当前位置:网站首页>Data backup and recovery of PgSQL
Data backup and recovery of PgSQL
2022-06-24 19:32:00 【Jade label】
cd /opt/opsmgr/web/components/postgresql96linux64.1/bin
Enter the corresponding pg Database bin Under the table of contents :
Perform backup operations
./pg_dump -U postgres -d hosp_xxx > /home/backup/hosp_xxx.sql
Perform recovery operations
/psql -U postgres -d hosp_xxx < /home/backup/hosp_xxx.sql
Of course, other parameters can also be added
Perform backup operations
./pg_dump -h 10.19.125.197 -p 7017 -U nms_nmsdb_user -d nms_nmsdb > /home/backup/nms_nmsdb.sql
Perform recovery operations
./psql -h 10.19.125.197 -p 7017 -U nms_nmsdb_user -d nms_nmsdb < /home/backup/nms_nmsdb.sql
Other parameters can be referred to :
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_e964c8bd0102vb3n.html
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_8840603d0102wku9.html
stay linux in Postgresql How the database executes script files
(2016-07-08 10:43:51)
![]() Reprint ▼
Reprint ▼
label : itlinuxpostgrespostgresql | classification : postgresql |
stay linux in Postgresql How to restore the database ? perform sql Script files ? The specific steps are as follows :
One 、 Restore database backup files
1、 Backup the database to a file xxx.backup Use the connection tool to copy to /opt Next , This is not fixed , Place at random ;
2、 stay linux Open the terminal , Switch to postgres user , The order is
su - postgres ( establish postgresql The user created when the database ),
then cd To your installation postgresql Of bin Under the table of contents , My installation is in /opt Next , The order is
cd /opt/postgres/9.3/bin
Enter the command after opening
./psql
Enter your database password , Get into postgres database ;
3、 Create your database first , command
create database xxx;
4、 And then to xxx Database recovery database backup file , The order is
./pg_restore -U postgres -W -d xxx( Your database ) -v "/opt/xxx.backup"( Your backup file location )
Two 、 stay postgres In the implementation of sql Script files
1、 stay linux Open the terminal , Switch to postgres user , then cd To your installation postgresql Of bin Under the table of contents ( ditto ),
cd /opt/postgres/9.3/bin
2、 Put your xxx.sql Copy the document to /opt/ Next , Then execute the following commands
./psql -s xxx(xxx Is the database you want to execute ) -f /opt/xxx.sql
3、 ... and 、 Under the science
1、 Database backup , The order is as follows :
./pg_dump -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres -W -F c -b -v -f "/opt/xxx.backup" xxx
2. In the database installation directory bin Next ,./psql Access to database , Input password ,\c xxx( Database name ) Enter the specified database
\i File path
pgsql Command web site
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_e964c8bd0102vb3n.html
advertisement
× Sina home page login registration
v Killers v The blog of
http://blog.sina.com.cn/chenjunweibk [ subscribe ][ Mobile subscription ]
Home page blog directory about me
The personal data
v Killers v
v Killers v
Microblogging
Add a friend to send a note
Write a message and pay attention
Blog 10th anniversary map
Blog level :
Blog points :27 integral
Blog visit :8,054
Focus on popularity :0
Complimentary gold pen :0
Give a golden pen :0
The badge of honor : Light up the medal of honor, exchange pictures, exchange blogger services, exchange private blog articles, exchange gold pens
Related blogs
The makeup is light and transparent , The skin seems to breathe , The secret of Korean super clean oxygen base makeup !
Charactizing a fine spring
borrow arrows with thatched boats , Why doesn't Cao Cao launch a rocket ?
Know history
High blood pressure “ In the early ” Just as dangerous
Yejin Dynasty
All the original “ Keeping in good health ” It's all in vain ! After reading it, I won't worry about it
Kan Zhaocheng
Suning 6.18 Promotion challenges JD to lower the price 10% Behind it is the release of retail ecological value
Jiajinghua
Jurong City is full of hot flowers
Galloping photography
Hong Quan Zhang : A letter let me see the pattern of secretaries in Qingdao and Dongying
Hong Quan Zhang
Xiao Zhan's backup club was renamed : Xiao Zhan Video Conference , Deliver positive energy through practical actions !
