routine_end')
# DDP mode
# If rank It's not equal to -1, Then use DistributedDataParallel Pattern
# local__rank by GPU Number ,rank For the process , for example rank =3 ,local_rank= 0 It means the first one 3 The first block in a process GPU
if cuda and RANK != -1:
model = DDP(model, device_ids=[LOCAL_RANK], output_device=LOCAL_RANK)
# Model attributes................................ Model property settings .........................................
nl = de_parallel(model).model[-1].nl # number of detection layers (to scale hyps)
# Set the coefficient of classification loss according to the number of categories of your data set Positioning loss and confidence loss coefficient
hyp['box'] *= 3 / nl # scale to layers
hyp['cls'] *= nc / 80 * 3 / nl # scale to classes and layers
hyp['obj'] *= (imgsz / 640) ** 2 * 3 / nl # scale to image size and layers
hyp['label_smoothing'] = opt.label_smoothing # towards hyp Intermediate placement label_smoothing Properties of , If you pass in --label-smoothing Is to open the class balance tab
model.nc = nc # attach number of classes to model Number of associated categories
model.hyp = hyp # attach hyperparameters to model , Associated super parameters
# Get the category weight from the training sample label ( And the number of targets in the category --- That is, category frequency -- In inverse proportion )
model.class_weights = labels_to_class_weights(dataset.labels, nc).to(device) * nc # attach class weights
# Get the name of the category
model.names = names
# Start training........................................ Start training .......................................................
t0 = time.time()
# Get the number of iterations of warm-up training , That is, the number of warm-up exercises
nw = max(round(hyp['warmup_epochs'] * nb), 1000) # number of warmup iterations, max(3 epochs, 1k iterations)
# nw = min(nw, (epochs - start_epoch) / 2 * nb) # limit warmup to < 1/2 of training
last_opt_step = -1
# initialization mAP and results Value
maps = np.zeros(nc) # mAP per class
results = (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) # P, R, [email protected], [email protected], val_loss(box, obj, cls)
'''
Set the number of rounds of learning rate attenuation
The purpose is to interrupt after training .--resume Then the training can also normally link up with the previous training to reduce the learning rate
'''
scheduler.last_epoch = start_epoch - 1 # do not move
# adopt torch1.6 The above comes with api Set hybrid accuracy training
scaler = amp.GradScaler(enabled=cuda)
# If you pass in --patience Parameters , perform train.py Medium EarlyStopping function The number of training does not increase the performance by more than epochs when , Stop training
stopper = EarlyStopping(patience=opt.patience)
compute_loss: ComputeLoss = ComputeLoss(model) # initialization model Of loss
# Corresponding to the size yes 640 Training ,640 verification
# Being used How many threads
# The results are in runs/train/exp Next
# Training that epochs
LOGGER.info(f'Image sizes {imgsz} train, {imgsz} val
'
f'Using {train_loader.num_workers * WORLD_SIZE} dataloader workers
'
f"Logging results to {colorstr('bold', save_dir)}
"
f'Starting training for {epochs} epochs...')
