当前位置:网站首页>torch_ How to use scatter. Scatter() in detail
torch_ How to use scatter. Scatter() in detail
2022-07-24 15:40:00 【Cyril_ KI】
1. Parameters
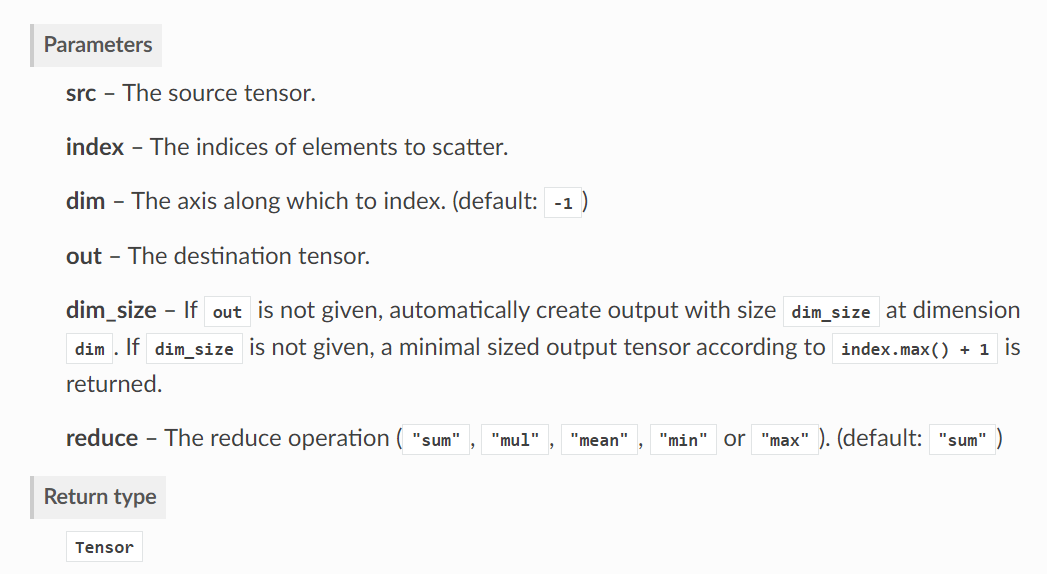
In particular ,scatter The function is to make index At the corresponding position of the same index in src Elements operate in some way , for example sum、mean etc. , Then the results of these operations are spliced according to the index order . Let me explain with specific examples .
2. Example
2.1 A simple example
Initialize first src and index:
src = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) # (3, 3)
index = torch.tensor([0, 0, 1], dtype=torch.int64)
Then use scatter function :
out = scatter(src, index, dim=0, reduce='mean')
We observe index=[0, 0, 1], The first 0 Position and number 1 Both positions are 0, The first 2 The positions are 1. in other words , We need to src pass the civil examinations 0 Elements and number 1 The average of elements becomes an element , Then the first 2 Elements find mean That is, it is an element . If index=[1, 0, 0], It means that we need to src pass the civil examinations 1 Elements and number 2 The average of elements becomes an element , And the first 0 The first element remains unchanged .
that src How to define the first few elements in ? And that's where it comes in dim Parameters .
dim=0 It means we need to be right src Dimensions 0 To operate :
tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.],
[7., 8., 9.]])
namely src pass the civil examinations 0 Elements are [1, 2, 3], The first 1 Elements are [4, 5, 6], The first 2 Elements are [7, 8, 9].
And if the dim=1, Is the first 0 Elements are [1, 4, 7], The first 1 Elements are [2, 5, 8], The first 2 Elements are [3, 6, 9].
therefore , If you have the following code :
src = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) # (3, 3)
index = torch.tensor([0, 0, 1], dtype=torch.int64)
out = scatter(src, index, dim=0, reduce='mean')
Then we should put src No 0 Elements are [1, 2, 3] And the 1 Elements are [4, 5, 6] Average as [2.5, 3.5, 4.5], Then the first 2 Elements [7, 8, 9] remain unchanged , namely :
tensor([[2.5000, 3.5000, 4.5000],
[7.0000, 8.0000, 9.0000]])
2.2 Sequence problem
In the example above index=[0, 0, 1], The final result will be src pass the civil examinations 0 Elements and number 1 The average of elements is placed in position 0, then src pass the civil examinations 2 Elements remain unchanged and are placed in position 1.
If index=[1, 1, 0], The result is :
tensor([[7.0000, 8.0000, 9.0000],
[2.5000, 3.5000, 4.5000]])
You can find , The above result is that src pass the civil examinations 2 Elements [7, 8, 9] Keep the same and put it in position 0, And then src pass the civil examinations 0 Elements [1, 2, 3] And the 1 Elements [4, 5, 6] Find the average to keep unchanged and put it in position 1.
in other words , No matter what index How to change , Are priority will index in 0 Place the operation result of the corresponding position .
2.3 Dimension problem
If src The dimensions are (4, 3), And we need to be right dim=0 operation , That is, there are four elements , that index The length of should be 4, That is, the following operations are illegal :
src = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]) # (4, 3)
index = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0], dtype=torch.int64)
out = scatter(src, index, dim=0, reduce='mean')
print(out)
Report error as :
RuntimeError: The expanded size of the tensor (4) must match the existing size (3) at non-singleton dimension 0. Target sizes: [4, 3]. Tensor sizes: [3, 1]
The right thing to do is :
src = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]) # (4, 3)
index = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0, 2], dtype=torch.int64)
out = scatter(src, index, dim=0, reduce='mean')
print(out)
Output is :
tensor([[ 7.0000, 8.0000, 9.0000],
[ 2.5000, 3.5000, 4.5000],
[10.0000, 11.0000, 12.0000]])
边栏推荐
- [acwing] 909. Chess game
- With this machine learning drawing artifact, papers and blogs can get twice the result with half the effort!
- Varnish4.0 cache agent configuration
- Class assignment (6) - 575. Word division (word)
- 微调LayoutLM v3进行票据数据的处理和内容识别
- 【洛谷】P1908 逆序对
- 2022 robocom world robot developer competition - undergraduate group (provincial competition) -- question 1: don't waste gold (finished)
- vscode常用快捷键
- pip 安装报错 error in anyjson setup command: use_2to3 is invalid.
- [adaptiveavgpool3d] pytorch tutorial
猜你喜欢