Floating rain Tung
【 To film 】 Walk into “ The most beautiful bookstore in Beijing ”, The reading space is like a dreamland
Beauty travels all over the world
Last week's hot spots soared, and tomorrow's point of view still depends on me
Fengyun online 66
more >>
Recommend Bo Wen
To view more >>
Text font size : Big in Small
PostgreSQL Database backup and restore commands (2014-11-10 16:30:10)
label : it
7、 ... and 、pg_dump:
pg_dump Is a backup PostgreSQL Database tools . It can even perform a full and consistent backup while the database is being used concurrently , Without blocking other users' access to the database . The dump format generated by the tool can be divided into two types , Scripts and archive files . The script format contains many SQL The plain text format of the command , these SQL The command can be used to rebuild the database and restore it to the state it was in when the script was generated , This operation requires the use of psql To complete . As for the filing format , If you need to rebuild the database, you must work with pg_restore Use tools together . In the reconstruction process , You can select the recovered objects , You can even reorder the items that need to be restored before restoring . This command is used as follows :
pg_dump [option...] [dbname]
1. Select... From the command line
Options explain
-a(--data-only) Just output data , No output mode ( Definition of data object ). This option only makes sense for plain text formatting . For archive format , You can call pg_restore Specify options when .
-b(--blobs) stay dump Contains large objects .
-c(--clean) Create a database object in the output SQL Before the command , First, output the... To delete the database object SQL command . This option only makes sense for plain text formatting . For archive format , You can call pg_restore Specify options when .
-C(--create) First, output the command to create the database , Then reconnect to the newly created database . For scripts in this format , It doesn't matter which database you are connected to before running . This option only makes sense for plain text formatting . For archive format , You can call pg_restore Specify options when .
-E encoding Create the... With the specified character set dump file .
-f file Output to specified file , If there is no such option , Then output to standard output .
-F format
p(plain): Plain text format SQL Script files ( default ).c(custom): The output is suitable for pg_restore Custom archive format for . This is the most flexible format , It allows for rearrangement of loaded data and object definitions . This format is compressed by default .t(tar): The output is suitable for pg_restore Of tar The archive . Using this archive allows you to reorder and / Or exclude database objects . Same as i It may also be possible to limit which data can be recovered during recovery .
-n schema Dump only schema The content of . If this option is not declared , All non system schemas in the target database are dumped . This option can also be specified more than once , To specify different pattern The pattern of .
-N schema Do not dump matches schema The content of , Other rules and -n Agreement .
-o(--oids) As part of the data , Output object IDs for each table (OID).
-O(--no-owner) Do not output the setting object ownership SQL command .
-s(--schema-only) Only output object definitions ( Pattern ), Don't output data .
-S username Specify the superuser name to use when closing the trigger . It's only in use --disable-triggers It only matters when .
-t table Only output the data of the table . It is possible that there are multiple tables with the same name in different modes , If so , Then all matching tables will be dumped . By specifying this parameter more than once , You can dump multiple tables at once . You can also specify and psql Same pattern, To match more tables .( About pattern, The basic way to use it is to think of it as unix The wildcard , namely * For any character ,? Represents any single character ,.(dot) Express schema and object Separator between , Such as a*.b*, Said to a At the beginning schema And with b Database object at the beginning . without .(dot), Will simply represent the database object . Basic regular expressions can also be used here , Such as [0-9] Representation number .)
-T table Exclude the specified table , Other rules and -t Consistent options .
-x(--no-privileges) Do not export access information (grant/revoke command ).
-Z 0..9 Declare the compression level used in formats that support compression . ( Currently, only custom formats support compression )
--column-inserts Export data with insert into table_name(columns_list) values(values_list) The command says , This operation is slower than other operations , But in special cases , For example, the position of data table fields may change or new fields may be inserted into the middle of the original field list . because columns_list Be specified as , Therefore, the data will not be imported into the wrong field during import .
--inserts The exported data is in insert The command says , instead of copy command . Even with insert than copy Slow down , But for future import to other non PostgreSQL The database of is more meaningful .
--no-tablespaces Do not output the command to set the table space , With this option , All objects will be restored to execution pg_restore In the default table space .
--no-unlogged-table-data For not included in the log (unlogged) Data sheet for , Its data will not be exported , As for whether to export its Schema Information , Depending on other options .
