当前位置:网站首页>Thoroughly understand the factory mode
Thoroughly understand the factory mode
2022-06-22 14:41:00 【happysnaker】
The article has been included in my warehouse :Java Share your study notes with free books
Pattern type
The factory mode belongs to the creator mode , Related to the creation of objects , The factory method pattern is used for the class , The abstract factory pattern is used for objects . The create class pattern defers part of the creation of objects to subclasses , Create objects from subclasses ; The creative object pattern defers it to another object .
Pattern design intent
Factory mode hides complex object creation work , Only one interface is exposed for the customer to use , The specific creation work is managed by the factory and encapsulated to the user , Separate the creation and use of objects , Reduce coupling , Easy to manage , Can well support change .
For some classes , The creation of its objects may require a series of complex parameters or a lot of preparation code , When this task is done by the customer , If the customer creates multiple complex objects , Not to mention that this code may be difficult to write , It will also cause unnecessary code duplication , The object generated by the factory will not cause code duplication , Because the code in the factory can be reused countless times after being written once , Can reduce the amount of code , And users don't have to pay attention to the hard code , Increase readability , for example Spring In the framework beanFactory That's it .
Besides , Separate the creation and use of objects , All creation work is managed by the factory , Factories can manage classes and adapt to corresponding business changes , Without exposing to customers , For example, if a product A Upgrade to AA, We can put... Directly in the factory return new A() Change it to return new AA(), The client still calls factory.createProductA() Without changing the code , If the customer is through new A() Create objects in the form of , Then we need to find all the code and change it to new AA(), This is a huge task in a huge project .
When the objects used by customers may change , For example, at the beginning A Product and later want to use B Product time , In the ordinary way, we may have to change all new Method , If you use simple factory mode , You can do this simply by changing the configuration file without changing the customer code , If you use factory method patterns or abstract factory patterns , Then you can adjust the constructor of the factory or use set Injection to achieve this , Greatly reduce the inadaptability caused by changes .
All of the above is due to decoupling the use and creation of classes , This is the core idea and design intention of the whole factory mode . No matter when , High cohesion 、 Low coupling is always a consideration in writing .
The factory mode is specifically divided into simple factories 、 Factory method and abstract factory pattern , These methods are consistent with the above design intent , But at the same time meet different needs 、 Adapt to different scenes .
Simple factory (Simple Factory)
Design
Define an interface for creating objects , Create a subclass to determine which instance to create by passing in parameters .
Applicable scenario
- The factory class is responsible for less production .
- When a class is unsure of the class of the object it must create , With uncertainty .
- The customer knows the parameters that need to be passed into the factory and doesn't care about the specific class creation logic .
Code instance
Suppose we have the following requirements : A game manufacturer developed A、B、C Three games , A tester was asked to try out the game .
// Define the game interface
interface Game {
public void play();
}
//A game
class GameA implements Game{
public void play(){
System.out.println("Playing GameA");};
}
//B game
class GameB implements Game{
public void play(){
System.out.println("Playing GameB");};
}
//C game
class GameC implements Game{
public void play(){
System.out.println("Playing GameC");};
}
class GameFactory {
public Game createGame(char type) {
switch (type) {
case 'A':
return new GameA();
case 'B':
return new GameB();
case 'C':
return new GameC();
}
return null;
}
}
// Tester ( Customer ) class
class Tester {
private char type;
public Tester(char type) {
this.type = type;
}
public void testGame() {
GameFactory gameFactory = new GameFactory();
// Get game instances through a simple factory
Game game = gameFactory.createGame(type);
// Try the game
game.play();
}
}
// Code testing
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ask the tester to try the game A
Tester tester = new Tester('A');
tester.testGame();
}
}
In the test code Test This is what we write in the class :
Tester tester = new Tester('A');
In fact, we don't write types directly in engineering , Instead, import the configuration file :
Tester tester = new Tester(config.GAME_TYPE);
So if we want to have testers test different games , I can modify it config In the configuration file GAME_TYPE( It can be an array ) Information ( You can also use reflection ), This allows the code to adapt to change .
If the construction preparation of each class is consistent initialization ( The above code returns directly without any preparation ), Consider using a hash table to store the relationship between parameters and instances , Can reduce a lot of if-else sentence . In this case, we need to initialize and store relevant instances in the hash table in advance without considering whether the program will use , It may cause unnecessary waste of resources , But on the other hand , Every time we get an instance, we return HashMap Cloning of instances in , This ratio new More efficient operation —— This is actually the design pattern of Xiangyuan . however , In most cases, we still need to perform different initialization operations on different instances , At this point, a large number of judgment statements are still required .( If the class is really consistent and Map cache , In fact, this design pattern is the strategy pattern , Policy pattern is the most basic design pattern in programming , Most of us use it intentionally or unintentionally —— Define algorithm interfaces and implement different algorithms by subclasses , Define related classes to select these subclasses .)
UML Class diagram