MySQL学习笔记(总结)

Windows10安装免安装版redis

2022 RoboCom 世界机器人开发者大赛-本科组(省赛)RC-u4 攻略分队 (已完结)

Kubectl_好用的命令行工具:oh-my-zsh_技巧和窍门

Which is a good noise reduction Bluetooth headset? Ranking of the most cost-effective noise reduction Bluetooth headsets

接参处理和@Param

Arduino ide esp32 firmware installation and upgrade tutorial
![[shaders realize pixelate mosaic effect _shader effect Chapter 7]](/img/0f/3e8d9468d94b14217875c7e447aa15.png)
[shaders realize pixelate mosaic effect _shader effect Chapter 7]

Intuitive understanding of various normalization

Still using listview? Use animatedlist to make list elements move
随机推荐
With this machine learning drawing artifact, papers and blogs can get twice the result with half the effort!
降噪蓝牙耳机哪个好?性价比最高的降噪蓝牙耳机排行
Five principles of solid are indispensable for good architecture design
报错【项目报错】
【着色器实现Pixelate马赛克效果_Shader效果第七篇】
Application modification log path log4j.properties
2022 RoboCom 世界机器人开发者大赛-本科组(省赛)RC-u4 攻略分队 (已完结)
MATLAB image defogging technology GUI interface - global balance histogram
MySQL source code analysis -- data structure of index
未来数据库需要关心的硬核创新
[shaders realize pixelate mosaic effect _shader effect Chapter 7]
Lsyncd set up synchronous image - use lsyncd to realize real-time synchronization between local and remote servers
Kubernetes版本对接对象存储
Lsyncd real time synchronization
Feign for 20 minutes every day
2022 RoboCom 世界机器人开发者大赛-本科组(省赛)-- 第五题 树与二分图 (已完结)
C. Recover an RBS
Kubectl_好用的命令行工具:oh-my-zsh_技巧和窍门
R语言ggplot2可视化:ggplot2可视化基本散点图(scatter plot)、通过在theme_bw中指定参数base_size来改变轴标签的大小、并控制网格线和轴标签的大小
Error in anyjson setup command: use_ 2to3 is invalid.