-h(--host=host) Appoint PostgreSQL The hostname of the server .
-p(--port=port) Specify the listening port of the server , If not specified , Is the default 5432.
-U(--username=username) Login user name for this operation , If -O Option not specified , Of this database Owner Will be the logged in user .
-w(--no-password) If the currently logged in user does not have a password , You can specify this option to log in directly .
2. Application example :
# -h: PostgreSQL The host of the server is 192.168.149.137.
# -U: Login user is postgres.
# -t: Export table names to test The data table at the beginning , Such as testtable.
# -a: Just export data , Do not export objects schema Information .
# -f: The output file is in the current directory my_dump.sql
# mydatabase Is the target database for this operation .
/> pg_dump -h 192.168.149.137 -U postgres -t test* -a -f ./my_dump.sql mydatabase
#-c: First output the delete database object SQL command , Create a database object in the output SQL command , This is very convenient for deploying a clean initial system or building a test environment .
/> pg_dump -h 192.168.220.136 -U postgres -c -f ./my_dump.sql mydatabase
# export mydatabase Database information . Through psql You can specify the database again when importing with the command , Such as :/> psql -d newdb -f my_dump.sql
/> pg_dump -h 192.168.220.136 -U postgres -f ./my_dump.sql mydatabase
# The export mode is my_schema And with test Database object name starting with , But not including my_schema.employee_log object .
/> pg_dump -t 'my_schema.test*' -T my_schema.employee_log mydatabase > my_dump.sql
# export east and west All database objects in the schema . The following two commands are equivalent , Only the latter uses regular .
/> pg_dump -n 'east' -n 'west' mydatabase -f my_dump.sql
/> pg_dump -n '(east|west)' mydatabase -f my_dump.sql
8、 ... and 、pg_restore:
pg_restore Used to recover pg_dump Any file exported that is not in plain text format , It rebuilds the database to the state it was in when it was saved . For files in archive format ,pg_restore Selective recovery is possible , You can even reorder the data before recovery .
pg_restore It can be operated in two modes . If you specify a database , The archive will be restored directly to the database . otherwise , You must create the database manually first , After that pg_restore Restore data to the newly created database . This command is used as follows :
pg_restore [option...] [filename]
1. List of command line options :
Options explain
filename Specify the backup file to restore , If there is no statement , Use standard input .
-a(--data-only) Only recover data , Without restoring the table schema ( Data object definition ).
-c(--clean) Clean up before creating database objects ( Delete ) they .
-C(--create) Create the database before restoring it .( When using this option , The database name needs to be specified by -d Option assignment , This option only performs the most basic CREATE DATABASE command . It should be noted that , All data in the archive file will be restored to the database specified in the archive file ).
-d dbname With the database dbname Establish a connection and restore data directly to the database .
-e(--exit-on-error)
If you are sending to the database SQL An error was encountered while commanding , The exit . The default is to continue execution and display an error count at the end of the recovery .
-F format Specify the format of the backup file . because pg_restore The format will be determined automatically , Therefore, it is not necessary to specify the format . If specified , It can be one of the following formats :t(tar): Use this format to allow reordering and / Or exclude the table schema information , It is also possible to limit mounted data during recovery . c(custom): The format is from pg_dump Custom format for . This is the most flexible format , Because it allows you to reorder the data , Table schema information can also be overloaded , By default, this format is compressed .
-I index Restore only the specified index .
-l(--list) List the contents of the backup , The output of this operation can be used as -L Input of options . Be careful , If the filter option -n or -t together with -l Options , They will also limit the items listed .
-L list-file Restore only at list-file The entries listed in , The order of recovery is the order in which the entries appear in the file , You can also edit the file manually , And rearrange the positions of these entries , And then the recovery operation , With semicolon (;) The opening behavior comment line , Comment lines are not imported .
-n namespace Restore only the specified mode (Schema) Database objects for . This option can be used with -t Option combination , To restore the specified data object .
-O(--no-owner) Do not output the setting object ownership SQL command .
-P function-name(argtype [, ...])
Restore only the specified named function . The name should be exactly the same as in the dumped content list .
-s(--schema-only) Only restore the table structure ( Data definition ). Do not recover data , The sequence value will be reset .
