当前位置:网站首页>[cloud co creation] what magical features have you encountered when writing SQL every day?
[cloud co creation] what magical features have you encountered when writing SQL every day?
2022-07-23 20:40:00 【Hua Weiyun】
The main contents of this paper are :
One SQL The first magical feature of
Two SQL The second magical feature of
3、 ... and SQL The third magical feature of
Four Why are Gaussian database features excellent

One SQL The first magical feature of
In daily development, we often perform aggregate queries on tables , But only in SELECT The clause says 3 Content : adopt GROUP BY Aggregate key specified by clause 、 Aggregate functions (SUM 、AVG etc. )、 Constant , It doesn't matter if you don't understand. Let's take an example
Let me explain
There is a student class schedule (tbl_student_class) as well as The data are as follows
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tbl_student_class;CREATE TABLE tbl_student_class ( id int(8) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ' Since the primary key ', sno varchar(12) NOT NULL COMMENT ' Student number ', cno varchar(5) NOT NULL COMMENT ' Class number ', cname varchar(20) NOT NULL COMMENT ' Class name ', PRIMARY KEY (id)) COMMENT=' Student class schedule ';-- ------------------------------ Records of tbl_student_class-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO tbl_student_class VALUES ('1', '20190607001', '0607', ' Movies 7 class ');INSERT INTO tbl_student_class VALUES ('2', '20190607002', '0607', ' Movies 7 class ');INSERT INTO tbl_student_class VALUES ('3', '20190608003', '0608', ' Movies 8 class ');INSERT INTO tbl_student_class VALUES ('4', '20190608004', '0608', ' Movies 8 class ');INSERT INTO tbl_student_class VALUES ('5', '20190609005', '0609', ' Movies 9 class ');INSERT INTO tbl_student_class VALUES ('6', '20190609006', '0609', ' Movies 9 class ');I want to count all classes ( Class number 、 Class name ) How many people are there in one 、 And the largest student number , How do we write this query SQL ? I think everyone can write with their feet
SELECT cno,cname,count(sno),MAX(sno) FROM tbl_student_classGROUP BY cno,cname;But someone will think ,cno and cname It's one-on-one ,cno Once it's established ,cname Are you sure , that SQL Can we write like this ?
SELECT cno,cname,count(sno),MAX(sno) FROM tbl_student_classGROUP BY cno;Wrong execution report
[Err] 1055 - Expression #2 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY clause and contains nonaggregated column 'test.tbl_student_class.cname' which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause; this is incompatible with sql_mode=only_full_group_by Prompt information :SELECT The second expression in the list (cname) be not in GROUP BY In the clause of , At the same time, it is not ** Aggregate functions **; This is related to sql Pattern :ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY Incompatible ha What then? GROUP BY After that, you can't directly refer to the original table ( be not in GROUP BY Clause ) Column in ? Don't worry , We'll see it slowly
1.0 SQL Pattern
MySQL Servers can be in different SQL Run in mode , And you can apply these patterns in different ways for different clients , Depending on sql_mode The value of the system variable .DBA You can set the global SQL Pattern to match site server operational requirements , And each application can have its session SQL Mode is set to its own requirements .