# ---------------------------------------------- Start the iteration epoch -------------------------------------------------------
for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs):
model.train() # Start training
# Update image weights (optional, single-GPU only)
if opt.image_weights:
'''
If you set the image sampling policy
Then, according to the previously initialized image sampling weight model.class_weights as well as maps coordination Number of categories per picture
adopt random.choice Generate image index indices So as to sample
What kind of images does this real dataset use , Focus can be set , If the original maps The larger ,1-maps It becomes smaller
Such a big one maps The weight of is set For the small , for example There are many labels in the dataset classese After this operation weights It will also be smaller
'''
cw = model.class_weights.cpu().numpy() * (1 - maps) ** 2 / nc # class weights
iw = labels_to_image_weights(dataset.labels, nc=nc, class_weights=cw) # Get the weight of image sampling
dataset.indices = random.choices(range(dataset.n), weights=iw, k=dataset.n) # rand weighted idx
# Update mosaic border (optional)
# b = int(random.uniform(0.25 * imgsz, 0.75 * imgsz + gs) // gs * gs)
# dataset.mosaic_border = [b - imgsz, -b] # height, width borders
# Average loss information printed when initializing training
mloss = torch.zeros(3, device=device) # mean losses
if RANK != -1:
'''
DDP Scramble data under the model ,ddp.sampler The random sampling data is based on epoch+ seed As random seeds
Every time epoch Different , Random seeds are different
'''
train_loader.sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
pbar = enumerate(train_loader)
LOGGER.info(('
' + '%10s' * 7) % ('Epoch', 'gpu_mem', 'box', 'obj', 'cls', 'labels', 'img_size'))
if RANK in [-1, 0]:
# tqdm Create a progress bar , Facilitate the display of information during training
pbar = tqdm(pbar, total=nb, bar_format='{l_bar}{bar:10}{r_bar}{bar:-10b}') # progress bar
optimizer.zero_grad() # Zero clearing
for i, (imgs, targets, paths, _) in pbar: # batch -------------------------------------------------------------
# Calculate the number of iterations iteration
ni = i + nb * epoch # number integrated batches (since train start)
imgs = imgs.to(device, non_blocking=True).float() / 255 # uint8 to float32, 0-255 to 0.0-1.0
# Warmup
'''
Warm up ( front nw Sub iteration )
stay front nw In the next iteration , Select... According to the following methods accumulate And the learning rate
'''
if ni <= nw:
xi = [0, nw] # x interp nw = max(round(hyp['warmup_epochs'] * nb), 1000) We have already defined how many times to warm up
# compute_loss.gr = np.interp(ni, xi, [0.0, 1.0]) # iou loss ratio (obj_loss = 1.0 or iou)
accumulate = max(1, np.interp(ni, xi, [1, nbs / batch_size]).round())
for j, x in enumerate(optimizer.param_groups):
'''
bias The learning rate has increased from 0.1 Down to the benchmark learning rate lr*lf(epoch)
The learning rate of other parameters ranges from 0 Add to lr* lf(epoch)
lf Attenuation function for cosine annealing set above
'''
# bias lr falls from 0.1 to lr0, all other lrs rise from 0.0 to lr0
x['lr'] = np.interp(ni, xi, [hyp['warmup_bias_lr'] if j == 2 else 0.0, x['initial_lr'] * lf(epoch)])
# Pillar momentum Also from the 0.9 Slowly to hyp['momentum']
if 'momentum' in x:
x['momentum'] = np.interp(ni, xi, [hyp['warmup_momentum'], hyp['momentum']])
# Multi-scale
# Multiscale training , from imgsz* 0.5 , imgsz* 1.5 + gs Select the size randomly
if opt.multi_scale:
sz = random.randrange(imgsz * 0.5, imgsz * 1.5 + gs) // gs * gs # size
sf = sz / max(imgs.shape[2:]) # scale factor
if sf != 1:
ns = [math.ceil(x * sf / gs) * gs for x in imgs.shape[2:]] # new shape (stretched to gs-multiple)
imgs = nn.functional.interpolate(imgs, size=ns, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# Forward
# Mixed precision training
with amp.autocast(enabled=cuda): # autocast The context should only contain the forward process of the network ( Include loss The calculation of ) , Do not include back propagation
pred = model(imgs) # forward Forward operation
# In front of 437 Right and left of the line , compute_loss: ComputeLoss = ComputeLoss(model) It's initialized model Of loss
# The main application is loss.py Medium ComputeLoss Class instantiates a ComputerLoss,
# By using the fl_gamma: Greater than 0 Set up , Enable Focallost ,focallost The main solution is Target detection phase one-stage The problem of imbalance between positive and negative samples
# meanwhile , ComputeLoss Medium It's called metrics.py Medium bbox_iou , Enabled by default Ciou=True , That is to say By default Ciou To investigate the positioning loss of the frame
loss, loss_items = compute_loss(pred, targets.to(device)) # loss scaled by batch_size
if RANK != -1:
loss *= WORLD_SIZE # gradient averaged between devices in DDP mode
if opt.quad:
loss *= 4.
