当前位置:网站首页>2、 MySQL Foundation
2、 MySQL Foundation
2022-06-26 11:31:00 【Wayne830】
open phpstudy Medium MySQL and Nginx,Win+R Shortcut key input cmd Call out command window , Input mysql -uroot -p Instructions , Enter password to enter command mode .
Indexes
1、DDL
1.1 Database operation
Use DDL Statement can create 、 Inquire about 、 modify 、 Delete database .
1.1.1 Query the database
show databases;# Show the current mysql Database list for
show create database < Database name >;# Displays the created of the database with the specified name SQL Instructions
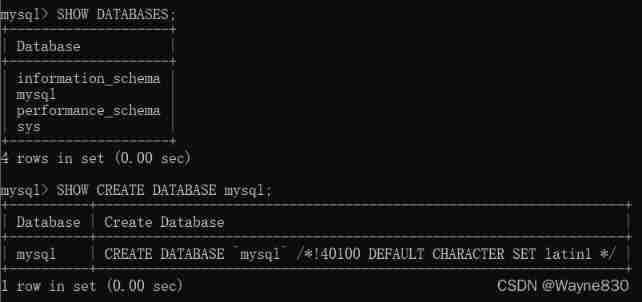
1.1.2 Create database
create database < Database name >;# Create a database and name it
create database if not exists < Database name >;# If the currently created database does not exist, create Otherwise, do not create
create database < Database name > character set < Target character set >;# Specify the character set of the database while creating the database
# Character set : The encoding format in which data is stored in a database utf8/gbk Support Chinese format

1.1.3 modify the database : Modify the character set of the database
alter database < Database name > character set < Target character set >;# Modify the character set of the library

1.1.4 Delete database : Delete all data tables in the database and the data in the data tables
drop database < Database name >;# Delete the database with the specified name
drop database if exists < Database name >;# If the database exists, delete

