当前位置:网站首页>To understand the difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and the difference in pathogenicity
To understand the difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and the difference in pathogenicity
2022-06-25 07:55:00 【Guhe Niubo】
Gu He health

Gram positive and negative bacteria
In everyday life , We often see Drugs or antibacterial product indication I'll write like this , Effective against Gram-positive bacteria , Sensitive to Gram-negative bacteria , Or it is effective against Gram-negative bacteria , Not effective against Gram-positive bacteria . Many people may not know or understand the difference between the two .
This paper mainly introduces Gram positive and negative bacteria , The difference between them , Representative strains and specific drugs, etc .
1884 year , Bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram Invented Gram staining To identify and distinguish bacteria . This technique divides bacteria into two broad groups , namely Gram positive bacteria (G+) And gram negative bacteria (G-). The distinction is mainly between these two types of bacteria cell wall The ingredients are different , thus To color Also caused by different .
The physiological structure of these two kinds of bacteria , The cause of the disease and the antibacterial effect are different , therefore , Distinguish pathogenic bacteria It's a Gram-positive bacterium , Or negative bacteria , Clinically determined infection and Choose medication Aspects are of great significance .
Gram negative bacteria cause Most patients have basic diseases or poor physique , Diarrhea caused by intestinal bacterial infection is mostly caused by the intestinal flora Gram negative bacteria Caused by , Such as E. coli 、 Salmonella 、 Shigella , Brucella etc. , Treat this kind of bacterial infection , Generally, three generations of cephalosporins and quinolones are used . Note that most Gram-negative bacteria are resistant or insensitive to penicillin .
Most pyogenic cocci All belong to Gram positive bacteria , They can produce exotoxins to make people sick , Common strains Yes staphylococcus 、 streptococcus 、 Diplococcus pneumoniae 、 Listeria 、 Anthrax 、 Diphtheria bacilli 、 Tetanus etc. . Especially in the human intestines , Gram positive pathogenic bacteria are more likely to cause disease . Most infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria can be treated with a fairly small amount of antibiotics . penicillin 、 Clozacillin and erythromycin are sufficient to cover 90% Gram positive infection .
Besides , some Broad spectrum antibiotics It has antibacterial effect on both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria , Such as ampicillin 、 Gentamicin 、 Oxytetracycline 、 Fosfomycin, ciprofloxacin, etc , But the effect may not be optimal . Besides , Sulfonamides Also belong to Broad spectrum antibacterial drugs .
In clinical application , If the bacterial infection Compare clear , Use as much as possible Narrow spectrum antibiotics , If not clear , Optional Broad spectrum antibiotics . therefore , In the clinical treatment of diseases , First of all, we should have a detailed understanding of the role and use of drugs , And then based on The type of infection or the result of diagnosis should be reasonably selected , Only in this way can we achieve The best treatment effect . otherwise , Improper drug selection , There will be Ineffective or worse Result .
Gram's Yang / The main difference between negative bacteria
The main difference between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is Thickness of peptidoglycan layer and The presence or absence of an external lipid membrane .
- Gram positive bacteria have thick peptidoglycan cell wall structure , It is purple in Gram staining test / Blue .
- Gram negative bacteria have thin cell walls , It is red to pink in the Gram staining test .
Gram staining of different bacteria

A) Rod-shaped Gram-positive Bacillus anthracis in cerebrospinal fluid samples ( Cause anthrax ), It also contains white blood cells .B) Gram positive Staphylococcus aureus ( Purple or purple ) And gram negative Escherichia coli ( Pink ) Gram stain of , They are the most commonly used gram stain reference bacteria . Reference source :Wikipedia commons and tmedweb)
Gram positive bacteria
// Lack of adventitia , More susceptible to antibiotics
The cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria contain peptidoglycans 、 Lipids 、 Phosphoglucuronic acid and phosphoteichoic acid . This structural component is different from that of peptidoglycan and outer membrane ( By lipids 、 Protein and lipopolysaccharide composition ) Composed of the cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria . Although gram positive bacteria have Thick peptidoglycan layer , But they are more susceptible than Gram-negative bacteria to certain antibiotics that target the cell wall , Because of them Lack of adventitia .
// Common pathogenic bacteria
The most common gram-positive bacteria include staphylococcus 、 streptococcus 、 Bacillus 、 Clostridium sp 、 Listeria 、 Corynebacterium, etc . The representative species of these Gram-positive bacteria are Pathogenic , And may cause a variety of diseases .
// A treatable antibiotic
penicillin It affects Gram-positive bacteria One of the main antibiotics .
Erythromycin is another powerful antibiotic used to treat Gram-positive bacterial infections . Erythromycin belongs to a class of antibiotics called macrolides , It belongs to the same class as azithromycin and clarithromycin . It is usually used by people who are allergic to penicillin .
Trimethoprim / Sulfamethoxazole , Clindamycin , Clindamycin , Doxycycline , Vancomycin can also be used in Specific Gram-positive bacterial infections .
Gram negative bacteria
// Layers of resistance are harder to kill : The cell walls are harder , The outer membrane can be changed
Gram negative bacteria have Hard protective shell . Their Peptidoglycan layer Gram positive bacilli Much thinner .
When their cell walls are disturbed , Gram negative bacteria can Release endotoxin , The symptoms are worse . meanwhile , Most antibiotics try to get close to their target , Must pass through the outer membrane . for example , Hydrophilic antibiotics pass through porin . Gram negative bacteria They can be modified by changing their hydrophobic properties or by mutations in porins Change their outer membrane . This is for these bacterial cells It creates resistance .
// Hidden mystery : More dangerous than Gram-positive bacteria
Compared with Gram-positive bacteria , Gram negative bacteria are more dangerous as disease organisms , Because of the existence of the outer membrane Capsule or mucous layer . In this way , Microbes can hide surface antigens , This antigen can Trigger the human immune response .
Gram negative bacteria are a group of notorious bacteria , can Lead to a variety of diseases , Including pneumonia 、 Meningitis 、 gonorrhea 、 bacterial dysentery 、 Cholera 、 Gastritis, etc. . In the intensive care unit (ICU) Of patients , At high risk of morbidity and mortality , It is easier to meet such bacteria , So they have Important clinical significance .
// A treatable antibiotic
Many different kinds of antibiotics have been developed to kill Gram-negative bacteria , For example, cephalosporins 、 Folic acid antagonists 、 Piperacillin - Tazobactam 、 Ureapenicillin 、 Lactam -β- lactamase inhibitor 、 Carbapenems and quinolones . They are specially developed for Gram-negative bacteria , But sometimes it is also effective for some gram-positive bacteria .
Summary of the differences between Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria

Reference source :microbenotes
These are the main differences between Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria , Next we will focus on gram Yang / Negative bacteria , from Bacterial characteristics , Shape representation , Cell structure Other aspects , For a more detailed introduction .
Bacterial characteristics
Characteristics of Gram-positive bacteria
The definition of Gram-positive bacteria is based on their brief washing with alcohol in Gram staining Ability to retain crystal violet dye . Gram positive bacteria are purple .
These bacteria have very unique characteristics , It can be distinguished from other types of bacteria . These include :
- One of the characteristics of Gram-positive bacteria is the existence of cytoplasmic lipid membrane surrounded by cell wall
- The cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria contain peptidoglycans 、 Polysaccharide 、 Teichoic acid and protein
- When viewed under a microscope , Gram positive bacteria were purple after Gram staining test
- The volume of periplasm is much smaller than that of Gram-negative bacteria
- There is a thick peptidoglycan layer
- With phosphoteic acid , Lipoteichoic acid is used as a chelating agent , It can also be used for certain types of adhesion
- Some species have certain surface appendages , Such as flagella , Can help them move
- Gram positive bacteria without flagella have two basal rings that support them
- Peptidoglycan chains pass through bacterial enzymes DD- Transpeptidase crosslinks to form rigid cell walls
- Some gram-positive bacteria have a capsule composed of polysaccharides
- They have a membrane attached to the peptidoglycan layer S layer
- They don't have the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria
- The cell wall structure of Gram-positive bacteria is complex , Easy to absorb foreign matters
- They rarely have hairy structures called pili . Fimbriae can be seen in a small number of Gram-positive bacteria , Such as Streptococcus and Corynebacterium
Characteristics of gram negative bacteria
In the process of Gram staining , Gram negative bacteria are washed with alcohol Will lose the color of crystal violet dye , and Absorb the pink color of saffron / Red .
Gram negative bacteria can be found in almost every living area on earth .
- They have an outer membrane made of lipopolysaccharide . The outer membrane contains lipopolysaccharide (LPS, By lipids A、 Central polysaccharide and O Antigen composition )
- They have a periplasmic space ( more ), The outer membrane is separated from the cytoplasmic layer .
- There is an inner cell membrane ( cytoplasm )
- There is a thin peptidoglycan layer ( Thicker in Gram-positive bacteria )
- Their cell walls have outer membranes , The adventitia is further divided into outer and inner lobes . The outer leaves contain lipids A、O Lipopolysaccharide composed of antigen and core polysaccharide , The inner leaf is composed of phospholipids .
- The pores exist in the outer membrane , Pores as specific molecules
- There is no teichoic acid or lipoteichoic acid
- There is also a covalent connection between peptidoglycan chain and outer membrane , It's called Braun lipoprotein
- With a few exceptions , Most do not produce spores
Shape representation
Characterization of the shape of Gram-positive bacteria
Although most bacteria are distinguished by Gram staining dyes , But microscopic observations reveal more features that can be used to define and characterize these bacteria .
according to shape The definition of , Gram positive bacteria can be divided into Two types of :
- Cocci —— The diameter is 0.5-1.0 um Round or oval shaped bacteria . They are paired 、 chain 、 Clustered or appearing alone . For example, Staphylococcus 、 streptococcus 、 Pneumococcus .
- bacillus —— Also in rod shape ; They are rod-shaped bacteria , Rounded ends 、 cone 、 Square or swollen . Their length is 1-10um, Width is 0.3-1.0um. For example, Bacillus .
Other special shapes formed by Gram-positive bacteria include :
- Tetrad —— A coccal shape , In four square clusters , for example Micrococcus( Micrococcus sp ).
- Octopus —— Collenchyma shape , Four or eight stacks , For example, Sarcocystis .
Gram Characterization of the shape of the negative bacteria
Microscopic observation range of gram negative bacteria cells from Rod to Bacillus , from Cocci to spirals , Spiral shape is the most common shape . However , Some show special shapes , Such as coccobacterium 、 Tetrad 、 fence 、 Trichome, etc . for example :
- bacillus ——Escherichia coli ( E. coli )
- Cocci —— It's a combination of cocci and bacilli , Include Hemophilus influenza( Haemophilus influenzae )
- Streptobacillus is rod-shaped , They are linked together in chains , for example Streptobacillus moniliformis ( Streptococcus moniliformis )
- Trichomes are a series of columnar rod-shaped cells , It can be wrapped in a sheath
- Spirochetes are also called spirochetes , For example, Treponema pallidum
- Filamentous Gram-negative bacteria have filamentous shapes , for example ,Norcadia spp ( Nocardia sp )
Cell structure
Gram positive bacteria
Gram positive bacteria Cell walls contain peptidoglycans 、 Lipids 、 Phosphoglucuronic acid and phosphoteichoic acid . This structural component is different from that of peptidoglycan and outer membrane ( By lipids 、 Protein and lipopolysaccharide composition ) Composed of the cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria . therefore , Gram positive bacteria The cell walls are thick , And absorbed the crystal violet dye dyed by gram . therefore , The Gram-positive bacteria under the microscope are purple .
Structural characteristics of cell wall of gram positive bacteria