# Backward Back propagation
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
# Optimize , Optimize : Model back propagation accumulate And then update the parameters once according to the accumulated gradient
if ni - last_opt_step >= accumulate:
'''
scaler.step() First, the value of the gradient unscale Come back
If the value of the gradient is not infs perhaps NaNs , So called optimizer.step() To update the weights .
otherwise , Ignore step call , So as to ensure that the weight is not updated ( Not destroyed )
'''
scaler.step(optimizer) # optimizer.step Update parameters
# Be ready to , See if you want to increase scaler
scaler.update()
optimizer.zero_grad() # Gradient clear
# use EMA Methods average the parameters of the model , In order to improve the test indicators and increase the people of the model , Reduce model weight jitter
if ema:
ema.update(model)
last_opt_step = ni
# Make a note of Some of the information , Show some information
if RANK in [-1, 0]:
# Print video memory , Rounds carried out , Loss ,target The number and The image size Etc
mloss = (mloss * i + loss_items) / (i + 1) # update mean losses, Calculation How many times do you train Average loss
mem = f'{torch.cuda.memory_reserved() / 1E9 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0:.3g}G' # (GB)
pbar.set_description(('%10s' * 2 + '%10.4g' * 5) % (
f'{epoch}/{epochs - 1}', mem, *mloss, targets.shape[0], imgs.shape[-1]))
callbacks.run('on_train_batch_end', ni, model, imgs, targets, paths, plots, opt.sync_bn)
# end batch ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Every batch After completion , Will adjust the learning rate
# Scheduler
lr = [x['lr'] for x in optimizer.param_groups] # for loggers
scheduler.step() # Adjust the learning rate
# .................................................... Judge whether it is the last round of training , If yes, start the validation set .........................
if RANK in [-1, 0]:
# mAP
callbacks.run('on_train_epoch_end', epoch=epoch)
# add to include Properties of
ema.update_attr(model, include=['yaml', 'nc', 'hyp', 'names', 'stride', 'class_weights'])
# Judge that epoch Whether it's the last round
final_epoch = (epoch + 1 == epochs) or stopper.possible_stop
# Test the test set , And calculate mAP Equal index
# The test was conducted with EMA Model , If you pass in --noval Parameters , noval Namely true, not noval Namely false , That is to say Validation set validation will not be started
if not noval or final_epoch: # Calculate mAP
results, maps, _ = val.run(data_dict,
batch_size=batch_size // WORLD_SIZE * 2,
imgsz=imgsz,
model=ema.ema,
single_cls=single_cls,
dataloader=val_loader,
save_dir=save_dir,
plots=False,
callbacks=callbacks,
compute_loss=compute_loss)
# Update best mAP , Update the best mAP
fi = fitness(np.array(results).reshape(1, -1)) # weighted combination of [P, R, [email protected], [email protected]]
if fi > best_fitness:
best_fitness = fi
log_vals = list(mloss) + list(results) + lr
callbacks.run('on_fit_epoch_end', log_vals, epoch, best_fitness, fi)
# Save model................................................. Save the model ...................................
# preservation & Loading belt checkpoint The model is used for inference or resuming training
# Save the model , And preserved epoch,results,optimizer Etc
# optimizer Saving will not be completed in the last round
# model What is kept is EMA Model of
if (not nosave) or (final_epoch and not evolve): # if save
ckpt = {'epoch': epoch,
'best_fitness': best_fitness,
'model': deepcopy(de_parallel(model)).half(),
'ema': deepcopy(ema.ema).half(),
'updates': ema.updates,
'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),
'wandb_id': loggers.wandb.wandb_run.id if loggers.wandb else None,
'date': datetime.now().isoformat()}
# Save last, best and delete, Save the latest weights to last.pt in
torch.save(ckpt, last)
# See if it's assembled fitness, If yes, save the weight to best.pt in
if best_fitness == fi:
torch.save(ckpt, best)
if (epoch > 0) and (opt.save_period > 0) and (epoch % opt.save_period == 0):
torch.save(ckpt, w / f'epoch{epoch}.pt')
del ckpt
callbacks.run('on_model_save', last, epoch, final_epoch, best_fitness, fi)
# Stop Single-GPU
if RANK == -1 and stopper(epoch=epoch, fitness=fi):
break
# Stop DDP TODO: known issues shttps://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/4576
# stop = stopper(epoch=epoch, fitness=fi)
# if RANK == 0:
# dist.broadcast_object_list([stop], 0) # broadcast 'stop' to all ranks
# Stop DPP
# with torch_distributed_zero_first(RANK):
# if stop:
# break # must break all DDP ranks
# end epoch ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# end training -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
if RANK in [-1, 0]:
# Print epoch Total time
LOGGER.info(f'
{epoch - start_epoch + 1} epochs completed in {(time.time() - t0) / 3600:.3f} hours.')