1.2 Data sheet ( Relationship ) operation
Data sheet : That is, two-dimensional tables , It consists of multiple rows and columns , Each column in the table is called a field ( attribute ), Each row is called a tuple .
Use DDL Statement can create 、 Inquire about 、 Delete 、 Modify data sheet .
Before operating on table relationships , You need to specify the database where the current data table operation is located .
use < Database name >;# Use / Switch database
1.2.1 Create data table
create table < Table name >( Field name 1 type 1 constraint 1, Field name 2 type 2 constraint 2,... Field name n type n constraint n);
1.2.2 Query data table
show tables;# View the data table in the current library
desc < Table name >;# View the table structure of the specified table name
1.2.3 Delete data table
drop table < Table name >;# Delete the specified table
drop table if exists < Table name >;# Delete the data table when it exists
1.2.4 Modify data sheet
alter table < Original table name > rename to < Target table name >;# Rename the original table name to the target table name
alter table < Table name > character set < Target character set >;# Modify the character set of the specified table
alter table < Table name > add < Field name > < Field type >;# Add fields to the structure of the specified table
alter table < Table name > modify < Target field name > < The target type >;# Change the target field name type to target type
alter table < Table name > change < Original field name > < Target field name > < The target type >;# Modify the name and type of the field name
alter table < Table name > drop < Target field name >;# Delete target field
1.2.5 data type : The column in the data table supports the type of data storage
1.2.5.1 value type
MySQL There are many data types to store values , Different types of storage have different ranges or forms
| type | Memory size | Range | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| tinyint | 1byte | A signed :-128~+127 Unsigned :0~+255 | Subminiature integer Such age 、 height |
| smallint | 2byte(16bit) | A signed :-32768~+32767 Unsigned :0~+65535 | Small integer |
| mediumint | 3byte | A signed :- 2 23 2^{23} 223~+ 2 23 2^{23} 223-1 Unsigned :0~+ 2 24 2^{24} 224-1 | Medium integer |
| int/integer | 4byte | A signed :- 2 31 2^{31} 231~+ 2 31 2^{31} 231-1 Unsigned :0~+ 2 32 2^{32} 232-1 | Integers Commonly used |
| bigint | 8byte | A signed :- 2 63 2^{63} 263~+ 2 63 2^{63} 263-1 Unsigned :0~+ 2 64 2^{64} 264-1 | Large integer |
| float | 4byte | Single precision | |
| double | 8byte | Double precision | |
| decimal | decimal(m,n) must Specify integer digits m position Decimal places n position Such as decimal(2,3) Indicates that the maximum number is 99.999 |
1.2.5.2 Character type : The type of character sequence stored
| type | Sequence length range | explain |
|---|---|---|
| char(n) | 0~255byte | Fixed length string , most 255 Characters n Indicates the specified length of this type If not enough n, Then automatically add ’\u0000’ That is, the space |
| varchar(n) | 0~65535byte | Variable length string , most 65535 Characters n Specifies the maximum length of this type |
| tinyblob | 0~255byte | Store binary strings |
| blob | 0~65535byte | Store binary strings |
| mediumblob | 0~1677215byte | Store binary strings |
| longblob | 0~4294967295byte | Store binary strings |
| tinytext | 0~255byte | Text data |
| tiny | 0~65535byte | Text data |
| mediumtext | 0~1677215byte | Text data |
| longtext | 0~4294967295byte | Text data |
1.2.5.3 The date type
MySQL String type can be used to store time in the database , But in some cases, you need to query based on time period ( For example, query the data within a certain time period ) It is not easy to realize
| type | Format | explain |
|---|---|---|
| date | year-month-day | date Only the month, year and day are stored |
| time | hour:minute:second | Time Store only hours, minutes and seconds |
| year | year | year Only for years |
| datetime | year-month-day hour:minute:second | Detailed time |
| timestamp | yearmonthday hourminutesecond | Detailed timestamp |
1.2.6 Field constraints
When creating a data table , Specify the data restriction requirements for the columns of the data table . Common constraints are non empty constraints (not null)、 Unique constraint (unique)、 Primary key constraint (primary key)、 Foreign key constraints (foreign key)
1.2.6.1 Non empty constraint : The value of the specified column in the restriction data table cannot be empty
1.2.6.2 Unique constraint : The values of multiple data in the restricted data table cannot be repeated
1.2.6.3 Primary key constraint : Non empty and unique , The primary key can be a column , It can also be a combination of multiple columns
▲ Primary key auto growth (auto_increment): In some cases , The primary key in the data table is automatically increased according to the added data , You can set the primary key auto growth attribute . When adding a record to a data table , The primary key is based on the previous record ( Include deleted records ) The primary key of is automatically increased .
1.2.6.4 Combined the primary key : Set the combination of multiple columns in the data table as the primary key of the table
primary key( Field name 1, Field name 2...);# The unique primary key constraint can also be expressed in this way
# A federated primary key cannot directly use multiple... When creating a table primary key The way
1.2.6.5 Foreign key constraints
1.2.7 Examples of data table related operations
1.2.7.1 Create a student information table 
USE test;# Use test database
CREATE TABLE stu_info(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
sex VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
age TINYINT NOT NULL,
birthday DATE NOT NULL,
telephone VARCHAR(15) UNIQUE,
address VARCHAR(20)
);


ALTER TABLE stu_info RENAME TO student_information;# Change the table name to student_information
ALTER TABLE student_information ADD remark VARCHAR(100);# Add note column reamrk
ALTER TABLE student_information MODIFY age INT;# take age Attribute original tinyint Change the type to int type
ALTER TABLE student_information DROP remark;# Delete the remarks column reamrk

1.2.7.2 Create a library management table 
USE test;# Use test database
CREATE TABLE books_table(
books_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
books_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
books_author VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
books_remark VARCHAR(100)
);

 adopt phpMyAdmin The tool inserts the data in the example into the table
adopt phpMyAdmin The tool inserts the data in the example into the table 
# Insert data statement
INSERT INTO `books_table` (`books_id`, `books_name`, `books_author`, `books_remark`) VALUES ('1', 'Java', 'Kathy Sierra', NULL), (NULL, 'Python', 'Mark Lutz', NULL), (NULL, 'C++', 'Stephen Prata', NULL);
# Query table structure
SELECT * FROM `books_table`;