Gram positive bacteria have a thick multilayer cell wall composed of peptidoglycans ( Because it contains a mixture of peptides and sugars ). Because peptidoglycans are present in most bacteria , But not in mammalian cells , Therefore, it is a good target for antibacterial drugs ( For example, cell wall synthesis inhibitors , Including penicillin 、 Cephalosporins and vancomycin ).
These antibiotics interfere with transpeptidase ( Also known as penicillin binding protein or PBP Activity of ) Catalyzes the cross-linking between adjacent glycan chains in the cell wall .
The cell wall also contains teichoic acid fibers , Helps bacteria attach to the host cell membrane ( For example, mucosal cells ) On , It will cause septic shock after release , Similar to the endotoxin released by gram-negative bacteria (LPS) The resulting infection .
β- Lactamase ( Penicillinase ) It is a family of enzymes produced by bacteria , Hydrolyzable β- Lactam antibiotics ( Many of them are also bacterial ) Four atoms of β- Lactone ring , So as to inactivate its antibacterial properties .
Bacterial cell membranes can also contain ABC Efflux pump this may lead to antibiotic resistance and resistance to drugs that have intracellular mechanisms of action ( for example DNA Gyrase inhibitors or protein synthesis inhibitors ) Multidrug resistance (MDR).
Crystal violet dye is attached to the thick peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria , They are dyed purple or purple when viewed under an optical microscope .
Peptidoglycan
It is also called the cytoplasm (murein), Of bacterial cell wall content 90%.
—— Maintain shape , And maintain the strength and elasticity of the cell wall
It is a high-quality polymer , By two identical sugar derivatives (N- Acetylglucosamine and N- Acetyl muramic acid ) as well as L- Three differences rarely found in amino acid chains and proteins D- Amino acids, ( namely D- Glutamate 、D- Alanine and racemic diaminoheptanoic acid ) form , can Protect cell walls from peptidase attack .
D- Amino acids and L- Amino acids are linked to N- Acetyl teichoic acid ,L- Amino acids, especially lysine, can replace middle diaminoacrylic acid .
This interconnection of peptidoglycan subunits makes peptidoglycans have Strong ability to maintain the shape and integrity of bacteria , And Elasticity and ductility .
Peptidoglycans also have Permeability , Allow molecules to pass in and out of bacterial cells .
—— Biosynthesis of peptidoglycans
Inhibiting the synthesis of peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell wall is the molecular target of many antibacterial drugs , Include β- Lactam antibiotics ( penicillin 、 cephalosporin 、 Carbapenems and monocyclic lactams ) and Glycopeptide antibiotics ( Vancomycin and other newer analogues ).
The two main molecular targets of these drugs are Transpeptidase , Also known as penicillin binding protein (PBP), Because they combine with penicillin , And glycosyltransferases (GT) It can be inhibited by glycopeptides such as vancomycin .
PBPs There are many subtypes , A given bacterial strain can express a variety of PBPs. these PBP In its physiological characteristics and interaction with antibiotics Sensitivity There may be Different . Depending on PBP Subtype , Glycosyltransferases can exist as individual enzymes or as dimers associated with transpeptidases .
Gram positive cell wall biosynthesis
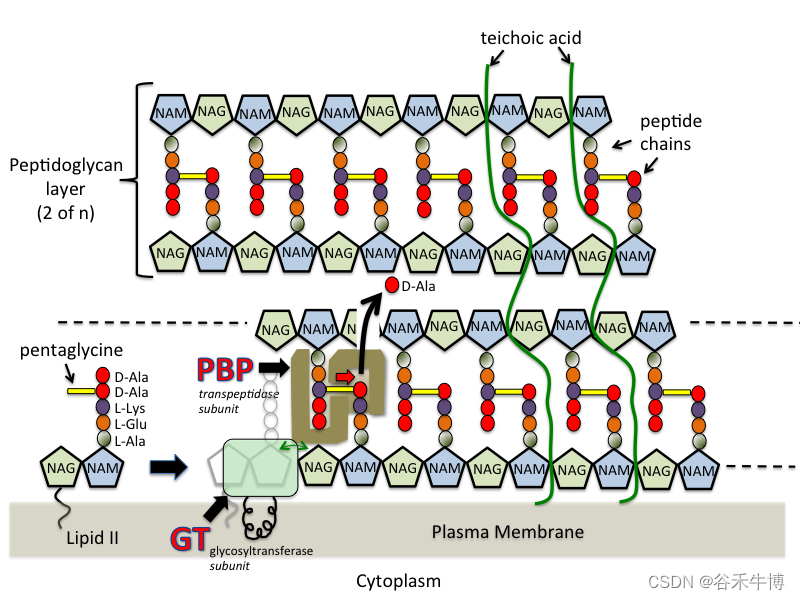
Image from (Wikipedia Commons and tmedweb)
The bacterial cell wall is made up of repeated N- Acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N- Acetyl muramic acid (NAM) Subunit chain composition .NAM Subunits with short peptide chains .
The composition of the peptide chain varies from bacterium to bacterium , But the proximal alanine is usually L-Ala, The two at the far end are usually D-Ala. Cell wall transpeptidase that also binds to penicillin ( Penicillin binding protein :PBPs) Forming bonds between peptide side chains , And expel the terminal from one of the peptide side chains D- Alanine .
Once the crosslink is formed ,PBP Will break away from the wall . With glycosyltransferase (GT) Isolate the enzyme domain NAM and NAG The activity of the residues forms a link . Some high molecular weight PBP( for example PBP2) It is an enzyme complex containing transpeptidase and glycosyltransferase domains .
Teichoic acid fibers are present in the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria , It consists of a polymer of glycerophosphate or phosphoribosyl alcohol . They are involved in the attachment of bacteria to mucosal cells , Can induce septic shock , Similar to the release of Gram-negative bacteria LPS( Endotoxin ).
Phosphoteic acid
This is from Glycerol copolymer Composed of Reinforce the wall .
Teichoic acid is Water soluble Of , Of the total dry weight of the bacterial cell wall 50%.
It either directly With peptidoglycans Covalent linkage , or And cell membrane ( Lipoteichoic acid ) Connect . adopt 6- hydroxyl N- Acetyl muramic acid is directly linked to peptidoglycan .
With a negative charge , Extend to peptidoglycan surface , Make the bacterial cell wall negatively charged .
It also helps Maintain cell walls Structure .
It's in the gram Yin The sexual bacteria are completely non-existent .
Lipids
They have a thin layer of lipids under the peptidoglycan , about 2-5%, Its effect is Anchoring bacterial cell walls .
Gram negative bacteria
cell wall
—— The cell walls are very complex
Binding to the main role of the extracellular membrane , Add a layer of peptidoglycan , Its functional characteristics are complex , Here is a description of the cell wall and its functional parts .
The cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria has a layer 2-7nm Peptidoglycan thin layer and 7-8nm Thick outer membrane .
—— The surrounding space is large
Under the microscope , Cell membrane and cell wall Between There is a space , Called periplasm Periplasmic space . It can be found in both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria , But in the gram negative In bacteria , The surrounding space is large .
The cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria
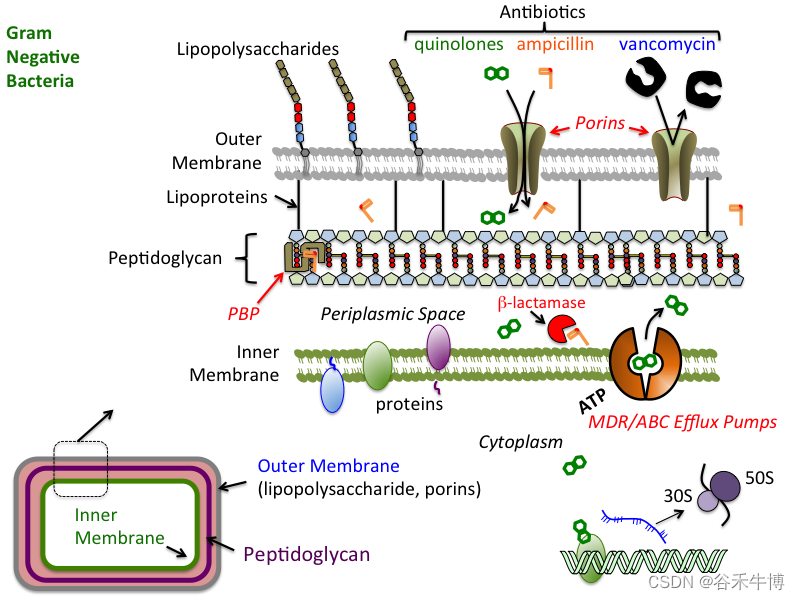
On the structure , The Gram-negative cell wall consists of two layers outside the cell membrane : A thin layer of peptidoglycan ( Too thin to absorb a large amount of methyl violet stain ) And an outer membrane ( Gram negative bacteria are unique ), Usually contains promoting small (<700 Da) Hydrophilic molecules ( For example, sugar 、 Amino acids and vitamins ) Diffuse porin .
Many antibiotics ( For example, many penicillins and cephalosporins ) They can also reach their active sites through the diffusion of porins .
However , Vancomycin (1449 Da) The quality of is too big , Unable to reach its action site through porin , This makes it ineffective against Gram-negative bacteria . therefore , The outer membrane provides Gram-negative bacteria with inherent resistance to certain antibiotics “ Internal resistance ”, It can be further modified by changing the expression level of porin or changing the pore characteristics of porin to reduce the permeability of antibiotics .
The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria also contains lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Or endotoxin , Can be excreted by bacteria , Cause a strong immune response in the host .
Periplasmic space
The periplasmic space of Gram-negative bacteria consists of Several proteins form , These proteins Help to obtain nutrition , For example, hydrolases that attack nucleic acids and phosphorylated molecules , And binding proteins that actively assist in the transport of substances into bacterial cells . Periplasmic space also has Synthetic peptidoglycans and repair Decoration Of toxic elements that may cause damage to cells enzyme .
Peptidoglycan
The cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria has a layer Thin peptidoglycan layer , Located above the plasma membrane , About% of cell dry weight 5%. The thickness does not exceed 4 nanometer , Some bacteria such as E. coli have only 2 Nano thick peptidoglycans .
Adventitia and lipopolysaccharide
Gram negative bacteria also have a second lipid bilayer , Located outside the peptidoglycan layer . This outer membrane is linked to peptidoglycans via Braun lipoproteins . The tight connection between outer membrane and peptidoglycan is Maintain outer membrane As Many toxic molecules and antibiotics Impermeable barrier Necessary .
On the adventitia Adhesion sites It also strengthens the Gram-negative cell wall , These adhesion sites are located in Allow cells to contact and Membrane fusion Play a role in . Substances enter cells through these adhesion sites .
Gram negative bacteria structure