for f in last, best:
if f.exists():
# call general.py Medium strip_optimizer( ) function ............................. Split the optimizer information in the weight file ...............
strip_optimizer(f) # strip optimizers
# If it is the best , Call again Validation set to validate the model
if f is best:
LOGGER.info(f'
Validating {f}...')
results, _, _ = val.run(data_dict,
batch_size=batch_size // WORLD_SIZE * 2,
imgsz=imgsz,
model=attempt_load(f, device).half(),
iou_thres=0.65 if is_coco else 0.60, # best pycocotools results at 0.65
single_cls=single_cls,
dataloader=val_loader,
save_dir=save_dir,
save_json=is_coco,
verbose=True,
plots=True,
callbacks=callbacks,
compute_loss=compute_loss) # val best model with plots
if is_coco:
callbacks.run('on_fit_epoch_end', list(mloss) + list(results) + lr, epoch, best_fitness, fi)
callbacks.run('on_train_end', last, best, plots, epoch, results)
LOGGER.info(f"Results saved to {colorstr('bold', save_dir)}")
# Video memory release
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
return results
def parse_opt(known=False):
# establish Parameter resolution object parser()
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# add_argument() Is to add One What attribute
# nargs refer to ---> Should read The number of command line parameters for , * Express 0 Or more , + Express 1 Or more
# action -- The command line Action when parameters are encountered , action='store_true' , Indicates that the variable is set to as long as it has a parameter passed during runtime True
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default=ROOT / 'yolov5s.pt', help='initial weights path')
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='', help='model.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/coco128.yaml', help='dataset.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--hyp', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/hyps/hyp.scratch.yaml', help='hyperparameters path')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=300)
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=16, help='total batch size for all GPUs, -1 for autobatch')
parser.add_argument('--imgsz', '--img', '--img-size', type=int, default=640, help='train, val image size (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--rect', action='store_true', help='rectangular training')
parser.add_argument('--resume', nargs='?', const=True, default=False, help='resume most recent training')
parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='only save final checkpoint')
parser.add_argument('--noval', action='store_true', help='only validate final epoch')
parser.add_argument('--noautoanchor', action='store_true', help='disable autoanchor check')
parser.add_argument('--evolve', type=int, nargs='?', const=300, help='evolve hyperparameters for x generations')
parser.add_argument('--bucket', type=str, default='', help='gsutil bucket')
parser.add_argument('--cache', type=str, nargs='?', const='ram', help='--cache images in "ram" (default) or "disk"')
parser.add_argument('--image-weights', action='store_true', help='use weighted image selection for training')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--multi-scale', action='store_true', help='vary img-size +/- 50%%')
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='train multi-class data as single-class')
parser.add_argument('--adam', action='store_true', help='use torch.optim.Adam() optimizer')
parser.add_argument('--sync-bn', action='store_true', help='use SyncBatchNorm, only available in DDP mode')
parser.add_argument('--workers', type=int, default=8, help='max dataloader workers (per RANK in DDP mode)')
parser.add_argument('--project', default=ROOT / 'runs/train', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
parser.add_argument('--quad', action='store_true', help='quad dataloader')
parser.add_argument('--linear-lr', action='store_true', help='linear LR')
parser.add_argument('--label-smoothing', type=float, default=0.0, help='Label smoothing epsilon')
parser.add_argument('--patience', type=int, default=100, help='EarlyStopping patience (epochs without improvement)')
parser.add_argument('--freeze', nargs='+', type=int, default=[0], help='Freeze layers: backbone=10, first3=0 1 2')
parser.add_argument('--save-period', type=int, default=-1, help='Save checkpoint every x epochs (disabled if < 1)')
parser.add_argument('--local_rank', type=int, default=-1, help='DDP parameter, do not modify')
# Weights & Biases arguments
parser.add_argument('--entity', default=None, help='W&B: Entity')