Delete the last row of data , Add another row of data at the end
DELETE FROM `books_table` WHERE `books_table`.`books_id` = 3;
INSERT INTO `books_table` (`books_id`, `books_name`, `books_author`, `books_remark`) VALUES (NULL, 'C', 'Martin Richards', NULL);

2、DML
2.1 Add data
insert into < Table name > ( Field name 1, Field name 2,..., Field name n) values ( value 1, value 2,..., value n);
# The added value is the same as values The field names before are in the same order That is, to form a one-to-one correspondence
insert into < Table name > values ( value 1, value 2,..., value n);
# Omitting the field name means adding the data of all fields in the table The order of values is consistent with the order of fields in the table
2.2 Delete data
delete from < Table name > [where < Conditions >];
2.3 Modifying data
update < Table name > set < Field name 1>=< value 1>,< Field name 2>=< value 2>... [where < Conditions >];
2.4 DML Example : Create class student information table

USE test;# Use test database
CREATE TABLE class_info(
stu_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
stu_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
stu_gender VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
stu_nativeplace VARCHAR(20),
stu_grade VARCHAR(5) NOT NULL
);

# Add data in table
INSERT INTO class_info (stu_id,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_grade) VALUES (1001,'Mike','male','A');
INSERT INTO class_info (stu_name,stu_gender,stu_nativeplace,stu_grade) VALUES ('Tom','male','Shanghai','B');
INSERT INTO class_info (stu_name,stu_gender,stu_nativeplace,stu_grade) VALUES ('Jenny','female','Hongkong','A');
INSERT INTO class_info (stu_name,stu_gender,stu_grade) VALUES ('Mary','female','B');
INSERT INTO class_info (stu_name,stu_gender,stu_nativeplace,stu_grade) VALUES ('Jim','male','Beijing','A');

# Delete stu_id by 1005 Data tuple of
DELETE FROM class_info WHERE stu_id=1005;
# modify stu_id by 1004 Of stu_nativeplace and stu_grade
UPDATE class_info SET stu_nativeplace='Chengdu',stu_grade='A' WHERE stu_id=1004;
SELECT * FROM class_info;# Query statements display table information

# Set all tuples to stu_nativeplace Change it to Beijing
UPDATE class_info SET stu_nativeplace='Beijing';
SELECT * FROM class_info;# Query statements display table information

3、DQL
3.1 Query basic syntax
select < Field name 1, Field name 2...> from < Table name > [where < Conditions >];# Query the specified field name in the specified table
select * from < Table name > [where < Conditions >];# Query all field names in the specified table
3.2 where Clause : Used to filter data that meets certain conditions
[ sentence ] where < Conditions >;
explain : stay where clause , If multi condition query , You need to pass the logical operator (and or not) Connect multiple conditions ; If interval query , You can use between a and b( Equivalent to interval [a,b]) Statement to query .
3.3 like Clause
stay where Clause , You can use like Keyword to realize fuzzy query .
SELECT * FROM stus WHERE name LIKE '%o%';# stay stus Query in table name contain o Alphabetic data
| Symbol | meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| % | Any number ( Include 0) The characters of | %o% Indicates that the string contains letters o |
| _ | Any character | _o% Represents a string o Of is at the second letter __o% Represents a string o Of is at the third letter |
3.4 DQL Examples and query result processing
Add... To the class student information table in the above example stu_birth Field to store the student's year of birth .
# New fields
ALTER TABLE class_info ADD stu_birth INT;
# Update data
UPDATE class_info SET stu_birth=2005 WHERE stu_id=1001;
UPDATE class_info SET stu_birth=2006 WHERE stu_id=1002;
UPDATE class_info SET stu_birth=2004 WHERE stu_id=1003;
UPDATE class_info SET stu_birth=2003 WHERE stu_id=1005;
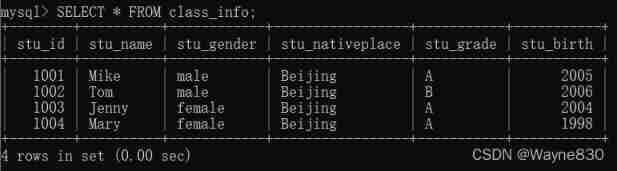
# Query data stu_birth Calculate the age and alias it stu_age
SELECT stu_name,2022-stu_birth AS stu_age FROM class_info;