Picture source :Jeff Dahl,wikipedia
The outer membrane is mainly composed of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) form , Lipopolysaccharide is a large complex molecule composed of lipids and carbohydrates . Lipopolysaccharide is composed of 3 Units make up : Lipids A、 Core polysaccharides and O Side chain .
Lipids A By two Glucosamine derivatives form , Each derivative contains three fatty acids and pyrophosphates , Any remaining portion of lipopolysaccharide will Protruding from the membrane surface .
O Side chains are also called O antigen , Is a chain extending outward from the core . It consists of sugars that cause variation between bacterial strains . these O Antigens are also responsible for Bacteria evade antibody responses .
// The role of outer membrane and its lipopolysaccharide
—— Lipopolysaccharide is responsible for protecting cell walls from external attack
LPS With a negative charge , Make the battery surface negatively charged . therefore , This stabilizes the membrane structure .
Lipids A It is a toxic component of lipopolysaccharide , So it acts as an endotoxin .
—— Antitoxin enters , Prevent loss of ingredients
Adventitia and its lipopolysaccharide Helps prevent antibiotics 、 Bile salts and other toxic elements enter and destroy cells .
The outer membrane is composed of porins , Make it have Permeability , Allow small molecules ( Like glucose ) Get into . vitamin B12 And other larger molecules are transported through the outer membrane through specific carriers .
The outer membrane also helps prevent the loss of ingredients , Especially from the periplasmic space .
It stands for bacteria and pathology
Examples of common gram-positive bacteria and diseases
The following table describes the main Gram-positive pathogens , Their basic morphological characteristics and the diseases they cause in humans .