parser.add_argument('--upload_dataset', nargs='?', const=True, default=False, help='W&B: Upload data, "val" option')
parser.add_argument('--bbox_interval', type=int, default=-1, help='W&B: Set bounding-box image logging interval')
parser.add_argument('--artifact_alias', type=str, default='latest', help='W&B: Version of dataset artifact to use')
# use parse_args() Function to parse the obtained parameters
# That is to say, this sentence Got We type... From the command line Content and carried out analysis , Other properties are defaulted
opt = parser.parse_known_args()[0] if known else parser.parse_args()
return opt
def main(opt, callbacks=Callbacks()):
# Checks, RANK The value of is defined at the beginning
if RANK in [-1, 0]:
# call general.py In the document print_args() Function to print relevant information
print_args(FILE.stem, opt)
# call general.py In the document check_git_status() function , # This function checks whether the current branch version is git Same as the previous version , If not ,
# If the version is backward, users will be reminded , This function is in the trian.py Function is used in
check_git_status()
# Before the final test , Take a look at it requirements.txt In demand Whether the operating environment is installed , If not, update and download
check_requirements(exclude=['thop'])
# Resume , If the command we enter on the keyboard has --resume , That is, breakpoint training , And no hyperparametric evolution is specified
if opt.resume and not check_wandb_resume(opt) and not opt.evolve: # resume an interrupted run
# If you pass in --resume Namely true , isinstance(opt.resume, str) It's wrong
# call general.py Medium get_latest_run() Get the weight file of recent training last.pt to ckpt
ckpt = opt.resume if isinstance(opt.resume, str) else get_latest_run() # Specify the path of the most recently run model
# Judge ckpt Is it a document , If it is not a file, an error is reported
assert os.path.isfile(ckpt), 'ERROR: --resume checkpoint does not exist' # Warning : The recovery point checked does not exist
# If it's a file , Go to the superior directory to find opt.yaml To resume training
with open(Path(ckpt).parent.parent / 'opt.yaml', errors='ignore') as f:
opt = argparse.Namespace(**yaml.safe_load(f)) # replace
opt.cfg, opt.weights, opt.resume = '', ckpt, True # reinstate
LOGGER.info(f'Resuming training from {ckpt}') # Print information : From ckpt ( The latest last.pt File office ) Break point training
else:
# Otherwise, it would be No, resume , Or into --evolve , So hyperparametric evolution , above not opt.evolve Namely false, Then execute the following statement
opt.data, opt.cfg, opt.hyp, opt.weights, opt.project =
check_file(opt.data), check_yaml(opt.cfg), check_yaml(opt.hyp), str(opt.weights), str(opt.project) # checks
assert len(opt.cfg) or len(opt.weights), 'either --cfg or --weights must be specified'
# If something goes wrong , len(opt.cfg) or len(opt.weights), To print, you must specify ——cfg or ——weights
if opt.evolve:
opt.project = str(ROOT / 'runs/evolve')
opt.exist_ok, opt.resume = opt.resume, False # pass resume to exist_ok and disable resume
opt.save_dir = str(increment_path(Path(opt.project) / opt.name, exist_ok=opt.exist_ok))
# That is, hyperparametric evolution cannot be related to Breakpoint training , If Turn on hyperparametric evolution , You must specify one first cfg perhaps weights
# opt.save_dir =runs/evolve/exp
# Use torch_utils in select_device() function According to device Value Make device selection
device = select_device(opt.device, batch_size=opt.batch_size)
# DDP mode
"""
Distributed training related settings
Set up DDP Parameters of the pattern
world_size : Indicates the number of global processes
global_rank: Process number
"""
if LOCAL_RANK != -1:
assert torch.cuda.device_count() > LOCAL_RANK, 'insufficient CUDA devices for DDP command'
assert opt.batch_size % WORLD_SIZE == 0, '--batch-size must be multiple of CUDA device count'
# The batch size must be CUDA Integral multiples of the device
assert not opt.image_weights, '--image-weights argument is not compatible with DDP training'
# --image-weights Parameters and DDP Training incompatible
assert not opt.evolve, '--evolve argument is not compatible with DDP training' # -evolve Parameters and DDP Training incompatible
torch.cuda.set_device(LOCAL_RANK)
device = torch.device('cuda', LOCAL_RANK) # according to Gpu Select the equipment with the number of
# Initialize the process array
dist.init_process_group(backend="nccl" if dist.is_nccl_available() else "gloo")
# Train opt.evole If it is false , That is, there is no hyperparametric evolution
if not opt.evolve:
# Just start training ...................................................
train(opt.hyp, opt, device, callbacks)
if WORLD_SIZE > 1 and RANK == 0:
LOGGER.info('Destroying process group... ') # Destroying process group , start WORLD_SIZE =1 ,RANK by -1 , So I won't execute this sentence
dist.destroy_process_group()
# That is, hyperparametric evolution cannot be related to Breakpoint training , If Turn on hyperparametric evolution , Must learn to specify a first cfg perhaps weights
# Evolve hyperparameters (optional), It began to evolve hyp Parameters in
'''
yolov5 A method of hyperparametric optimization is provided –Hyperparameter Evolution, That is, hyperparametric evolution . Hyperparametric evolution is a kind of utilization Genetic algorithm (ga) (GA)
The method of hyperparametric optimization , We can use this method to select a more appropriate super parameter . The default parameters provided are also passed in COCO Data sets are evolved using hyperparameters .
Because hyperparametric evolution will consume a lot of resources and time , If the result of default parameter training can meet your use , It is also a good choice to use default parameters .
'''
else: # evolve If it's true, start hyperparametric evolution
# hyp Parameter evolution in An evolutionary list of meta ( Mutation scale , minimum value , Maximum limit )
meta = {'lr0': (1, 1e-5, 1e-1), # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
'lrf': (1, 0.01, 1.0), # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
'momentum': (0.3, 0.6, 0.98), # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
'weight_decay': (1, 0.0, 0.001), # optimizer weight decay
'warmup_epochs': (1, 0.0, 5.0), # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
'warmup_momentum': (1, 0.0, 0.95), # warmup initial momentum
'warmup_bias_lr': (1, 0.0, 0.2), # warmup initial bias lr
'box': (1, 0.02, 0.2), # box loss gain
'cls': (1, 0.2, 4.0), # cls loss gain
'cls_pw': (1, 0.5, 2.0), # cls BCELoss positive_weight
'obj': (1, 0.2, 4.0), # obj loss gain (scale with pixels)
'obj_pw': (1, 0.5, 2.0), # obj BCELoss positive_weight
'iou_t': (0, 0.1, 0.7), # IoU training threshold
'anchor_t': (1, 2.0, 8.0), # anchor-multiple threshold
'anchors': (2, 2.0, 10.0), # anchors per output grid (0 to ignore)
'fl_gamma': (0, 0.0, 2.0), # focal loss gamma (efficientDet default gamma=1.5)
'hsv_h': (1, 0.0, 0.1), # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_s': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_v': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
'degrees': (1, 0.0, 45.0), # image rotation (+/- deg)
'translate': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image translation (+/- fraction)
'scale': (1, 0.0, 0.9), # image scale (+/- gain)
'shear': (1, 0.0, 10.0), # image shear (+/- deg)
'perspective': (0, 0.0, 0.001), # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
'flipud': (1, 0.0, 1.0), # image flip up-down (probability)
'fliplr': (0, 0.0, 1.0), # image flip left-right (probability)
'mosaic': (1, 0.0, 1.0), # image mosaic (probability)
'mixup': (1, 0.0, 1.0), # image mixup (probability)
'copy_paste': (1, 0.0, 1.0)} # segment copy-paste (probability)
# Open the file of the super parameter
with open(opt.hyp, errors='ignore') as f:
hyp = yaml.safe_load(f) # load hyps dict , Also is to hyp Document to hyp
if 'anchors' not in hyp: # anchors commented in hyp.yaml , That is, how many prior boxes are generated for each feature graph , If anchors be not in , Set to 3
hyp['anchors'] = 3
opt.noval, opt.nosave, save_dir = True, True, Path(opt.save_dir) # only val/save final epoch
# ei = [isinstance(x, (int, float)) for x in hyp.values()] # evolvable indices
# That is to say . After evolution evolve_yaml, evolve_csv Store in , opt.save_dir =runs/evolve/exp Next
evolve_yaml, evolve_csv = save_dir / 'hyp_evolve.yaml', save_dir / 'evolve.csv'
if opt.bucket: # If the incoming is --bucket , Is cloud disk Google
os.system(f'gsutil cp gs://{opt.bucket}/evolve.csv {save_dir}') # download evolve.csv if exists
# At this point we already know the original hyperparameter hyp and One List of hyperparametric evolution rules meta
'''
The evolutionary algorithm here is : According to the previous training hyp To identify a base hyp Re evolution mutation :