Patterns can affect MySQL Supported by SQL Syntax and what it does Data validation check , This makes it possible to use MySQL And will be MySQL It's easier to use with other database servers . Please check the official website for more details :Server SQL Modes
MySQL Different versions , The content will be slightly different ( Include default values ), Pay attention to your own MySQL Keep the same version
SQL There are two main types of patterns : Syntax supports classes and data checking classes , Common ones are as follows
Syntax support class
ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY
about GROUP BY Aggregation operation , If in SELECT Column in 、HAVING perhaps ORDER BY Column of clause , Not in the GROUP BY It appears that , So this SQL It's illegalANSI_QUOTES
Enable ANSI_QUOTES after , You can't use double quotes to refer to strings , Because it's interpreted as an identifier . After setting it up ,update t set f1="" …, Will be submitted to the Unknown column ‘’ in field list Such grammatical mistakesPIPES_AS_CONCAT
hold || Think of it as a concatenation operator for strings, not or Operator , This and Oracle The database is the same , And string concatenation function CONCAT() It's kind of similarNO_TABLE_OPTIONS
Use SHOW CREATE TABLE Will not output MySQL The special grammar part , Such as ENGINE , This is in use mysqldump Span DB When species migrate You need to considerNO_AUTO_CREATE_USER
Don't create users automatically , In giving MySQL When the user authorizes , We are used to using GRANT … ON … TO dbuser, Create users along the way . When this option is set, it will be connected with oracle The operation is similar to , Users must be established before authorization
1.1 Data checking class
- NO_ZERO_DATE
Think of date ‘0000-00-00’ illegal , It has something to do with whether to set the following strict mode
1、 If strict mode is set , be NO_ZERO_DATE Natural satisfaction . But if it is INSERT IGNORE or UPDATE IGNORE,’0000-00-00’ Still allow and only show warning;
2、 If in a non strict mode , Set up NO_ZERO_DATE, The effect is the same as above ,’0000-00-00’ Allow but show warning; If not set NO_ZERO_DATE,no warning, As fully legal value ;
3、NO_ZERO_IN_DATE It's similar to the above , The difference is to control the date and the day , Whether it can be 0 , namely 2010-01-00 Is it legal ;
- NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
Use ALTER TABLE or CREATE TABLE Appoint ENGINE when , The required storage engine is disabled or not compiled , How to deal with . Enable NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION when , Then throw the error directly ; When this value is not set ,CREATE Replace... With the default storage engine ,ATLER No changes , And throw a warning
- STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
Set it up , Indicates that strict mode is enabled . Be careful STRICT_TRANS_TABLES It's not a combination of strategies , Single finger INSERT、UPDATE How to deal with low or invalid value :
1、 The handle mentioned above ‘’ Pass to int, Illegal in strict mode , If non strict mode is enabled, it becomes 0, Produce a warning;
2、Out Of Range, To insert the maximum boundary value ;
3、 When a new line is to be inserted , Does not include no explicit... In its definition DEFAULT The non of clause NULL Column value , The column is missing a value
1.2 The default mode
When we haven't modified the configuration file ,MySQL It has its own default mode ; Different versions , The default mode is different
-- see MySQL edition SELECT VERSION();-- see sql_modeSELECT @@sql_mode;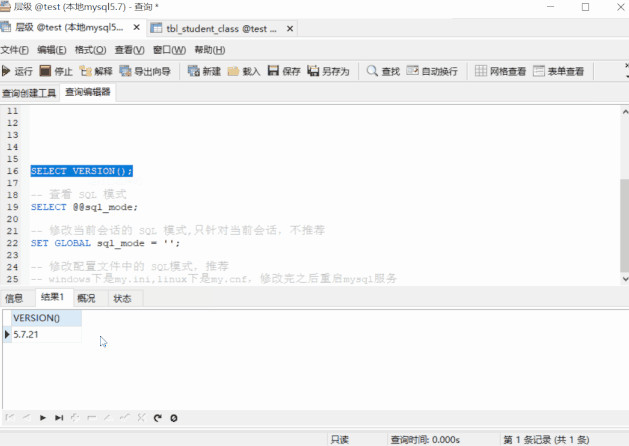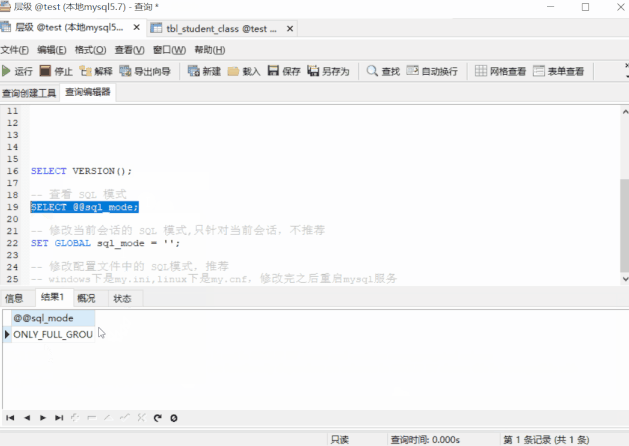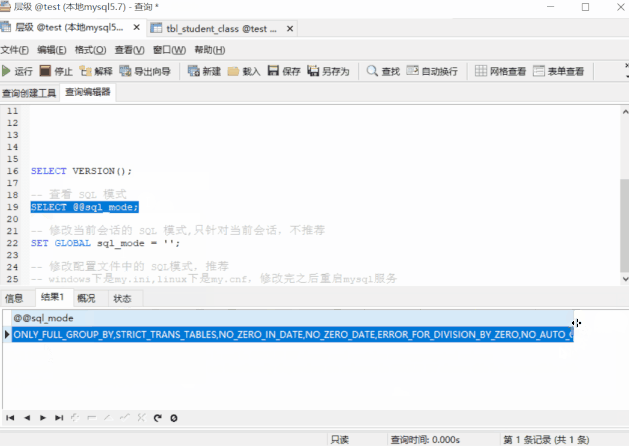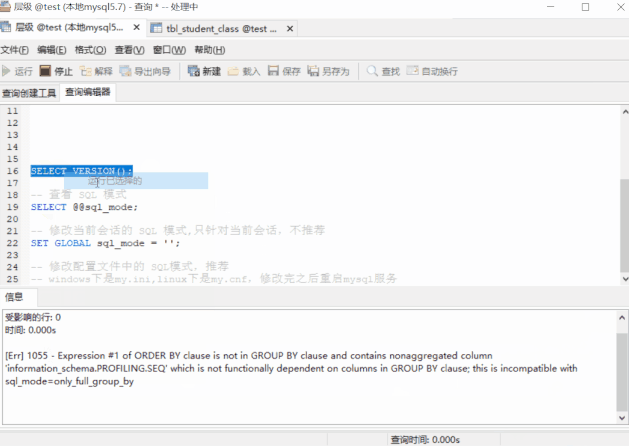
We can see ,5.7.21 The default mode of contains
ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION And the first one :ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY Will restrain : When we do aggregate queries ,SELECT The column of cannot directly contain non GROUP BY Column in clause . So if we get rid of that pattern ( from “ Strict mode ” To “ Loose mode ”) Well ?
We found that , The above report is wrong SQL
-- In relaxed mode It can be executed SELECT cno,cname,count(sno),MAX(sno) FROM tbl_student_classGROUP BY cno;It works , However, this configuration is not recommended in general , Online environments tend to be “ Strict mode ”, instead of “ Loose mode ”; Although in the case , Whether it's “ Strict mode ”, still “ Loose mode ”, The results are all right , That's because cno And cname The only corresponding , If cno And cname It's not the only one , So in “ In relaxed mode ” cname The value of is random , This will lead to problems that are difficult to investigate , If you are interested, you can try ;
Two SQL The second magical feature of
2.1 Describe the problem
Today I want to compare two datasets
surface A altogether 50,000,000 That's ok , One of them is called 「ID」, surface B There is also a column called 「ID」. What I want to check is A How much is in the table ID stay B Inside the watch , The database uses snowflake, It is a multi tenant 、 transactional 、 Security 、 Highly scalable elastic database , Or call it the implementation of digital warehouse , Complete SQL Support and schema-less Data patterns , Support ACID The business of , Also available for traversal 、 Built in functions for flattening and nesting semi-structured data and SQL Expand , And support JSON and Avro Other popular formats ;
use query:
with A as( select distinct(id) as id from Table_A),B as ( select distinct(id) as id from Table_B ),result as ( select * from A where id in (select id from B))select count(*) from resultThe return is 26,000,000
in other words ,A due 24,000,000 Is it OK B Inside , Right
But I put the first 11 Yes in Change to not in after , The situation is a little beyond my expectation
with A as( select distinct(id) as id from Table_A),B as ( select distinct(id) as id from Table_B ),result as ( select * from A where id not in (select id from B))select count(*) from resultThe return result turned out to be 0, instead of 24,000,000
So I am snowflake Search the Forum , Find out 5 Years ago, someone replied below this post :
If you use NOT IN (subquery), it compares every returned value and in case of NULL on any side of comparison it stops immediately with non defined result if you use NOT IN (subquery), it compares every returned value and in case of NULL on any side of comparison it stops immediately with non defined result
That is to say , When you use not in,subquery( For example, the first 11 Yes select id from B) in If there is Null, Then it will stop immediately , Return undefined results , So the end result is 0;
How to solve
It's simple
2.2 Get rid of null value
In the 7 The line is limited where id is not null after , It turned out to be normal
with A as( select distinct(id) as id from Table_A),B as ( select distinct(id) as id from Table_B where id is not null),result as ( select * from A where id not in (select id from B))select count(*) from resultThe final result is 24,000,000, That's right
2.3 use not exists Instead of not in
Pay attention to the 11 That's ok , It was used not exists Instead of not in
with A as( select distinct(id) as id from Table_A),B as ( select distinct(id) as id from Table_B where id is not null),result as ( select * from A where not exists (select * from B where A.id=B.id))select count(*) from resultThe return result is also 24,000,000
Of course , It's definitely not bug Ha , It's a feature , Otherwise, I wouldn't have kept it for so many years , I know too little , I have to make up for it SQL Cry .