summary
The structure of the simple factory model is very simple , Easy to use , When there are few instances of objects, you can consider the simple factory pattern . adopt UML Class diagrams can find , The simple factory pattern encapsulates the logical process of creating classes for customers , Therefore, we can perform some complex initialization or other operations in the factory to help customers reduce their pressure , Users only need to know the specific parameters passed in to get the corresponding instances . The simple factory model can also cope with a moderate amount of business changes without affecting the customer code , In line with the design intent of the factory model .
The disadvantages of the simple factory model are also obvious , It's just like its name , It only applies to relatively simple scenarios , For the slightly complicated situation, the simple factory will be extremely large and difficult to maintain , When increasing or decreasing instances , We have to make a lot of changes to the factory , This violates the opening and closing principle . Besides , When the factory appears BUG when , The whole program will crash .
Factory method (Factory Method)
Design
Define an interface for creating objects , It is up to the subclass to decide which class to instantiate , Factory methods defer the instantiation of a class until the subclass implements .
Applicable scenario
- When a class is unsure of the class of the object it must create , With uncertainty .
- You expect high scalability .
- When a class wants its subclasses to specify the objects it creates .
- When a class delegates the responsibility of creating an object to one of several help subclasses , And the customer knows which helper subclass to use .
Code instance
Suppose we also have requirements : A game manufacturer developed A、B、C Three games , The tester is asked to try the corresponding game .
// Define the game interface
interface Game {
public void play();
}
//A game
class GameA implements Game{
public void play(){
System.out.println("Playing GameA");};
}
//B game
class GameB implements Game{
public void play(){
System.out.println("Playing GameB");};
}
//C game
class GameC implements Game{
public void play(){
System.out.println("Playing GameC");};
}
// Define factory ( Parent class )
interface GameFactory {
Game createGame();
}
// Helper subclass , game A factory
class GameAFactory implements GameFactory {
@Override
public Game createGame() {
return new GameA();
}
}
// Helper subclass , game B factory
class GameBFactory implements GameFactory {
@Override
public Game createGame() {
return new GameB();
}
}
// Helper subclass , game C factory
class GameCFactory implements GameFactory {
@Override
public Game createGame() {
return new GameC();
}
}
// Tester ( Customer ) class
class Tester {
private GameFactory gameFactory;
public Tester(GameFactory gameFactory) {
this.gameFactory = gameFactory;
}
public void testGame() {
// Get game instances through the factory
Game game = gameFactory.createGame();
// Try the game
game.play();
}
}
// Code testing
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ask the tester 1 Try the game A
GameFactory gameFactory = new GameAFactory();
Tester tester1 = new Tester(gameFactory);
tester1.testGame();
// Ask the tester 2 Also try the game A
Tester tester2 = new Tester(gameFactory);
tester2.testGame();
//... Tester 1000 Also try the game A
}
}
We can change the constructor or use set Method to change the factory , You can change less code to make all testers change the trial game ( In the worst case, you still need to change a lot of code ), It has good flexibility .
UML Class diagram