The specific methods :
Through every previous evolution results To determine each of the previous hyp The weight
With Every hyp And each hyp After the weight of There are two ways of evolution
The first one is single: According to each hyp Select a previous one at random hyp As base hyp , random.choice(range(n)) , weights=w
The second kind weighted: According to each hyp The weight of Yes, all the previous hyp To merge To obtain a base hyp (x*w.reeshape(n,1) ) .sum(0) / w.sum()
evolve.csv Will record after each evolution results+hyp
Every time you evolve ,hyp According to the previous result Sort from big to small ;
According to fitness Each evolution before the function calculation results in hyp The weight of
In determining which evolutionary approach single still weighted , To evolve
'''
# for _ in range(300) : How many times has it evolved
for _ in range(opt.evolve): # generations to evolve
if evolve_csv.exists(): # if evolve.csv exists: select best hyps and mutate , The path of preserving results after evolution exists
# Select parent(s) The parents in genetic algorithm
# Choose the way of evolution , If it is Choose the first one single
parent = 'single' # parent selection method: 'single' or 'weighted'
x = np.loadtxt(evolve_csv, ndmin=2, delimiter=',', skiprows=1) # load evolve_csv file
# x The value of is (p, R, mAP, F1, test_lossese=(box, obj, cls) ), After that is hyp Value
# At most... Before 5 The result of sub evolution
n = min(5, len(x)) # number of previous results to consider
x = x[np.argsort(-fitness(x))][:n] # top n mutations
# according to results Calculation hyp The weight of , call metrics.py Medium fitness()
w = fitness(x) - fitness(x).min() + 1E-6 # weights (sum > 0)
# If you choose the first method single Namely random.choice(range(n)) , weights=w.............................
if parent == 'single' or len(x) == 1:
x = x[random.choices(range(n), weights=w)[0]] # weighted selection
# If you choose the second way weighted Namely (x*w.reeshape(n,1) ) .sum(0) / w.sum() ..................
elif parent == 'weighted':
x = (x * w.reshape(n, 1)).sum(0) / w.sum() # weighted combination
# Mutate, Hyperparametric evolution
mp, s = 0.8, 0.2 # mp It means mutation probability Mutation probability , s refer to sigma
npr = np.random
npr.seed(int(time.time()))
# Get the initial value of mutation meta It's a dictionary , meta[k][0] Is to choose What kind of parameters
g = np.array([meta[k][0] for k in hyp.keys()]) # gains 0-1
ng = len(meta)
v = np.ones(ng)
# Set mutation
while all(v == 1): # mutate until a change occurs (prevent duplicates)
v = (g * (npr.random(ng) < mp) * npr.randn(ng) * npr.random() * s + 1).clip(0.3, 3.0)
# Add mutation to base hyp On
# [i+7] Because x Middle front 7 Numbers are results Indicators of ( p , R , mAP ,F1 , test_lossese=(box , obj ,cls) ), Then comes the super parameter hyp
for i, k in enumerate(hyp.keys()): # plt.hist(v.ravel(), 300)
hyp[k] = float(x[i + 7] * v[i]) # mutate
# trim hyp Within the specified range
# Constrain to limits
for k, v in meta.items():
hyp[k] = max(hyp[k], v[1]) # lower limit
hyp[k] = min(hyp[k], v[2]) # upper limit
hyp[k] = round(hyp[k], 5) # significant digits
# Train mutation. Training
results = train(hyp.copy(), opt, device, callbacks)
# Write mutation results
# write in results It's the same as hyp To evolve.csv in , evolve.csv Document the result of each behavior evolution
# The first in a line 7 A digital by ( p , R , mAP ,F1 , test_lossese=(box , obj ,cls) ) , And then hyp
# preservation hyp To yaml In the document
print_mutation(results, hyp.copy(), save_dir, opt.bucket)
# Plot results, call plots.py Medium plot_evolve() The function draws Evolution results
plot_evolve(evolve_csv)
# Hyperparametric evolution is complete , Where the results are saved , Use the best super parameters , Which is the result of your evolution , for example : python train.py --hyp {evolve_yaml}')
LOGGER.info(f'Hyperparameter evolution finished
'
f"Results saved to {colorstr('bold', save_dir)}
"
f'Use best hyperparameters example: $ python train.py --hyp {evolve_yaml}')
def run(**kwargs):
# Usage: import train; train.run(data='coco128.yaml', imgsz=320, weights='yolov5m.pt')
opt = parse_opt(True)