But I don't know what the original purpose of this feature design is , If subquery Back to undefined, You should make a mistake for me . This 「 characteristic 」 It's not just snowflake It shows , see StackOverflow Discuss above , Looks like Oracle There is also this 「 characteristic 」 Yeah
3、 ... and SQL The third magical feature of
image Web In an application scenario where services need to respond quickly ,SQL Its performance directly determines whether the system can be used ; Especially in some small and medium-sized applications ,SQL Performance of It is more about service The only criterion for rapid response
Strictly optimize query performance , It is necessary to understand the functional characteristics of the database used , Besides , It's not just that queries are slow SQL Statement itself , There may also be poor memory allocation 、 The file structure is unreasonable 、 Brush dirty pages and other reasons ;
So here are some SQL Magical properties , But it can't solve all the performance problems , But it can handle a lot of reasons SQL Performance problems caused by unreasonable writing
So let's try to introduce some implementations that don't rely on specific databases , send SQL Faster execution 、 Optimization techniques that consume less memory , Just adjust SQL Statement can achieve the general optimization Tip
3.1 Environmental preparation
What follows is from SQL The level unfolds , Not a database for a particular feature , in other words , The following content is basically applicable to any relational database ;
however , So many relational databases , Let's demonstrate the examples one by one , It's obviously not realistic ; We use the usual MySQL Just do it
MySQL edition : 5.7.30-log , Storage engine : InnoDB
Prepare two sheets : tbl_customer and tbl_recharge_record
3.2 Use efficient queries
For a query , Sometimes there are many SQL Realization , for example IN、EXISTS、 The interconversion between connections
In theory , Different ways to get the same results SQL Statements should have the same performance , But unfortunately , Query the execution plan generated by the optimizer To a large extent, it is affected by the external data structure
therefore , To optimize query performance , You have to know how to write SQL Statement to enable the optimizer to generate more efficient execution plans
3.3 Use EXISTS Instead of IN
About IN, I believe everyone is familiar with , Easy to use , It's easy to understand ; although IN Easy to use , But it has performance bottlenecks
If IN The parameter is 1,2,3 Such a list of values , Generally, no special attention is needed , But if the parameter is a subquery , So we need to pay attention
Most of the time , [NOT]IN and [NOT]EXISTS The results returned are the same , But when both are used for subqueries ,EXISTS It's going to be faster
Suppose we want to query the customer information with recharge record ,SQL How to write ?
I believe the first thing you think of is IN
IN It's really easy to use , It's also very understandable ; Let's take a look at its implementation plan 
Let's see EXISTS Implementation plan of :
What you can see is ,IN A temporary table has been created in the implementation plan of : <subquery2> , This leads to slower efficiency
So usually ,EXISTS Than IN There are two reasons for being faster
1、 If connecting columns (customer_id) Indexed on , So query
tbl_recharge_recordYou can query by index , Instead of full table query2、 Use EXISTS, Once a row of data is found, the query will be terminated , Not like using IN Scan the whole table the same way (NOT EXISTS It's the same thing )
If so IN When the parameter of is a subquery , Database first Execute subquery , The results are then stored in a temporary table ( inline view ), Then scan the entire view , In many cases, it's very resource intensive
Use EXISTS Words , The database does not generate temporary tables
But in terms of code readability ,IN than EXISTS good , Use IN It's a lot easier to see at a glance , Easy to understand
therefore , If you are sure to use IN Can also get results quickly , There's no need to change it to EXISTS 了
In fact, many databases are trying to improve IN Performance of
Oracle In the database , If we use on indexed columns IN, Also scan the index first
PostgreSQL From version Ben 7.4 It also improves the use Subquery as IN Query speed for predicate parameters
Maybe one day in the future , On any relational database ,IN All of them have the ability to communicate with EXISTS Same performance
3.4 Use connection instead IN
In fact, in my daily work , It's more about connecting instead of IN To improve query performance , Instead of EXISTS, It's not that the connection is better , It is EXISTS It's hard to master
Back to the question : Query the customer information with recharge record , If you use connections to achieve ,SQL How to write ?