summary
The factory method pattern is actually an extension of the simple factory pattern , The factory method pattern is highly extensible , If you want to add classes later , Just write a new help subclass , It is very convenient to produce or switch products , Without modifying the existing code , Perfectly conforms to the opening and closing principle ·.
Factory method pattern is an ideal design pattern in engineering , But its shortcomings are also obvious , When a customer creates a new product , You have to create a product factory , Increased code , And it is difficult to modify the parent class interface , Because once the interface is modified , You must modify many help subclasses .
Abstract factory (Abstract Factory)
Design
Provide an interface to create a series of related or interdependent objects , Delay instantiation of a class to subclasses .
Applicable scenario
- The code needs to interact with multiple related products of different families , But because we can't get the information in advance , Or for the sake of future scalability , You don't want the code to be built based on the concrete classes of the product, you just want to show the interface that created them .
- The objects to be created are a series of interrelated or interdependent product families .
- When products in a series are designed to be used together , Only objects in the same family are used in an application .
Code instance
Assume that the requirements are as follows : A brand insole can produce shoes of large size and corresponding insoles, and shoes of small size and corresponding insoles , Now a customer wants to buy a pair of shoes to wear .
// Define the shoe interface
interface Shoe {
void printShone();
}
// Define insole interface
interface Insole {
void printInsole();
}
// Specific products , Big shoes
class LargeShoes implements Shoe {
@Override
public void printShone() {
System.out.println(" Big shoes ");
}
}
// Specific products , Large insoles
class LargeInsole implements Insole {
@Override
public void printInsole() {
System.out.println(" Large insoles ");
}
}
// Specific products , Small shoes
class SmallShoes implements Shoe {
@Override
public void printShone() {
System.out.println(" Small shoes ");
}
}
// Specific products , Small insoles
class SmallInsole implements Insole {
@Override
public void printInsole() {
System.out.println(" Small insoles ");
}
}
// Define the complete shoe factory interface , A complete shoe consists of shoes and insoles
interface CompleteShoeFactory {
Shoe createShoe();
Insole createInsole();
}
// A large shoe factory , Production of matching large shoes and insoles
class CompleteLargeShoeFactory implements CompleteShoeFactory {
@Override
public Shoe createShoe() {
return new LargeShoes();
}
@Override
public Insole createInsole() {
return new LargeInsole();
}
}
// Small shoe factory , Production of matching small shoes and insoles
class CompleteSmallShoeFactory implements CompleteShoeFactory {
@Override
public Shoe createShoe() {
return new SmallShoes();
}
@Override
public Insole createInsole() {
return new SmallInsole();
}
}
// Customer class , Buy shoes
class Customer {
private CompleteShoeFactory factory;
public Customer(CompleteShoeFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
// Buy complete shoes
public void buyCompleteShoe() {
Shoe myShoe = factory.createShoe();
myShoe.printShone();
Insole myInsole = factory.createInsole();
myInsole.printInsole();
System.out.println(" I have already bought the matching products , Finally, there are shoes to wear !");
}
}
// Code test class
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Buy large shoes
// The singleton pattern is usually used here to generate factories
CompleteShoeFactory factory = new CompleteLargeShoeFactory();
Customer customer = new Customer(factory);
customer.buyCompleteShoe();
}
}
The benefits of understanding that the objects that an abstract factory needs to create are a series of interrelated or interdependent product families , For example, large shoes here are equipped with large insoles , Small shoes with small insoles , This is the corresponding product family , Consumers can either buy a larger product , Or buy a small product , It is impossible to buy large shoes with small insoles , This makes a concrete factory class appear only once in an application , Therefore, specific factory classes usually use Singleton design pattern establish , Because a specific factory class only appears once in an application , Then changing the product family would be very simple , We only need to modify one line of code —— The code when creating the factory , This has great flexibility .
UML Class diagram

