当前位置:网站首页>[C language] one dimensional array
[C language] one dimensional array
2022-06-25 07:18:00 【InfoQ】
The concept and use of arrays
int- Each element in the array has a sequence number , This number comes from 0Start , Not from the familiar 1Start , It's called subscript(Index). When using array elements , Indicate the subscript , for example :
- arrname[Index]
- arraName Is the array name ,index Subscript . for example :a[0] It means the first one 1 Elements ,a[3] It means the first one 2 Elements .
- When using arrays , We often use the elements in the array , however Then print out the values in turn ( That is to assign initial values to the elements in the array one by one ). Then use the loop structure to output ( That is, read the values of array elements in turn ) As shown in the following code :
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i;
int arr[10] = { 0 };
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)// take 1~10 Put it in the array
{
arr[i]=(i+1);
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("arr[%d] = %d\n", i, arr[i]);// Output the array in turn
}
return 0;
}



- So let's change the code above : Let the user enter ten numbers ! The code example is as follows :
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i;
int number[10] = {0};
printf("| Please enter ten numbers :|\n");
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
scanf("%d", &number[i]);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
printf("%d ", number[i]);
return 0;
}



Array name
- The array name isFirst elementThe address of . But there are②Exceptions :
- sizeof( Array name ) ——> The array name represents the entire array — It calculates the size of the entire array , Unit is byte .
- Address fetch (&) Array name ——> The array name represents the entire array — It takes out the address of the entire array .
The definition of one-dimensional array
- The type specifier represents : The type of all elements in the array , Is any basic data type or construction type .
- The array identifier represents : The name of the array type variable , The naming rules are consistent with the identifier of the variable name . This is also called , Array identifier .
- A constant expression represents : Defines the number of data elements stored in the array , That is, the length of the array .
- int a[10]; explain integer Array a, Yes 10 Elements .
- float b[10],c[20]; explain Single precision floating point Array b, Yes 10 Elements , Real array c, Yes 20 Elements .
- char ch[20];Description character array ch, Yes 20 Elements
A reference to a one-dimensional array
- After the array definition is completed , Use this array . You can use the elements of an array by referencing them . Be careful : The index to access the array is from0At the beginning .
- Array identifier[ Subscript ]
- arr[2];
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 0;
int arr[10] = { 0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);// Calculate the total element size of the array
arr[5] = 5;
arr[6] = 7;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}



🥏 There are a few things to note about arrays :
- The array is being created ,【】 Give a constant in parentheses , You can't use variables ! Be careful : Out-of-serviceconstKeyword decoration is given to it , Its essence is stillVariable .
- In the array , for example :arr[5] Can only be used in arr[0]、arr[1]、arr[2]、arr[3]、arr[4], They can't be used arr[5]. If you use it arr[5], Will lead toThe subscript crossing the lineThe situation of .
- The subscript can beInteger constantOr is itShaping expression.
- The type of array actually refers to the value type of array elements . For the same array , The data types of all its elements aresame.
- String words , Array subscript is the character that only knows your array subscript , barring'\0'.
Initialization of one dimensional array
- In addition to using assignment statements to assign values to array elements one by one , Initialization assignment and dynamic assignment methods can also be used .
- Array initialization assignment refers to giving initial values to array elements when defining an array . Array initialization is done in the compile phase . This will reduce running time , Increase of efficiency .
- int a = 10; // initialization
- int arr[5] = {1,2,3,4,5}; // Fully initialized
- int arr1[5] = {1,2,3}; // Incomplete initialization , Incomplete initialization , The remaining uninitialized elementsThe default is 0


- If your subscript does not specify a subscript , It will see how many elements you have by default, so as to help you determine the subscript of the array .
- int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
- int arr[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
- above ② Sentence codes are completely equivalent !!! It will be initialized according to the following data , To determine the subscript of the array !
One dimensional array memory storage mode
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 0;
int arr[10] = { 0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
//%p - Print in address format , In hexadecimal !
printf("arr[%d] = %p\n", i, &arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}



- One dimensional arrays are stored continuously in memory !
- As the array subscript grows , The address changes from ground to height !
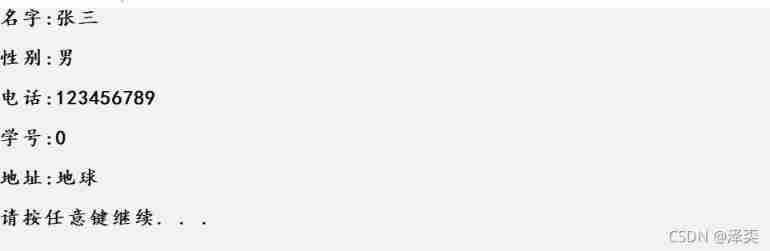
🥏 practice : Use a one-dimensional array to save student names !
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i; // Control loop variable
char *Arrname[5] = { 0 }; // Character pointer array
// Indirect addressing through dereference operation
Arrname[0] = " name : Zhang San ";
Arrname[1] = " Gender : male ";
Arrname[2] = " Telephone :123456789";
Arrname[3] = " Student number :0";
Arrname[4] = " Address : The earth ";
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%s\n", Arrname[i]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}


边栏推荐
- Blue Bridge Cup SCM module code (external interrupt) (code + comment)
- Make fertilizer Safi from crop residues locally to increase yield by 30% and improve soil
- Why use NoSQL with MySQL?
- 弱大数定理的意义与证明
- 哇哦,好丰富呀。
- 破万,我用了六年!
- Three laws of go reflection
- How to get the difference between two dates rounded to hours
- Kubernetes 集群中流量暴露的几种方案
- 1W字|40 图|硬核 ES 实战
猜你喜欢

CTFHub-Web-信息泄露-目录遍历
![[Shangshui Shuo series] day 5](/img/83/28834addd8198d4bcdc718eccf5754.png)
[Shangshui Shuo series] day 5

Kubernetes cluster dashboard & kuboard installation demo
![[Shangshui Shuo series] day 4](/img/9f/fb4e2be392756cc7aa8de2e9c5aec7.png)
[Shangshui Shuo series] day 4

Kubernetes 集群中流量暴露的几种方案

48 张图 | 手摸手教你微服务的性能监控、压测和调优

Americo technology launches professional desktop video editing solution

joda. Time get date summary

The significance and proof of weak large number theorem

Pratique de gestion hiérarchique basée sur kubesphere
随机推荐
[acnoi2022] the structure of President Wang
Unity get resource path
了解zbrush雕刻软件,以及游戏建模的分析
Expression of fatherly love
Loopholes in the missed scanning system of Lvmeng and its repair scheme
48 张图 | 手摸手教你微服务的性能监控、压测和调优
[Shangshui Shuo series] day 5
How to store the directory / hierarchy / tree structure in the database- How to store directory / hierarchy / tree structure in the database?
Americo technology launches professional desktop video editing solution
父爱的表达方式
What is the new business model of Taishan crowdfunding in 2022?
TorchServe避坑指南
The process of making wooden barrels with 3DMAX software: a three-step process
[tool sharing] a software that pays equal attention to appearance and skills
【工具分享】一款颜值与技能并重的软件
Are you still doing the dishes yourself? Teach you how to make dishwasher controller with single chip microcomputer
基于 KubeSphere 的分级管理实践
We are different
Love Terminator
Omni toolbox direct download