# Eliminate duplicate lines DISTINCT keyword
SELECT DISTINCT stu_nativeplace FROM class_info;

# Fuzzy query stu_name With y Data information at the end
SELECT * FROM class_info WHERE stu_name LIKE '%y';
# Fuzzy query stu_name Contain e Data information
SELECT * FROM class_info WHERE stu_name LIKE '%e%';

3.5 order by Sort
The records that meet the query conditions are arranged in ascending or descending order according to the values of the specified columns .
[ sentence ] [where < Conditions > order by < Field name 1> [asc],...,< Field name n> [asc]];# Tuples satisfying the conditions are arranged in ascending order ( Default )
[ sentence ] [where < Conditions > order by < Field name 1> desc,...,< Field name n> desc];# The tuples satisfying the conditions are arranged in descending order
3.6 Aggregate functions
SQL Some functions that can calculate the columns of the queried records are provided in . Common aggregate functions are :count、max、min、sum、avg etc. .
select < Function name >( Field name ) from < Table name > [where < Conditions >];
| function | meaning |
|---|---|
| count | Statistical function Count the number of tuples that meet the conditions |
| max | Maximum function The maximum value in the specified column when the condition is met |
| min | Minimum function Meet the minimum value in the specified column |
| sum | Sum function The sum of the specified column values when the conditions are met |
| avg | The average function The average value of the specified column value when the condition is met |
3.7 Other functions : Date function 、 String function
| function | application |
|---|---|
| Date function | When adding data to a date type It can be realized by taking the shape of YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss String type assignment Get the detailed time usage of the current system now() or sysdate() function Can also pass select now() or select sysdate() Get the current detailed time curtime() Get current system time ;curdate() Get the current system date |
| String function | concat( Multiple strings are separated by commas ) Concatenate multiple strings into one string upper( Field name ) Capitalize the column corresponding to the field name lower( Field name ) Lower case the field name corresponding to the column substring( Field name ,a,b) From the subscript a Began to intercept b Field names correspond to columns Be careful SQL The Chinese string subscript is from 1 Start |
3.8 Group query
grouping : Group the records in the data table according to the specified column .
select [< Field name 1>...< Field name n>],[< Aggregate functions >] from < Table name > [where < Conditions >] group by < Target group field >;
explain :select After use * Display the first record of each group after grouping query results . Afterwards, field names and aggregation functions are usually used to perform related operations on the grouped data .
▲ For the results of group query, use having Keyword restriction filter
select [< Field name 1>...< Field name n>],[< Aggregate functions >] from < Table name > [where < Conditions >] group by < Target group field > having < Conditions >;
where Conditions and having The difference between conditions : First, according to where Conditions are grouped after querying records from the database , After grouping according to having Filter query results by criteria . namely where The condition is to filter the original data table ,having The condition is to filter the data table after grouping ,having Keywords must be the same as group by Keywords appear at the same time .
3.9 Paging query
When there are many records in the data table , If you query all at once, it will be displayed to the user , User readability / The experience is not perfect , The data can be displayed in pages .
[ sentence ] limit a,b;#a and b Are all int type a To query the first data index ( from 0 Start ) b To get the number of query records If the number of remaining pieces is less than b Only the remaining records are displayed
Page number pageNum
Total number of records count
Each page shows the number of records pageSize
Total number of pages pageCount=count%pageSize==0?count/pageSize:count/pageSize+1
[ sentence ] limit (pageNum-1)*pageSize,pageSize;
4、 Multi watch combination
4.1 Connections