This way of writing can make full use of index ; and , Because there is no subquery , Therefore, the database will not generate intermediate tables ; therefore , Query efficiency is good
as for JOIN And EXISTS Which one is better , It's hard to say ; If there is no index , Probably EXISTS It will be a little better , If there is an index , Both are pretty much the same
3.5 Avoid sorting
Speaking of SQL Sort , The first thing we thought of was that : ORDERBY , Through it , We can output the results in the order of some specified columns
however , except ORDERBY The sort shown , There are still many operations inside the database to sort in secret ; Representative operations that can be sorted are as follows 
If you sort only in memory , Well, then. ; But if you need to sort on the hard disk due to insufficient memory , Then the performance will drop sharply
therefore , Try to avoid ( Or reduce ) Meaningless ordering , Can greatly improve the query efficiency
Flexible use of set operators ALL optional
SQL There is UNION 、 INTERSECT 、 EXCEPT Three set operators , The sub table represents the set operation Combine 、 intersection 、 Difference set
By default , These operators are sorted to eliminate duplicate data 
Using temporary It means sorting or grouping , Obviously this SQL No grouping , It's a sort operation
So if we don't care whether there are duplicate data in the results , Or know in advance that there won't be duplicate data , have access to UNIONALL Instead of UNION Try out , You can see , There is no sort operation in the execution plan 
about INTERSECT and EXCEPT It's the same , add ALL After the option is available No sorting
add ALL Optional is a very effective optimization tool , But the implementation of each database is uneven , As shown in the figure below 
Be careful :Oracle Use MINUS Instead of EXCEPT;MySQL It didn't happen at all INTERSECT and EXCEPT operation
3.6 Use EXISTS Instead of DISTINCT
To eliminate duplicate data , DISTINCT It will also sort
Remember to connect instead of IN The case of , If not DISTINCT
SQL: SELECT tc.*FROM tbl_recharge_record trr LEFTJOIN tbl_customer tc on trr.customer_id = tc.idThen the results will be Many duplicate records , So we must improve SQL
SELECTDISTINCT tc.*FROM tbl_recharge_record trr LEFTJOIN tbl_customer tc on trr.customer_id = tc.id You'll find that there's a... In the execution plan Using temporary, It means that sorting operation is used 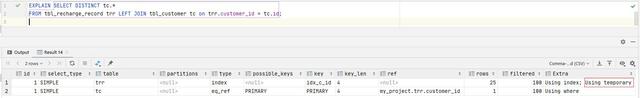
We use EXISTS To optimize 
You can see , Sort operations have been circumvented
3.7 Using indexes in extremum functions
SQL There are two extreme functions in the language : MAX and MIN, When you use both functions, you sort
for example : SELECTMAX(recharge_amount) FROM tbl_recharge_record
A full scan will be performed , And sort implicitly , Find out the maximum amount of a single recharge
But if there is an index on the parameter field , Then just scan the index , But you don't need to scan the whole table
for example :SELECTMAX(customer_id) FROM tbl_recharge_record;
It'll go through the index : idx_c_id scan , Find the biggest customer in the recharge record ID
But this way It's not that the sorting process is removed , It optimizes the search speed before sorting , So as to reduce the impact of sorting on the overall performance
It can be written in WHERE The conditions in the clause must not be written in HAVING In Clause
Let's look at two SQL And its implementation results 
You'll see
In terms of results , Two article SQL equally ; But in terms of performance , The second sentence is more efficient , There are two reasons :
Reduce the amount of sorted data
GROUP BY Clause aggregation is sorted , If you pass in advance WHERE Clause to filter out a branch , It can reduce the burden of sorting
Efficient use of indexes
3.8 WHERE Index can be used in the condition of clause
HAVING Clause is used to filter the views generated after aggregation , But a lot of times The aggregated views do not inherit the index of the original table structure