Examples of common gram-negative bacteria and diseases
Gram negative bacteria are known to be normal flora , Some can cause serious human infections , From community acquired infection to hospital infection .
Gram negative bacteria The structure of the adventitia Is one of its many remarkable features . Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) On the outer leaf of the membrane , Its lipids A Partly used for Endotoxin .
// Gram-negative bacterial infections : Can be life-threatening when serious
If for some reason , Gram negative bacteria can reach the circulatory system of animals , Lipopolysaccharide will activate the immune system , And trigger the innate immune response , Produce cytokines and hormone regulators . at present Cause inflammation , And may lead to Toxic reactions , This leads to fever 、 Shortness of breath and low blood pressure . This is why Gram-negative bacteria are known to cause life-threatening shock .
Some symptoms of endotoxic shock :
Fever and chills or hypothermia 、 inflammation 、 Rash 、 Shortness of breath 、 Increased heart rate 、 Low blood pressure 、 Multiple organ failure, etc .
The following table gives some examples of gram-negative pathogenic bacteria and their clinical characteristics when causing diseases and infections in human hosts .

Drug intervention
Antimicrobial agents for Gram-positive bacteria
As shown in the table above , Gram positive bacteria are known to cause a variety of infections , If not treated and managed in a timely and appropriate manner , It may have a disastrous impact on human beings .
Gram positive bacilli infection is treated with antibiotics . penicillin 、 Clozacillin and erythromycin can Treatment 90% Above Gram-positive bacteria .
Common gram-positive antimicrobial agents and their mechanism of action

However , Antibiotic resistance It is becoming a serious problem of gram-positive infection . Researchers are developing new drugs to help solve this problem . Antibiotics should only be used when absolutely necessary . Infection control standards need to be strictly followed , To prevent the development and spread of antibiotic resistant infections .
Antimicrobial agents for Gram-negative bacteria
Because of their outer membrane , These bacteria Resistant to lysozyme and penicillin . This is because there is an outer wall that protects the inner membrane and the cell wall .
In the periplasmic space ( The area between two cell membranes ) Enzymes that break down or change antibiotics have also been found in . Methods of treatment for gram negative bacterial infections include carboxyl 、 Amino and urea penicillin . To fight the enzymes that digest these drugs , Sometimes they are associated with β- Use in combination with lactamase inhibitors .β- Lactamase is an enzyme that exists in periplasm .
Antimicrobial agents that target bacterial pathogens are called antibiotics . These antibiotics initiate blocking or inhibiting mechanisms against bacterial cells , To induce bacterial cell proliferation and replication .
Examples of antibiotics used against gram negative bacteria