-S username Specify the superuser name to use when closing the trigger . It's only in use --disable-triggers It only matters when .
-t table Restore only the specified table Schema and / Or data , This option can also be used in conjunction with -n Option specifies the mode .
-x(--no-privileges) Do not restore access information (grant/revoke command ).
-1(--single-transaction) Execute the restore command in a single thing . This option implicitly includes --exit-on-error Options .
--no-tablespaces Do not output the command to set the table space , With this option , All objects will be restored to execution pg_restore In the default table space .
--no-data-for-failed-tables By default , Even if the table creation fails , If the table already exists , The data loading operation will not stop , As a result, it is easy to insert a large amount of duplicate data into the table . With this option , So if there is any error for this table , Loading this data table will be ignored .
--role=rolename Execute with the specified role name restore The operation of . generally , If the connection role does not have sufficient permissions for this recovery operation , Then you can use this option to switch to a role with sufficient permissions after establishing a connection .
-h(--host=host) Appoint PostgreSQL The hostname of the server .
-p(--port=port) Specify the listening port of the server , If not specified , Is the default 5432.
-U(--username=username) Login user name for this operation , If -O Option not specified , Of this database Owner Will be the logged in user .
-w(--no-password) If the currently logged in user does not have a password , You can specify this option to log in directly .
2. Application example :
# Through the first createdb command , With myuser Login as user , Create data with recovery newdb
/> createdb -U myuser newdb
# use pg_restore Ordered -l Options export my_dump.dat A detailed list of exported database objects in the backup file .
/> pg_restore -l my_dump.dat > db.list
/> cat db.list
2; 145344 TABLE species postgres
4; 145359 TABLE nt_header postgres
6; 145402 TABLE species_records postgres
8; 145416 TABLE ss_old postgres
10; 145433 TABLE map_resolutions postgres
# Change the contents in the above list file to the following form .
# The main modification is to note out the number 2、4 and 8 Three database objects of , Number at the same time 10 The object is placed in the header of the file , This is based on the list
# On file import ,2、4 and 8 Wait three objects will not be imported , In the process of recovery, you will first import the number 10 Data of the object , Then import the object 6 The data of .
/> cat new_db.list
10; 145433 TABLE map_resolutions postgres
;2; 145344 TABLE species postgres
;4; 145359 TABLE nt_header postgres
6; 145402 TABLE species_records postgres
;8; 145416 TABLE ss_old postgres
# The database specified during recovery is newdb, Which database objects will be imported and the import order will follow new_db.list The rules prompted in the file are imported .
/> pg_restore -d newdb -L new_db.list my_dump.dat
Nine 、psql:
PostgreSQL The interactive terminal , Equate to Oracle Medium sqlplus.
1. List of common command line options :
Options explain
-c command Appoint psql To perform a SQL command command( Enclose in double quotation marks ), Exit after execution .
-d dbname Name of the database to be connected .
-E Echo by \d And other backslash commands .
-f filename Use filename The data in the file is used as the command input source , Instead of interactively reading in queries . After processing the file ,psql End and exit .
-h hostname Declare the hostname of the running server
-l List all available databases , And then quit .
-L filename In addition to the normal output source , Output all query records to a file filename.
-o filename Redirect all queries to a file filename.
-p port Appoint PostgreSQL The listening port of the server .
-q --quiet Give Way psql Quietly perform the task being handled . By default psql Will print out the welcome and many other messages .
-t --tuples-only Turn off printing information such as column names and result row count footnotes .
-U username To the user username Connect to the database instead of the default user .
2. Examples of command line options :
#-d: Specify the database to connect to .
#-U: Specify the users of the connection .
#-c: hinder SQL Statement is the command to be executed for this operation .
/> psql -d posgres -U postgres -c "select * from testtable"
i
---
1
2
3
5
(4 rows)
#-t: The field title information and row count statistics in the above output results are not output .
#-q: The option and -t Option combination , It is very helpful to automate scripts . Such as :
# select 'copy ' || tablename || ' to ' || tablename || '.sql' from pg_tables
# From the above sql Statement , After redirecting to the output file , As the next time psql Input execution of .
/> psql -t -q -c "select * from testtable"
1
2
3
5
#-l: Lists the databases available in the current system .
/> psql -l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collation | Ctype | Access privileges
------------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
mydatabase | myuser | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
... ...