About HAVING, More details can be found at : magical SQL And HAVING → The easily despised protagonist
stay GROUP BY Clause and ORDER BY Use index in clause
Generally speaking ,GROUP BY Clause and ORDER BY Clauses are sorted
If GROUP BY and ORDER BY Is indexed , Then it can improve the query efficiency
Especially in some databases , If the column has a unique index , Then the sorting process itself will be omitted
- Use index
Using indexes is the most common SQL Optimization means , Everybody knows that , I'm afraid we don't know : There's an index , Why is the query still so slow ( Why the index doesn't work )
On the case that the index is not used , You can see : magical SQL It passed by → Do you really use the index , This article will not elaborate too much
In short, that is : Try to index the query , Avoid the situation that the index is not used
- Reduce temporary tables
stay SQL in , The result of the subquery is treated as a new table ( A temporary table ), This new table is the same as the original one , Can pass SQL To operate
however , There are two problems with frequent use of temporary tables
1、 A temporary table is equivalent to a backup of the original table data , Will consume memory resources
2、 A lot of times ( Especially when it comes to aggregation ), The temporary table does not inherit the index structure of the original table
therefore , Minimizing the use of temporary tables is also an important way to improve performance
- Flexible use HAVING Clause
When you specify filter criteria for aggregate results , Use HAVING Clause is the basic principle
But if you're right HAVING Not familiar with , We tend to find alternative ways to achieve , Just like this. 
However , For aggregate results There is no need to specially generate intermediate tables when specifying filter criteria , Use as follows HAVING Clause can 
HAVING Clauses and aggregation operations are performed simultaneously , So instead of generating a temporary table and then executing it WHERE Clause , It will be more efficient , And the code looks simpler
You need to use... For multiple fields IN Predicate time , Let them sum up in one place
SQL-92 Line to line comparison function is added in , thus , Comparison predicate = 、< 、> and IN The parameters of the predicate are no longer just scalar values , It should be a list of values
Let's take an example , Multiple fields use IN The predicate 
Two subqueries are used in this code , We can do column Aggregation Optimization , Put the logic together 
thus , Subqueries don't have to consider relevance , And it can only be executed once
It can be further simplified , stay IN Write a combination of multiple fields in 
simplified , Don't worry about the type conversion problem when connecting fields , It doesn't process fields , So you can use the index
First connect and then aggregate
When connection and aggregation are used at the same time , Advanced join operation can avoid intermediate table
Rational use of views
Views are a very convenient tool , We are Often used in daily work
however , If you define complex views without deep thinking , It can cause huge performance problems
Especially when you include operations in the following statements ,SQL It's going to be very inefficient , Execution can also become very slow 
Under the summary
There are several points in this paper , But in fact, there is only one core idea of optimization , That's finding the performance bottleneck , And then solve it ;
It's not just databases and computers SQL, In the computer world, hard disk is also the bottleneck of performance , That is to say File system access ( So by increasing memory , Or use faster access to the hard disk and other methods to improve performance )
Whether it's reducing sorting or using indexes , Or avoid the use of temporary tables , Its essence is to reduce the access to the hard disk !