Drug resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a major clinical problem in the world .
Multi drug resistant bacteria It is becoming more and more common among people , Without effective treatment , This infection can lead to Renal failure 、 septicemia , Even death .
Microorganisms inhibit many antimicrobial agents used in clinical treatment in many ways . These include Change the drug binding site Methods , Change the drug conformation Methods , Change membrane permeability Methods , Can lead to inactivation of drug resistance mechanisms .
For example, there are two membranes in Gram-negative bacteria , Adventitia and intima . Lipopolysaccharide is considered to be a very strong inducer of immune response , It has Three important ingredients : Lipids A、 Hydrophilic polysaccharides 、 antigen O The sparse waters of .
Hydrophobic domains are expressed outside the cell membrane . It is a hydrophobic component lipid a, It is responsible for endotoxin action .LPS It is variable in bacteria Of , And because of genetic variation , Some bacteria produce only one that is not Toll Receptor like recognition Weak antigen . However , There are a large number of Gram-negative bacteria groups that may cause such reactions . The immune system is also affected by some toll Like receptors 4 (TLR4) Thrill live , These receptors are present in many cells involved in the immune system , Like macrophages 、 monocyte 、 Neutrophils and dendritic cells .
from LPS and TLR4 Receptor mediated activation of innate immune response Result in an enhanced response , Produce cytokines 、 Chemokines and interferons, etc .
The response of the immune system Depending on the severity of the infection process And invasive bacteria LPS Structure , This is related to The virulence of bacteria of . therefore , Although some bacteria ( E.coli ) Can induce the immune system , But other bacteria ( Such as Helicobacter pylori ) Only with Weak antigenicity .
// New ideas for dealing with drug-resistant bacteria : Design new drugs according to the principle of charge interaction
2017 year , Professor of chemistry at the University of Illinois and co-author of the current study Paul Hergenrother(ACPP person in charge /MMG) stay 《 natural 》 The magazine reported that , One of the key findings is , If you add positively charged groups to them , For example, amines , Some antibiotics can Use specific membrane pores Penetrate the cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria .
This work shows that , Antibiotics Positively charged Amino group And bacteria In the hole Negative charge There is good interaction . These attractive forces cause antibiotics with amino groups to be arranged in a more energy friendly manner , Because it passes through the narrowest part of the hole in the contraction zone . Amine free antibiotics face a higher energy barrier to pass through pores .
This may mean that the future can Design new drugs ( Or modify the old medicine ), To attack and kill antibiotic resistant microorganisms .
FAQ
ask
What are the three differences between gram positive cells and gram negative cells ?
answer
Gram positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycans as their cell walls , Gram negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan and outer membrane .
Gram negative bacteria have lipopolysaccharides (LPS), Gram positive bacteria do not .
Some gram-positive bacteria contain mycotic acid , It forms a waxy layer on the cell wall .
ask
What is a Gram-positive infection ?
answer
An infection caused by Gram-positive bacteria , Such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)、 Vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE) And Clostridium difficile are common multidrug-resistant bacterial infections .
ask
Are gram positive bacteria easier to treat ?
answer
Gram positive bacteria , That is, those species that have a peptidoglycan outer layer , More likely to be killed —— Their thick peptidoglycan layer easily absorbs antibiotics and cleaning products . therefore , Certain detergents that easily kill Gram-positive bacteria do not destroy Gram-negative bacteria .
ask
Are many Gram-positive bacteria in the intestinal tract pathogenic ?
answer
Yes , Most of the Gram-positive bacteria in human gastrointestinal tract are opportunistic pathogens . Including Micrococcus 、 enterococcus 、 Staphylococcus aureus 、 Staphylococcus epidermidis 、 Saprophytic Staphylococcus 、 Streptococcus pneumoniae 、 Streptococcus viridis 、 Streptococcus pyogenes 、 Streptococcus agalactis 、 Clostridium tetanus 、 Botox 、 Clostridium perfringens 、 Clostridium perfringens 、 Clostridium difficile , Listeria monocytogenes, etc .
ask
Where are Gram-positive bacteria found ?
answer
According to Gram-positive bacteria , They can be found in human soil 、 Aquatic sediment 、 dust 、 The skin 、 oral cavity 、 Found in the gut or reproductive tract .
ask
Is gram positive coccus dangerous ?
answer
Gram positive bacteria may be cocci or bacilli . These bacteria, called resident bacteria, usually do not cause disease . Gram positive bacilli cause certain infections , Include : Anthrax .
ask
Are gram positive bacteria more resistant to antibiotics ?
answer
No . Compared with Gram-positive bacteria , Gram negative bacteria are more resistant to a variety of antibiotics . Because of their outer membrane , They are more resistant to antibiotics .
Gram positive bacteria are more likely to be killed , Because their thick peptidoglycan layer easily absorbs antibiotics and detergents . On the other hand , Gram negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer , Will not absorb any foreign matter around .
ask
Does gram positive bacteria have endotoxin ?
answer
Can't . Endotoxin has nothing to do with Gram-positive bacteria . These bacteria have no endotoxins , Because they have no outer membrane . On the other hand , Gram negative bacteria produce endotoxins .
These endotoxins are part of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria , It is released only when cells break down or bacteria die . Endotoxin is a heat stable lipopolysaccharide that forms the cell wall structure of Gram-negative bacteria - Protein complexes .
ask
Why are Gram-positive bacteria more sensitive to antibiotics ?
answer
Although Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer , But they are more susceptible than Gram-negative bacteria to the cell walls of some targeted antibiotics , Because they lack outer membrane .
Most antibiotics try to get close to their target , Must pass through the outer membrane . for example , Hydrophilic antibiotics pass through porin . therefore , Gram negative bacteria can change their outer membrane by changing their hydrophobic properties or by mutation of porin . This creates resistance to these bacterial cells . Gram positive bacteria lack this factor , So gram negative bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics than they are .
ask
Whether gram positive bacteria cause disease ?
answer
Yes , Most Gram-positive bacteria are pathogenic . Examples of pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria include Micrococcus 、 enterococcus 、 Staphylococcus aureus 、 Staphylococcus epidermidis 、 Saprophytic Staphylococcus 、 Streptococcus pneumoniae 、 Streptococcus viridis 、 Streptococcus pyogenes 、 Streptococcus agalactis 、 Clostridium tetanus 、 Botox 、 Clostridium perfringens 、 Clostridium perfringens 、 Clostridium difficile , Listeria monocytogenes, etc .