(4 rows)
#-o: Output the data result of the query statement to the specified file .
/> psql -c "select * from testtable" -o out
/> cat out
i
---
1
2
3
5
(4 rows)
3. Built in command list :
psql The format of the built-in command is a backslash followed by a command verb , Then there are arbitrary parameters . Parameters can be separated from command verbs and other parameters with a white space , If the parameter contains a blank character , The parameter must be enclosed in single quotation marks , If the parameter contains single quotation marks , You need to escape with a backslash , In addition, parameters within single quotation marks also support similar C Language printf Escape keywords supported by function , Such as \t、\n etc. .
command explain
\a If the current table output format is misaligned , Switch to aligned . If it is aligned , Switch to out of alignment .
\cd [directory] Switch the current working directory to directory. If there are no parameters, switch to the home directory of the current user .
\C [title] Add headers to query results (title), If there are no parameters, the current header will be canceled .
\c [dbname [ username] ] Connect to a new database , Also disconnect the current connection . If dbname Parameter is -, Indicates that the current database is still connected . If you ignore username, It means to continue to use the current user name .
\copy Its parameters are similar to SQL copy, The function is almost equal to SQL copy, An important difference is that the built-in command can export the contents of the table locally , Or import from the local database to the specified table , and SQL copy Export the data in the table to a file on the server , Or import from the server file to the data table . thus it can be seen ,SQL copy Is more efficient than the built-in command .
\d [pattern] Display and pattern Matching database objects , As shown in the table 、 View 、 Index or sequence . Show all columns , Their types , Table space ( If not the default ) And any special attributes .
\db [pattern] List all available tablespaces . If declared pattern, Then only those tablespaces that match the schema are displayed .
\db+ [pattern] Compared with the previous command , The permission information of each table space will also be added .
\df [pattern] List all available functions , And their parameters and returned data types . If declared pattern, Then only the matches are displayed ( Regular expressions ) Function of .
\df+ [pattern] Compared with the previous command , Additional information will be added to show each function , Including language and description .
\distvS [pattern] This is not a single command name : Letter i、s、t、v、S Each represents an index (index)、 Sequence (sequence)、 surface (table)、 View (view) And system tables (system table). You can declare some or all of these letters in any order to get a list of these objects .
\dn [pattern] List all available modes . If declared pattern, Then only the schema name of the matching schema is listed .
\dn+ [pattern] Compared with the previous command , It also adds permissions and comments to display each object .
\dp [pattern] Generate a list of available tables and their associated permissions . If declared pattern, Then list only the tables whose names match the patterns .
\dT [pattern] List all data types or show only those that match pattern Of .
\du [pattern] List all configured users or only those that match pattern Users of .
\echo text [ ... ] Print parameters to standard output , Separated by a space and followed by a new line . Such as :\echo `date`
\g [{filename | |command}] Send the contents of the current query result buffer to the server and store the output of the query in an optional filename Or direct the output to a separate execution command Of Unix shell.
\i filename From file filename And execute the query as if it were entered from the keyboard .
\l List the names of all databases on the server, their owners, and character set codes .
\o [{filename | |command}] Save the following query results to a file filename Or direct the following query results to an independent shell command.
\p Print the current query buffer to standard output .
\q sign out psql Program .
\r Reset ( Empty ) Query buffer .
\s [filename] Print out or save the command line history to filename. If omitted filename, History will be output to standard output .
\t Toggles whether to output columns / Header of field name and footnote of row count .
\w {filename | |command} Output the current query buffer to a file filename Or directed to Unix command command.
\z [pattern] Generate a list of all the tables in the database with access rights , List of views and sequences . If any pattern, Is treated as a regular expression , Show only matching tables , Views and sequences .
\! [command] Return to a separate Unix shell Or perform Unix command command. Parameters will not be further interpreted ,shell You will see all the parameters .
4. Application examples of built-in commands :
stay psql in , Most of the built-in commands are easy to understand , So here are just a few commands that I personally think are relatively confusing .