Four Why are Gaussian database features excellent
First Can release CPU Multi core computing resources
as everyone knows , On the one hand, the improvement of software computing power benefits from CPU Enhancement of hardware capability , On the other hand, it also benefits from the full use of CPU Computing resources for . At present, multi-core design is widely used in processors ,GaussDB(for MySQL) A single node can support up to 64 Nuclear CPU. Single thread query can use up to one core CPU resources , Limited performance improvement , It is far from meeting the requirements of reducing delay in the scenario of large data query of enterprises . therefore , The complex query analysis calculation process must consider making full use of CPU Multi core computing resources , Only by involving multiple cores in parallel computing tasks can the processing efficiency of query computing be greatly improved ;

The figure below shows the use of CPU Parallel computing of a table with multi-core resources count() Examples of processes : The table data is segmented and distributed to multiple cores for parallel computing ,** Each core calculates part of the data to get an intermediate count() result **, In the final stage, all intermediate results are aggregated to obtain the final result 
- And then there was Parallel queries
GaussDB(for MySQL) Support the query mode of parallel execution , It is used to reduce the processing time of analytical query scenarios , Meet the requirements of enterprise applications for low query delay . As described above , The basic implementation principle of parallel query is to Query tasks are segmented and distributed to multiple CPU Calculate on the core , make the best of CPU Multi core computing resources to shorten query time . Performance improvement of parallel queries , In theory and CPU There is a positive correlation between the number of kernels , That is, the higher the degree of parallelism, the more it can be used CPU The more cores , The higher the multiple of performance improvement ;
The picture below shows : stay GaussDB(for MySQL) Of 64U Query on instance 100G Data quantity COUNT(*) Query time consuming , Different query concurrency degrees correspond to different time consumption , The higher the concurrency, the shorter the query time 
It supports many types of parallel query operators , To meet different complex query scenarios of customers . Current latest version (2021-9) The supported parallel query scenarios include :
Primary key query 、 Secondary index query
Primary key scanning 、 An index scan 、 Range scan 、 Index equivalent query , Index reverse query
Parallel conditional filtering (where/having)、 Projection calculation
Parallel multi table JOIN( Include HashJoin、NestLoopJoin、SemiJoin etc. ) Inquire about
Parallel aggregate function operation , Include SUM/AVG/COUNT/BIT_AND/BIT_OR/BIT_XOR etc.
Parallel expression operation , Including arithmetic operations 、 Logical operations 、 General function operation and mixed operation, etc
Parallel grouping group by、 Sort order by、limit/offset、distinct operation
parallel UNION、 Subquery 、 View query
Parallel partition table query
The data types supported by parallel queries include : integer 、 Character 、 Time type 、 Floating point and so on
Other inquiries
The picture below is GaussDB(for MySQL) Parallel queries are for TPC-H Of 22 Performance test results of query scenarios , The amount of test data is 100G, Concurrent thread data is 32. The following figure shows how parallel queries compare to traditional queries MySQL Single thread Query performance improvement :32 Execute in parallel , Single table complex query has the highest improvement 26 Multiple performance , General promotion 20+ Multiple performance . Multiple tables JOIN The highest improvement of complex query is nearly 27 Multiple performance , General promotion 10+ Multiple performance , The sub query performance has also been greatly improved ;
To make a long story short
GaussDB(for MySQL) Parallel queries fully invoke CPU Multi core computing resources , It greatly reduces the processing time of analytical query scenarios , Greatly improve the database performance , It can well meet the low latency requirements of customers in a variety of complex query scenarios ;This article participates in Huawei cloud community 【 Content co creation 】 Activity number 18 period
https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/364560Mission 31: Use SQL What magical things have you encountered in the past 「 characteristic 」?
边栏推荐
- Drools(1):Drools简介
- 【力扣】三数之和
- LyScriptTools 扩展Script模块
- AB team score flow chart, get the names of the players who score three consecutive times and the names of the players who catch up with and surpass the opponents each time (PDD)
- Parity rearrangement of Bm14 linked list
- MongoDB-查询语句中逻辑运算符not、and、or、nor用法介绍
- NLP领域历史最全必读经典论文分类整理分享(附中文解析)
- OpenLayers官方实例全集
- 使用高德地图JS API 2.0加载起点终点路径轨迹
- 种树最好的是现在
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
考研 | 高等数学 Chapter4 不定积分
QT 设置缓存和编译输出路径
AB team score flow chart, get the names of the players who score three consecutive times and the names of the players who catch up with and surpass the opponents each time (PDD)
【Kernel】驱动开发学习之Platform平台总线模型
源启数字化:既有模式,还是开源创新?|砺夏行动
OpenLayers实例-Advanced Mapbox Vector Tiles-高级Mapbox矢量贴图
信号的理解
CDR插件开发之Addon插件003 - 认识解决方案(sln)和项目(csproj)文件
关于网段CIDR的笔记
Flink Catalog解读
EXCEL的密码相关
ssm+mysql实现零食商城系统(电商购物)
Parity rearrangement of Bm14 linked list
MySQL(3)
MySQL's past and present life, Hello, MySQL
Solve the problem that the user clicks quickly and repeats the request within 1 second
[force deduction] sum of three numbers
不用MQTT C库就能实现MQTT连接、订阅和发布
How to solve the problem that the solid state disk cannot be found when installing win11?
If the order is not paid within 30 minutes, it will be automatically cancelled