for k, v in kwargs.items():
setattr(opt, k, v)
main(opt)
if __name__ == "__main__":
opt = parse_opt()
main(opt)
'''
python train.py --cfg models/yolov5s.yaml --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --data data/ab.yaml --img 640 --batch 16 --epoch 300
opt
weights : Loaded weight file The default is yolov5s.pt
cfg : The configuration file that stores the model structure The default is ''
data : Storage training 、 File of test data The default is data/coco128.yaml
hyp : Training super parameter configuration file The default is data/hyps/hyp.scratch.yaml
epochs : Total number of workouts The default is 300
batch-size : The size of each batch , One epochs= Total training amount /batch-size The default is 16
imgsz : Enter picture size The default is 640
noval : No validation , The default is False , That is, if you do not specify this parameter It will be verified , But the validation takes place at the last epoch
rect : Whether to use rectangular reasoning The default is False
resume : Breakpoint training ( Continue training from the last time you interrupted training ) The default is False
nosave : Do not save the model The default is False
noautoanchor Do not actively adjust anchor The default is False
evolve : Whether to carry out hyperparametric evolution The default is False
cache : Whether to cache pictures to memory in advance , To speed up training The default is False
device : Training equipment ,cpu / 0 / 0,1,2,3 The default is ' '
multi-scale Whether to carry out multi-scale training The default is False
single-cls : Whether the dataset has only one category The default is False
adam : Whether to use adam Optimizer The default is False
sync-bn : Whether to use cross card synchronization BN, Only in DDP Use... In mode
workers : dataloader Maximum worker Number The default is 8
label-smoothing Label smoothing operation The default is 0.0
patience : Training times will not increase performance more than the specified number of times , Stop training early The default is 100
project : The default is ROOT / 'runs/train' That is to say, it will be in runs Create under file train Folder
name : The default is exp That is to say, it will be in val Create under folder exp Folder to store the results
bucket : Google cloud disk bucket The default is False
exist-ok : The default is False help='existing project/name ok, do not increment'
quad : The default is False help='quad dataloader'
linear-lr : The default is False help='linear LR'
freeze : The default is [0] help='Freeze layers: backbone=10, first3=0 1 2'
save-period The default is -1, help='Save checkpoint every x epochs (disabled if < 1)'
local_rank : The default is -1, help='DDP parameter, do not modify'
image-weights The default is False help='use weighted image selection for training'
Weights & Biases arguments
entity : The default is None, help='W&B: Entity'
upload_dataset : The default is False help='W&B: Upload data, "val" option'
bbox_interval : The default is -1 help='W&B: Set bounding-box image logging interval'
artifact_alias : The default is latest help='W&B: Version of dataset artifact to use'
'''
…
you did it
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

cmd看控制台输出红桃、方块、黑桃、梅花乱码解决

Splunk: Auto load Balanced TCP Output issue

rabbmitMQ 简单模式<一>

Are you a technology manager or a project manager?

(问题解决) 缺少gcr.io/kubebuilder/kube-rbac-proxy:v0.8.0

R数据分析:临床预测模型中校准曲线和DCA曲线的意义与做法

3DE save to Favorites

PHP uses composer

倍福TwinCAT3第三方伺服电机——以汇川IS620N伺服为例子

VIM from dislike to dependence (18) -- advanced search mode
随机推荐
std::make_shared特点
AtCoder Beginner Contest 252(dijkstra,逆向思维)
【Leetcode】17回溯(电话号码的字母组合)
倍福TwinCAT3第三方伺服电机——以汇川IS620N伺服为例子
webview报错
泛微 E-cology V9 信息泄露漏洞
动态规划-使用最小花费爬楼梯为例
golang并发编程之Mutex互斥锁实现同步和原子操作(atomic)
Fastdfs5.0.11 installation
How did we solve the realsense color bias problem?
Vs loading symbols causes program to start slowly
Nepal graph learning Chapter 2_ A bug before version v2.6.1 caused OOM
128陷阱——源码分析
3de 保存到收藏夹
魔法方法《六》__enter__和__exit__
Scheduling function: Splunk operator Controller Manager
所有项目的资源
MySQL index creation, optimization analysis and index optimization
Analyzing iceberg merge tasks to resolve data conflicts
Rabbmitmq simple mode < 1 >