# \c: The horizontal line (-) Indicates that the current database is still connected ,myuser Is a new user name .
postgres=# \c - myuser
Password for user myuser:
postgres=> SELECT user;
current_user
--------------
myuser
(1 row)
# Carry out arbitrary SQL sentence .
postgres=# SELECT * FROM testtable WHERE i = 2;
i
---
2
(1 row)
# \g The command will change the previous SQL The result of the command is output to the specified file .
postgres=# \g my_file_for_command_g
postgres=# \! cat my_file_for_command_g
i
---
2
(1 row)
# \g The command will change the previous SQL The results of the command are piped to the specified Shell command , Such as cat.
postgres=# \g | cat
i
---
2
(1 row)
# \p Print the previous SQL command .
postgres=# \p
SELECT * FROM testtable WHERE i = 2;
# \w Put the previous SQL Command output to the specified file .
postgres=# \w my_file_for_option_w
postgres=# \! cat my_file_for_option_w
SELECT * FROM testtable WHERE i = 2;
# \o and \g contrary , This command will be followed by psql The output result of the command is output to the specified file , Until the next independent \o,
# Subsequent command results will no longer be output to this file .
postgres=# \o my_file_for_option_o
postgres=# SELECT * FROM testtable WHERE i = 1;
# The result of terminating the following command is also output to my_file_for_option_o In file .
postgres=# \o
postgres=# \! cat my_file_for_option_o
i
---
1
(1 row)
Enter the following command
./psql -d postgres -U postgres -c "select * from cmdb_resource_index"
Prompt error :
psql: could not connect to server: No such file or directory
Is the server running locally and accepting
connections on Unix domain socket "/tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432"?
The reason is port and ip Is not specified , Use the default port and ip(5432 and localhost) As a result of ,
So the solution is as follows , add ip And port number :
./psql -d nms_nmsdb -U postgres -h 10.19.125.197 -p 7017 -c "select * from cmdb_static_bigData"
The relevant useful links are :
https://www.cnblogs.com/louissica/p/10827113.html
Problem description
I installed a package that contains PostgreSQL 8.4 Of Bitnami Django stack.
When I run psql -U postgres when , I received the following error :
psql: could not connect to server: No such file or directory
Is the server running locally and accepting
connections on Unix domain socket "/var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432"?
PG It must be running ,pg_hba.conf The file is shown below :
# TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all md5
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 md5
What gives ?
pg Running ”Proof”:
[email protected]:/home/assaf# ps axf | grep postgres
14338 ? S 0:00 /opt/djangostack-1.3-0/postgresql/bin/postgres -D /opt/djangostack-1.3-0/postgresql/data -p 5432
14347 ? Ss 0:00 \_ postgres: writer process
14348 ? Ss 0:00 \_ postgres: wal writer process
14349 ? Ss 0:00 \_ postgres: autovacuum launcher process
14350 ? Ss 0:00 \_ postgres: stats collector process
15139 pts/1 S+ 0:00 \_ grep --color=auto postgres
[email protected]:/home/assaf# netstat -nltp | grep 5432
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:5432 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 14338/postgres
tcp6 0 0 ::1:5432 :::* LISTEN 14338/postgres
[email protected]:/home/assaf# The best solution
This problem comes from installing a version number that does not exist postgres software package . Although... Will be installed postgres And it will be the correct version , But the script for setting up the cluster will not run correctly ; This is a packing problem .
If you are right about postgres Be satisfied with , You can run a script to create this cluster and run postgres. however , There is a simpler way .
First remove the old postgres install . The problem now is 9.1, So I assume you have installed
sudo apt-get remove --purge postgresql-9.1
Now just reinstall
sudo apt-get install postgresql-9.1
Note the package name and version number . HTH.
Second best solution
The error message means Unix-domain Socket , So you need to adjust netstat Call to not exclude them . So there is no option -t Try :
netstat -nlp | grep 5432
I guess the server is actually listening on sockets /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432 Instead of the client trying to connect /var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432. This is Debian or Ubuntu Upper use hand-compiled or third-party PostgreSQL Typical problems with software packages , because Unix-domain The source default value of the socket directory is /tmp, but Debian Package and change it to /var/run/postgresql.
Possible solutions :
Use third-party The client provided by the software package ( Call
/opt/djangostack-1.3-0/postgresql/bin/psql). May be uninstalled completely Ubuntu-supplied software package ( Due to other reverse dependencies , It can be difficult to ).Repair third-party The socket directory of the package is linked to Debian /Ubuntu compatible .