ask
What are the common infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria ?
answer
Anthrax 、 diphtheria 、 diarrhea 、 Meningitis 、 nausea 、 Skin infection 、 urinary tract infection .
ask
Which antibiotic is effective against Gram-positive bacteria ?
answer
Penicillin is an effective antibiotic against Gram-positive bacteria 、 Cloxacillin and erythromycin , It's almost covered 90% Gram positive bacteria infection . Others are vancomycin 、 Trimethoprim / Sulfamethoxazole , Clindamycin , Clindamycin, etc .
ask
What are the common human diseases caused by gram-negative bacteria ?
answer
Gram negative bacteria can cause infection in medical institutions , Including pneumonia 、 Bloodstream infection 、 Wound or surgical site infection and meningitis . There is also cholera 、 Plague 、 Typhoid fever 、 Meningitis and urinary tract infection are common bacterial diseases .
ask
Why are gram negative bacteria more harmful than gram positive bacteria ?
answer
The cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria is hard , Not susceptible to antibiotics , Endotoxin is released under the action of antibiotics .
ask
What kills gram negative bacteria ?
answer
These antibiotics include cephalosporins ( Cefatriaxone - Cefotaxime 、 Ceftazidime et al )、 Fluoroquinolones ( Ciprofloxacin 、 Levofloxacin )、 Aminoglycosides ( Gentamicin 、 Amikacin ) etc.
ask
What is the secretory system of Gram-negative bacteria ?
answer
Gram negative bacteria have a widely closed secretory system , Can transfer tiny molecules 、DNA、 Amino acids, 、 protein .
ask
Where does gram negative bacteria come from ?
answer
Gram negative bacteria are everywhere , Almost all the life supporting environments on the earth . Gram negative bacteria include the model organism E. coli , And many pathogenic bacteria , Such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa 、 Neisseria gonorrhoeae 、 Chlamydia trachomatis and Yersinia pestis .
ask
How to naturally remove gram negative bacteria ?
answer
Natural antibiotics . Some natural antibiotics are garlic 、 honey 、 Cabbage 、 Grapefruit seed extract 、 Raw apple vinegar 、 Extra virgin coconut oil 、 Fermented food, etc .
disclaimer : The contents of this official account are only for exchange and reference , Not as a diagnostic and medical basis . Main references :
Oliveira J, Reygaert WC. Gram Negative Bacteria. 2022 Mar 26. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan–. PMID: 30855801.
Carroll K.C., & Hobden J.A., & Miller S, & Morse S.A., & Mietzner T.A., & Detrick B, & Mitchell T.G., & McKerrow J.H., & Sakanari J.A.(Eds.), (2019). Jawetz, Melnick, & Adelberg’s Medical Microbiology, 27e. McGraw Hill.
Acheson DWK (2015): Patient information: Food poisoning (foodborne illness) (Beyond the Basics). In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Apicella M (2015): Treatment and prevention of meningococcal infection. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Baum SG (2016): Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in adults. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/2/16
Crowe SE (2016): Bacteriology and epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16.
Crowe SE (2016b): Treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16.
File TM (2016): Treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in adults in the outpatient setting. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Ghanem KG (2016): Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection in adults and adolescents. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Hicks CB, Clement M (2016): Syphilis: Treatment and monitoring. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/2/16
Kanafani ZA, Kanj SS (2014): Acinetobacter infection: Epidemiology, microbiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, and diagnosis. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/10/16
Kanafani ZA, Kanj SS (2016): Acinetobacter infection: Treatment and prevention. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/10/16
Kelly CP, Lamont JT (2015): Clostridium difficile in adults: Treatment. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/2/16
Koulenti D et al (2009): Spectrum of practice in the diagnosis of nosocomial pneumonia in patients requiring mechanical ventilation in European intensive care units. Critical Care Med 37(9):2360-2369. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a037ac
Lamont JT (2016): Clostridium difficile in adults: Epidemiology, microbiology, and pathophysiology. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/2/16
Li X-Z, Nikaido H (2004): Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Drugs. 64(2):159–204.
Lowy FD (2016): Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in adults: Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Pegram PS, Stone SM (2016): Botulism. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Riley LW (2015): Natural history, microbiology, and pathogenesis of tuberculosis. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/2/16
Sauvage E et al (2008): The penicillin-binding proteins: structure and role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:234–258. DOI:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00105.x
Southwick F (2008): Infectious Diseases. A Clinical Short Course. McGraw Hill/Lange.
Sterling TR (2016): Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV-uninfected adults. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/2/16
Stevens DL, Bryant A (2015): Group A streptococcus: Virulence factors and pathogenic mechanisms. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Stevens DL (2016): Group A streptococcal (Streptococcus pyogenes) bacteremia in adults. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Swygard H et al (2016): Treatment of uncomplicated gonococcal infections. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Wanke CA (2015): Pathogenic Escherichia coli. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 7/28/16
Wanke CA (2015b): Travelers' diarrhea: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Yeh S (2015): Microbiology, epidemiology and treatment of Haemophilus influenzae. In: UpToDate, Basow, DS (Ed), Waltham, MA. Cited 8/1/16
Sagar Aryal,Gram-Positive Vs Gram-Negative Bacteria- 31 Differences With Examples. Microbenotes.2022,January 9
Jawertz M., Alderbergs., Medical Microbiology 28th Edition.
Prescott M. L., Microbiology. 5th Edition
Lippincott Microbiology in review: 3rd edition
Faith Mokobi,Gram-Positive Bacteria- Cell Wall, Examples, Diseases, Antibiotics,2021, April 15
Faith Mokobi,Gram-Negative Bacteria- Cell Wall, Examples, Diseases, Antibiotics ,2021 ,April 15
边栏推荐
- 线程+线程问题记录
- Fairmot yolov5s to onnx
- 洛谷P2839 [国家集训队]middle(二分 + 主席树 + 区间合并)
- RMQ区间最大值下标查询,区间最值
- Atlassian Confluence 远程代码执行漏洞(CVE-2022-26134漏洞分析与防护
- 1742. 盒子中小球的最大数量
- El input to add words to the tail
- How much do you know about electronic components on PCB?
- 洛谷P2486 [SDOI2011]染色(树链+线段树 + 树上区间合并 )
- C WinForm panel custom picture and text
猜你喜欢