MySQL Is a relational database , Not only can data be stored , It can also maintain the relationship between data . Establish foreign key constraints by adding fields to the data table . There are four types of association between data : One to one connection 、 One to many connection 、 Many to one Association 、 Many to many connection .
4.1.1 One to one connection
There are often instances of one-to-one relationships in life , Such as the relationship between person and ID card , A person has only one ID card , One ID card only corresponds to one person ; Users and user details of a platform , A user has only one detail , One detail only corresponds to one user .
▲ The method of establishing a one-to-one relationship
Method 1: The primary key link : Set the primary key in the two tables , According to the nature of the primary key , The primary key attribute of data in each table is unique , A unique corresponding and unique association is formed between tables . That is, the data with the same primary key in the two tables are related data .
Method 2: The only foreign key : Add a foreign key constraint field in any table to be associated with the primary key of another table , And the foreign key constraint field adds a unique unique Constraints to achieve a one-to-one association .
4.1.2 One to many 、 Many to one Association
There is often one to many in life / Many to one relationship instances , Such as the relationship between class and students , One class corresponds to more than one student , contrary , Many students correspond to a class .
▲ Build one to many / Many to one association method : stay “ many ” Add foreign keys and... To the table corresponding to the end of “ One ” The primary key of the corresponding table at one end of the , So as to establish one to many data / Many to one Association .
4.1.3 Many to many connection
There are often many to many relationships in life , Such as the relationship between students and course selection , Multiple students can choose multiple courses , Multiple courses can also be selected by multiple students .
▲ The method of establishing many to many association : In addition, create a relationship table to maintain many to many associations . Define two foreign keys in the relational table , Associate with the primary keys of two tables respectively .
4.2 Foreign key constraints
Foreign key constraint is to add a foreign key constraint to one table and the primary key of another table ( only ) After the correlation , The data added by this foreign key constrained field must exist in the associated primary key field . That is, the field of the foreign key constraint is a subset of the associated primary key field .
Example : The relationship between students and classes ( Add a foreign key to the student table to associate with the primary key of the class table )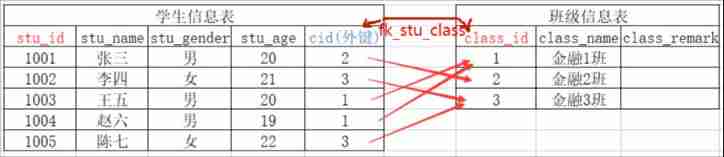
CREATE DATABASE db01;# Create database db01
USE db01;
# Create class information table
CREATE TABLE class_info(
class_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
class_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
class_remark VARCHAR(50)
);
# Foreign key constraint definition
constraint < Foreign key Association logical name > foreign key(< Foreign key of the current table >) references < Associated table name >(< The primary key of the associated table name >);
# Create a student information table
CREATE TABLE stu_info(
stu_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
stu_name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
stu_gender VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
stu_age INT NOT NULL,
cid INT,# The foreign key is the same as the associated primary key type
CONSTRAINT fk_stu_class FOREIGN KEY(cid) REFERENCES class_info(class_id)
);
# Add data to the class information table
INSERT INTO class_info (class_name) VALUES ('finance 1');
INSERT INTO class_info (class_name) VALUES ('finance 2');
INSERT INTO class_info (class_name) VALUES ('finance 3');
# Add data to the student information table
INSERT INTO stu_info (stu_id,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age,cid) VALUES (1001,'zhangsan','male',20,2);
INSERT INTO stu_info (stu_id,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age,cid) VALUES (1002,'lisi','female',21,3);
INSERT INTO stu_info (stu_id,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age,cid) VALUES (1003,'wangwu','male',20,1);