Use
-H localhostadopt TCP /IP Connect .Use
-h /tmpOr equivalentPGHOSTSet to point to the correct directory .Do not use third-party package .
The third solution
You can use psql -U postgres -h localhost To force through TCP instead of UNIX Domain socket connection ; Your netstat The output shows PostgreSQL The server is listening localhost The port of 5432.
You can use different netstat Call to find PostgrSQL Local used by the server UNIX Socket :
netstat -lp --protocol=unix | grep postgres
in any case ,PostgreSQL The interfaces that the server listens to are postgresql.conf Middle configuration .
The fourth option
Just create a soft link like this :
ln -s /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432 /var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432
The fifth option
It works for me :
edit :postgresql.conf
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/9.3/main/postgresql.conf
Enable or add :
listen_addresses = '*'
Restart the database engine :
sudo service postgresql restart
Besides , You can check the file pg_hba.conf
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/9.3/main/pg_hba.conf
And add your network or host address :
host all all 192.168.1.0/24 md5
The sixth scheme
I have to be in Debian Squeeze Compiled on PostgreSQL 8.1, Because I use Project Open, It's based on OpenACS, Will not be updated in the version of PostgreSQL Up operation .
The default compilation configuration will unix_socket Put it in /tmp in , But depends on PostgreSQL Of Project Open Will not work , Because it is in /var/run/postgresql Search for unix_socket.
postgresql.conf There is a setting in to set the socket location . My question is , I can set /tmp and psql Work , But not the project open , Or I can set it to /var/run/postgresql and psql It doesn't work , But the project opens .
One solution to this problem is to /var/run/postgresql Set socket , And then according to Peter The recommended operation of psql, As shown below :
psql -h /var/run/postgresql
This runs locally with local permissions . The only drawback is that it is simpler than ”psql” Type more .
Another suggestion put forward by someone is to establish a symbolic link between two sites . It also works , But the link disappeared after the reboot . Use -h Parameters may be easier , however , I am here /etc/init.d Medium PostgreSQL A symbolic link is created in the script . I am here ”start” Partially placed symbolic link create command . Of course , When I issue a stop and start or restart command , It will try to recreate an existing symbolic link , But in addition to the warning messages , There may be no damage .
As far as I'm concerned , instead of :
ln -s /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432 /var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432
I have a
ln -s /var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432 /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432
And in postgresql.conf Zhongming definitely will unix_socket Set to /var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432.
The seventh option
I make it work by doing this :
dpkg-reconfigure locales
Select your preferred locale and run
pg_createcluster 9.5 main --start
(9.5 It is my postgresql edition )
/etc/init.d/postgresql start
And how it works !
sudo su - postgres
psql
The eighth scheme
Explain :
Do this
export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"
And this one. . (9.3 It is my present PostgreSQL edition . Write down your version !)
sudo pg_createcluster 9.3 main --start
The ninth option
In my case , It was edited by me /etc/postgresql/9.5/main/pg_hba.conf Caused by the spelling of the input
I have changed :
# Database administrative login by Unix domain socket
local all postgres peer
to :
# Database administrative login by Unix domain socket
local all postgres MD5
however MD5 Must be lowercase md5:
# Database administrative login by Unix domain socket
local all postgres md5
The tenth option
I use postgres-9.5 The server cannot solve this problem . after 3 Days of zero progress trying every fix on this and other sites , I decided re-install The server , And lost 5 Day's work . however , I did replicate this problem on the new instance . This may provide some ideas on how to solve it , And then take the disastrous approach that I did .
First , Ban postgresql.conf All logging settings in . This is part of :
# ERROR REPORTING AND LOGGING
Comment on everything in this section . Then restart the service .
On reboot , Use /etc/init.d/postgresql start or restart I find it helpful to be in super user mode when rebooting . I opened a x-window For this operation . You can use sudo -i Establish super user mode .
Use the following simple command to verify that you can access the server :psql -l -U postgres
If this doesn't solve the problem , Please consider the following :
When trying to find a solution , I am changing the ownership of many folders . I know I might try to put these folders under ownership and chmod Restore 2 God . If you have confused the ownership of these folders and do not want to completely clean up the server , Then please start tracking the settings of all affected folders , To restore it to its original state . You may want to try a parallel installation on another system , And systematically check the ownership and settings of all folders . Monotonous , But you can access your data .