summary
The objects created by the abstract factory pattern are a series of interrelated or interdependent product families , Easy to exchange product lines , Be able to better cope with changes . Because the products of an object are designed to work together , Therefore, it is also conducive to maintaining product consistency , If the simple factory mode is adopted , Then we have to create four factories —— Big shoe factory 、 Big insole factory 、 Small shoe factory and insole factory , The number of classes introduced has also increased , And users may accidentally create large shoes and small insoles , Make the result unsuitable , Using the abstract factory pattern can better solve this problem .
The drawback of the abstract factory pattern is that as factory interfaces become more and more functional , It will become more and more bulky , Because all subclasses must implement the interface , This is to ensure that the product types of different series are consistent , Besides , In the future, you want to add new categories or delete categories , Have to make changes to all subclasses .
Conclusion
Factory mode includes simple factory mode , Factory method model , Or the abstract factory pattern , They are very similar in form and characteristics , And the ultimate goal is to decouple . When use , We don't have to care whether this pattern is factory method pattern or abstract factory pattern , Because the evolution between them is often incomprehensible . Often you will find that , The factory method model used by Ming Ming , When new demands come , With a little modification , After adding a new method , Because the products in the class constitute the product families in different hierarchies , It becomes the abstract factory pattern ; And for the abstract factory pattern , When a method is reduced so that the offered product no longer forms a product family , It evolved into a factory method model .
therefore , When using factory mode , Whether the purpose of the six principles of design has been achieved .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

C# Winform 相册功能,图片缩放,拖拽,预览图分页

Network address translation nat
作为程序员,职业规划需要注意的四个阶段
利用图片实现APP元素定位sikulix
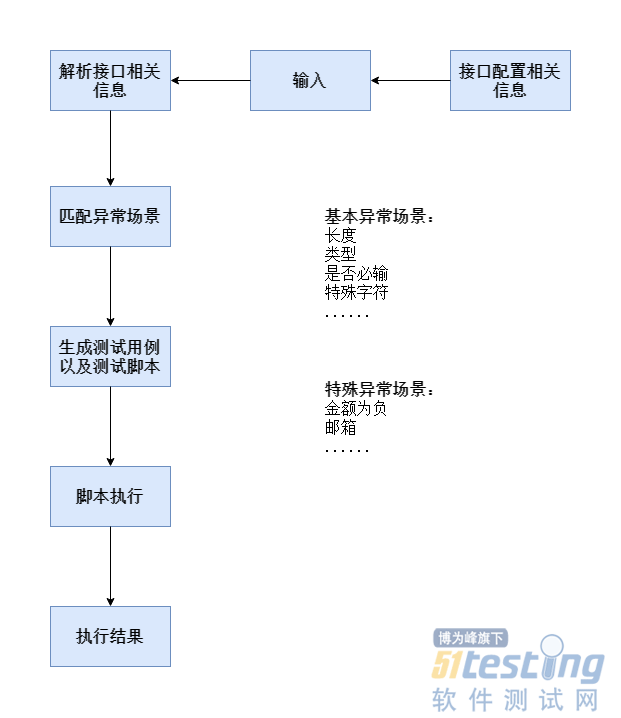
如何实现接口异常场景测试?测试方法探索与测试工具实现

How to add a mask to a VR panoramic work? What is the function?

transformers VIT图像模型向量获取

How to implement interface exception scenario testing? Exploration of test methods and implementation of test tools

【Pr】基础流程

VR全景拍摄,打破传统宣传雁过不留痕的僵局
随机推荐
How location coding (PE) works in transformers
七牛云上传图片
D security can call the system
基于SSM框架实现的甜品饮品店前后台管理系统甜品商城蛋糕店【源码+数据库】
Basic usage and FAQs of jasperreport report report generation tool
想知道股票开户优惠链接,如何得知?网上开户安全么?
Quickly understand the commonly used symmetric encryption algorithm, and no longer have to worry about the interviewer's thorough inquiry
Kukai TV ADB
数据库中如何使用SQL进行修改&删除
Do you know the scope and process of software project acceptance testing?
Common real machine debugging plug-ins for unity commercial games
Groovy list operation
【考研攻略】北京交通大学网络空间安全专业2018-2022年考研数据分析
Groovy语法介绍
Perceptron of machine learning
C # define and implement interface interface
How to protect WordPress websites from cyber attacks? It is important to take safety measures
MadCap Flare 2022,语言或格式的文档
CVE-2022-22965複現
ThoughtWorks. QRcode and zxing Net QR code, URL can be directly jumped