INSERT INTO stu_info (stu_id,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age,cid) VALUES (1004,'zhaoliu','male',19,1);
INSERT INTO stu_info (stu_id,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age,cid) VALUES (1005,'chenqi','female',22,3);
4.3 Link query
MySQL Can be used in join Keyword to realize the joint query of multiple tables , Connection query . It is divided into three operations according to different functions : Internal connection inner join、 Left connection left join、 The right connection right join.
Internal connection : Cartesian product of two tables .
[ sentence ] < Table name 1> inner join < Table name 2> [where < Conditions >];
# Note that you need to use two tables to query < Conditions > You need to specify the table name Format : Table name . Field name
#where The order of clause execution is that the first clause becomes a Cartesian product Then filter the data Low efficiency
[ sentence ] < Table name 1> inner join < Table name 2> [on < Conditions >] [where < Conditions >];
#on Clause execution order is to first judge whether the connection condition is true If it holds, it will regenerate into Cartesian product
# Use... In join queries on Clause to filter data in Cartesian product More efficient
# You can use where Clause to filter again
Left connection : Show all the data in the left table , If there is data in the right table that meets the connection conditions with the records in the left table , Then connect ; Otherwise, it will be displayed as NULL.
[ sentence ] < Left table name > left join < Right table name > on < Conditions > [where < Conditions >];
The right connection : Show all the data in the right table , If there is data in the left table that meets the connection conditions with the records in the right table , Then connect ; Otherwise, it will be displayed as NULL.
[ sentence ] < Left table name > right join < Right table name > on < Conditions > [where < Conditions >];
5、 practice
5.1 Relational algebra and SQL Sentence conversion
* video :https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Au411R7oG?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0
There are two relationships S(A,B,C,D) and T(C,D,E,F), Write the equivalent of the following query SQL expression ?
(1)σ A = 10 _{A=10} A=10(S)
SELECT * FROM S WHERE A=10;
(2) Π A , B Π_{A,B} ΠA,B(S)
SELECT A,B FROM S;
(3) S ⋈ T A < E S⋈T_{A<E} S⋈TA<E
SELECT * FROM S INNER JOIN T ON A<E;
(4) S ⋈ T S⋈T S⋈T
SELECT A,B,S.C,S.D,E,F FROM S INNER JOIN T ON S.C=T.C AND S.D=T.D;
(5) S ⋈ T S . C = T . C S⋈T_{S.C=T.C} S⋈TS.C=T.C
SELECT * FROM S INNER JOIN T ON S.C=T.C;
(6) Π C , D Π_{C,D} ΠC,D(S)×T
SELECT S.C,S.D,T.* FROM S INNER JOIN T;
(7)S*T
SELECT A,B,S.C,S.D,E,F FROM S LEFT JOIN T ON S.C=T.C AND S.D=T.D;
(8)S*T
SELECT A,B,T.C,T.D,E,F FROM S RIGHT JOIN T ON S.C=T.C AND S.D=T.D;
5.2 DQL Example
* video :https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV16r4y167Jf?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0
Create a student system table (Student_System), There are fields id、name、gender、chinese_mark、math_mark、english_mark、last_logintime、tel.
CREATE TABLE student_system(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
GENDER VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
CHINESE_MARK INT,
MATH_MARK INT,
ENGLISH_MARK INT,
LAST_LOGINTIME DATETIME,
TEL VARCHAR(20)
);
INSERT INTO student_system(ID,NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK,TEL) VALUES ('Carl','male',87,92,89,'3587325');
INSERT INTO student_system (NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK,LAST_LOGINTIME) VALUES ('Barry','male',90,94,90,now());
INSERT INTO student_system (NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK,LAST_LOGINTIME) VALUES ('Alice','female',95,92,92,'2022-01-31 09:00:00');
INSERT INTO student_system (NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK,TEL) VALUES ('Jack','male',89,89,91,'4412578');
INSERT INTO student_system (NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK,TEL) VALUES ('Jim','male',92,90,91,'2569493');
INSERT INTO student_system (NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK) VALUES ('Anne','female',89,85,87);
INSERT INTO student_system (NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK) VALUES ('Paul','male',85,87,89);
INSERT INTO student_system (NAME,GENDER,CHINESE_MARK,MATH_MARK,ENGLISH_MARK) VALUES ('Tom','male',90,95,88);