Importer des données dans MATLAB

Do you know why the PCB produces tin beads? 2021-09-30

基于RBAC 的SAAS系统权限设计

This article uses pytorch to build Gan model!

Six causes of PCB disconnection 2021-10-20

Ubuntu18下登录mysql 5.7设置root密码

Dietary intervention reduces cancer treatment-related symptoms and toxicity

挖掘微生物暗物质——新思路

將數據導入到MATLAB

网络模型——OSI模型与TCP/IP模型
随机推荐
[daily training] 207 Class Schedule Card
电子学:第012课——实验 11:光和声
This article uses pytorch to build Gan model!
opencv最小值滤波(不局限于图像)
57. insert interval
Force deduction 76 questions, minimum covering string
What are the problems with traditional IO? Why is zero copy introduced?
Invalid Navicat scheduled task
bat启动.NET Core
Take you through the normalization flow of GaN
微信小程序开通客服消息功能开发
一文了解 | 革兰氏阳性和阴性菌区别,致病差异,针对用药
MySQL interview - the response of executing SQL is relatively slow, and the troubleshooting ideas.
417-二叉树的层序遍历1(102. 二叉树的层序遍历、107.二叉树的层次遍历 II、199.二叉树的右视图、637.二叉树的层平均值)
CAN透传云网关CANIOT,CANDTU记录CAN报文远程收发CAN数据
牛客:飞行路线(分层图+最短路)
將數據導入到MATLAB
剑指offer刷题(中等等级)
socket问题记录
Mining microbial dark matter -- a new idea