After getting access , Systematically change postgresql.conf Of documents #ERROR REPORTING AND LOGGING Each relevant line in the section . Restart and test . I found that the default folder of logs caused a failure . I specially commented on log_directory. The default folder for deleting logs is /var /log /postgresql.
Reference material
[email protected]:/home/assaf# ps axf | grep postgres14338 ? S 0:00 /opt/djangostack-1.3-0/postgresql/bin/postgres -D /opt/djangostack-1.3-0/postgresql/data -p 543214347 ? Ss 0:00 \_postgres: writer process 14348 ? Ss 0:00 \_postgres: wal writer process 14349 ? Ss 0:00 \_postgres: autovacuum launcher process 14350 ? Ss 0:00 \_postgres: stats collector process 15139 pts/1 S+ 0:00 \_ grep --color=auto postgres [email protected]:/home/assaf# netstat -nltp | grep 5432 tcp 00127.0.0.1:54320.0.0.0:* LISTEN 14338/postgres tcp6 00::1:5432:::* LISTEN 14338/postgres [email protected]:/home/assaf#
边栏推荐
- TKDE2022:基于知识增强采样的对话推荐系统
- The script implements the automated deployment of raid0
- Starring V6 platform development take out point process
- 怎么使用R包ggtreeExtra绘制进化树
- Preliminary study nuxt3
- NFT双币质押流动性挖矿系统开发
- 西北工业大学遭黑客攻击?双因素认证改变局面!
- Pingcap was selected as the "voice of customers" of Gartner cloud database in 2022, and won the highest score of "outstanding performer"
- Programmers spend most of their time not writing code, but...
- [R tidyverse] use of select verb
猜你喜欢

php OSS文件读取和写入文件,workerman生成临时文件并输出浏览器下载

How do programmers do we media?

Game between apifox and other interface development tools

Power efficiency test

Interprétation de la thèse (SR - gnn) Shift Robust GNNS: Overcoming the Limits of Localized Graph Training Data
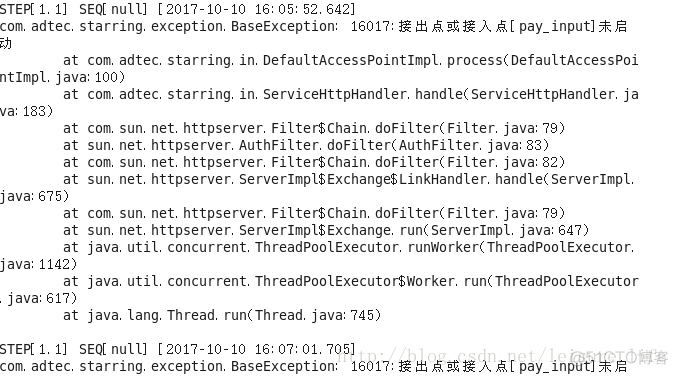
starring开发HttpJson接入点+数据库

Sr-gnn shift robot gnns: overlapping the limitations of localized graph training data

华为机器学习服务语音识别功能,让应用绘“声”绘色

The sharp sword of API management -- eolink

Vs2017 add header file path method
随机推荐
flink-sql的kafka的这个设置,group-offsets,如果指定的groupid没有提
多云模式并非“万能钥匙”
Application DDoS attack principle and defense method
Several ways of connecting upper computer and MES
企业网络管理员必备的故障处理系统
Volcano成Spark默认batch调度器
华为机器学习服务语音识别功能,让应用绘“声”绘色
实时渲染:实时、离线、云渲染、混合渲染的区别
Will the CDC read out of order when I use SQL
NFT质押流动性挖矿系统开发技术
程序员大部分时间不是写代码,而是。。。
【Go语言刷题篇】Go从0到入门4:切片的高级用法、初级复习与Map入门学习
How to use JWT authentication in thinkphp6
Technology implementation | Apache Doris cold and hot data storage (I)
R语言corrplot相关热图美化实例分析
What do I mean when I link Mysql to report this error?
Necessary fault handling system for enterprise network administrator
Xiaodi class massive data processing business short chain platform
Zadig + 洞态 IAST:让安全溶于持续交付
60 个神级 VS Code 插件!!