SELECT ID,NAME,CHINESE_MARK FROM student_system ORDER BY CHINESE_MARK DESC;
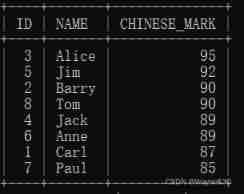
SELECT * FROM student_system ORDER BY CHINESE_MARK DESC,MATH_MARK DESC,ENGLISH_MARK DESC;

SELECT CONCAT(NAME,'-',GENDER) FROM student_system;

SELECT SUBSTRING(TEL,2,4) FROM student_system;

SELECT CHINESE_MARK,COUNT(ID) FROM student_system GROUP BY CHINESE_MARK;

SELECT MATH_MARK,COUNT(ID) FROM student_system WHERE CHINESE_MARK>=90 GROUP BY MATH_MARK HAVING MATH_MARK>90;

SELECT * FROM student_system LIMIT 0,4;

5.3 Multi table joint query
* video :https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Qu41197ht?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0
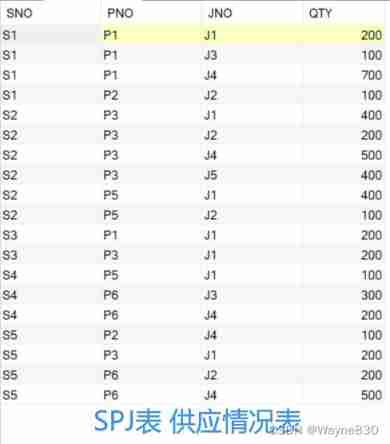
There is a SPJ database , Include S、P、J、SPJ common 4 A relationship model .
S(SNO,SNAME,STATUS,CITY)
P(PNO,PNAME,COLOR,WEIGHT)
J(JNO,JNAME,CITY)
SPJ(SNO,PNO,JNO,QTY)
among S It is the supplier table , By supplier code (SNO)、 Name of supplier (SNAME)、 Supplier status (STATUS)、 The supplier's city (CITY) constitute ;P It's a parts list , By part code (PNO)、 Part name (PNAME)、 Color (COLOR)、 weight (WEIGHT) constitute ;J It is the project list , By project code (JNO)、 Project name (JNAME)、 The city where the project is located (CITY) constitute ;SPJ It's a supply list , By supplier code (SNO)、 Part code (PNO)、 Project code (JNO)、 Quantity supplied (QTY) constitute . Of which supply quantity QTY The quantity of a certain part supplied by a supplier to an engineering project is QTY.


CREATE TABLE S(
SNO VARCHAR(5),
SNAME VARCHAR(100),
STATUS INT,
CITY VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE P(
PNO VARCHAR(5),
PNAME VARCHAR(100),
COLOR VARCHAR(100),
WEIGHT INT
);
CREATE TABLE J(
JNO VARCHAR(5),
JNAME VARCHAR(100),
CITY VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE SPJ(
SNO VARCHAR(5),
PNO VARCHAR(5),
JNO VARCHAR(5),
QTY INT
);
(1) Find out the names and cities of all suppliers
SELECT SNAME,CITY FROM S;
(2) Find out the names of all the parts 、 Color 、 weight
SELECT PNAME,COLOR,WEIGHT FROM P;
(3) Find out which suppliers to use S1 The engineering number of the parts supplied
SELECT JNO FROM SPJ WHERE SNO='S1';
(4) Find out the project J2 Name and quantity of various parts used
SELECT PNAME,QTY FROM SPJ INNER JOIN P ON SPJ.JNO='J2' AND SPJ.PNO=P.PNO;
(5) Find out the numbers of all parts supplied by Shanghai manufacturers
SELECT DISTINCT PNO FROM S INNER JOIN SPJ ON S.CITY='ShangHai' AND S.SNO=SPJ.SNO;
(6) Find out the engineering name of the parts made in Shanghai
SELECT DISTINCT JNAME FROM S INNER JOIN SPJ INNER JOIN J ON S.CITY='ShangHai' AND S.SNO=SPJ.SNO AND SPJ.JNO=J.JNO;
(7) Change the color of all the red parts to blue
UPDATE P SET COLOR='blue' WHERE COLOR='red';
(8) from S5 supply J4 Parts of P6 Change to S3 supply .
UPDATE SPJ SET SNO='S3' WHERE SNO='S5' AND PNO='P6' AND JNO='J4';
(9) Deleting a supplier number from a supplier relationship is S2 The record of , And delete the corresponding record from the supply situation relationship .
DELETE FROM S WHERE SNO='S2';
DELETE FROM SPJ WHERE SNO='S2';
(10) Please put (S2,J6,P4,200) Insert the supply situation relationship .
INSERT INTO SPJ (SNO,JNO,PNO,QTY) VALUES ('S2','J6','P4',200);
边栏推荐
- This paper introduces the simple operation of realizing linear quadratic moving average of time series prediction that may be used in modeling and excel
- NFS共享存储服务安装
- FasterRCNN
- 机器学习聚类——实验报告
- 请指教同花顺开户选选择哪家券商比较好?手机开户安全么?
- Random numbers in leetcode 710 blacklist [random numbers] the leetcode path of heroding
- 24 database interview questions that must be mastered!
- Using the methods in the repository to solve practical problems
- 统计遗传学:第二章,统计分析概念
- redux相关用法
猜你喜欢

介绍一下实现建模中可能用到的时间序列预测之线性二次移动平均,Excel的简单操作
![[redis series] redis learning 16. Redis Dictionary (map) and its core coding structure](/img/d5/db1931596c26090092aaa065103dbb.png)
[redis series] redis learning 16. Redis Dictionary (map) and its core coding structure

HUST网络攻防实践|6_物联网设备固件安全实验|实验三 FreeRTOS-MPU 保护绕过

PC qq Hall upload Update Modifying versioninfo

.net中,日志组件 Nlog,SerialLog, Log4Net的用法

量化初级 -- akshare获得股票代码,最简策略

Redux related usage
![In depth understanding of STM32 serial port experiment (register) [nanny level tutorial]](/img/b2/f09e220918a85b14a1993aa85f7720.png)
In depth understanding of STM32 serial port experiment (register) [nanny level tutorial]

PC QQ大厅 上传更新 修改versionInfo

loggie 编码以及换行符测试
随机推荐
One click deployment of your own community forum
中国十大证券app排名 开户安全吗
有手就行的移动平均法、指数平滑法的Excel操作,用来时间序列预测
Machine learning PCA - Experimental Report
[redis series] redis learning 16. Redis Dictionary (map) and its core coding structure
10 years' experience in programmer career - for you who are confused
QT connection MySQL data query failed
02 linked list of redis data structure
【Redis 系列】redis 学习十六,redis 字典(map) 及其核心编码结构
18:第三章:开发通行证服务:1:短信登录&注册流程,简介;(这儿使用短信验证码)
Laravel admin obtains non auto increment ID and submits hidden forms
Build document editor based on slate
Introduction to the strongest swarm cluster one click deployment + hydrogen bomb level container management tool
leetcode 715. Range 模块 (hard)
NFS共享存储服务安装
laravel-admin 用 原生JS实现声音提示,及自动播放
redux相关用法
laravel-admin隐藏按钮, 及设置按钮显示, 默认序列, form 表单的不可修改值
我想知道同花顺是炒股的么?手机开户安全么?
机器学习SVM——实验报告