当前位置:网站首页>Introduction of neural network (BP) in Intelligent Computing
Introduction of neural network (BP) in Intelligent Computing
2022-06-22 20:25:00 【Foreign rookie】
Catalog
1. Reasons for the popularity of neural networks
2. Definition of artificial neural network
3. Learning ability of artificial neural network
4. The basic principle of artificial neural network
5. Research progress of neural networks
6. Typical structure of neural network
6.1 Single layer perceptron network
6.3 Feedforward inner interconnection network
7. Learning algorithm of neural network
1. Reasons for the popularity of neural networks
The reason why artificial neural networks are so popular , From the characteristics and advantages of artificial neural network , Mainly in the following three aspects :
(1) With self-learning function . for example , When realizing image recognition , Just input many different image templates and corresponding recognition results into the artificial neural network , The network will use the self-learning function , Learn to recognize similar images slowly . The self-learning function is particularly important for prediction , It is expected that the future artificial neural network computer will provide economic forecasts for mankind , market prediction , Benefit forecast , Its application prospect is very great .
(2) With associative storage function . This association can be realized by using the feedback network of artificial neural network .(3) It has the ability to find the optimal solution at high speed . Find the optimal solution of a complex problem , It often requires a lot of computation , Using a feedback artificial neural network designed for a certain problem , Give full play to the computer's high-speed computing ability , The optimization solution may be found soon .
2. Definition of artificial neural network
A mathematical model of artificial neural network simulating human brain and its activities , It consists of a large number of processing units (process element) Interconnected in an appropriate manner to form , It is a large-scale nonlinear adaptive system .1988 year ,Hecht-Nielsen The following definitions have been given to artificial neural networks :
“ Artificial neural network is a parallel network 、 Distributed processing structure , It consists of a processing unit and an undirected signal channel called a connection . These processing units have local memory , And can complete local operations . Each processing unit has a single output connection , This output can be branched into multiple parallel joins as needed , And these parallel connections all output the same signal , That is, the signal of the corresponding processing unit and its signal are too small to change with the number of branches . The output signal of the processing unit can be any desired mathematical model , The operations performed in each processing unit must be completely local . in other words , It must only depend on the current values of all input signals reaching the processing unit through the input connection and the values stored in the local range of the processing unit .”
This definition mainly emphasizes the following aspects of neural networks 4 All aspects :
(1) parallel 、 Distributed processing structure ;
(2) The output of a processing unit can be arbitrarily branched and of constant size ;
(3) The output signal can be any mathematical model ;
(4) Local operation of processing unit
The processing unit here is the artificial neuron (artificial neuron ,AN).
according to Rumellhart ,MeClelland , Hinton And so on (paralleldistributed processing ,PDP) Model , The artificial neural network consists of 8 It is composed of three elements :
(1) A set of processing units (PE or AN);
(2) Activation status of the processing unit (a);
(3) Output function of each processing unit (f);
(4) The connection mode between processing units ;
(5) Transfer rules ;
(6) An activation rule that combines the input of the processing unit with the current state to generate an activation value (F);
(7) Learning rules for modifying connection strength through experience ;
(8) The environment in which the system operates ( Sample set ).

1987 year .Simpson Starting from the topological structure of artificial neural network , The following definition is given, which is not too strict but concise :
“ Artificial neural network is a nonlinear directed graph . The graph contains weighted edges that can store patterns by changing the weight size , And you can find patterns from incomplete or unknown inputs .”
For general applications , Artificial neural networks can be called PDP outside , It can also be called an artificial nervous system (ANS)、 neural network (NN)、 Adaptive systems (adaptive systems)、 Adaptive network (adap-tive networks), Join model (connectionism) And neural computers (neuron computer) etc. .
The artificial neural network not only simulates the biological neural system in form , It does have some of the brain in two ways basic feature :
(1) Neurons and their connections . From the form of system composition , Because the artificial neural network is inspired by the biological neural system , From the neuron itself to the connection pattern , They basically work in a way similar to the biological nervous system . there AN And biological neurons (BN) Corresponding , Connections that can change strength correspond to synapses .
(2) Storage and processing of information . In terms of performance characteristics , Artificial neural network also tries to simulate the basic operation mode of biological neural system . for example , Through the corresponding learning / Training algorithm , Abstract the data relation contained in a large data set , Just like people can constantly explore the law , Sum up the experience , A general rule or framework can be found from the previous examples , And then generate new instances as required .
3. Learning ability of artificial neural network
Artificial neural network can change its behavior according to its environment . in other words , Artificial neural network can accept the sample set submitted by users , According to the algorithm given by the system , Constantly modify the strength of the connections between neurons used to determine the behavior of the system , And after the basic composition of the network is determined , This change is made naturally according to the set of samples it receives . Generally speaking , Users do not need to adjust the learning algorithm of the network according to the sample set they encounter , in other words , Artificial neural network has good learning function .
The neural network is in contrast to the learning problems of traditional artificial intelligence systems . In the research of traditional artificial intelligence system , Although people are not satisfied with “ machine learning ” Enough attention has been paid to the problem and great efforts have been put into it , however , The poor self-learning ability of the system is still the biggest obstacle to the wide application of these systems , The artificial neural network has a good learning function , It makes people have a great interest in it . This characteristic of artificial neural network is called “ Nature has a learning function ”.
In the learning process , The artificial neural network continuously extracts the basic information contained in the set from the accepted sample set , It is stored in the system in the form of connection weights between neurons . for example , For a pattern , A network can be trained with its data containing different noises , On the premise that these data are properly selected , When the network encounters similar data with certain defects in the future , You can still get the complete schema corresponding to it . This shows that , An artificial neural network can learn to produce patterns on demand that it has never encountered . This function of artificial neural network is called “ abstract ”.
4. The basic principle of artificial neural network
The structure of neurons is as follows :

There are biological neurons in biology , What is the relationship between biological neurons and artificial neurons ?
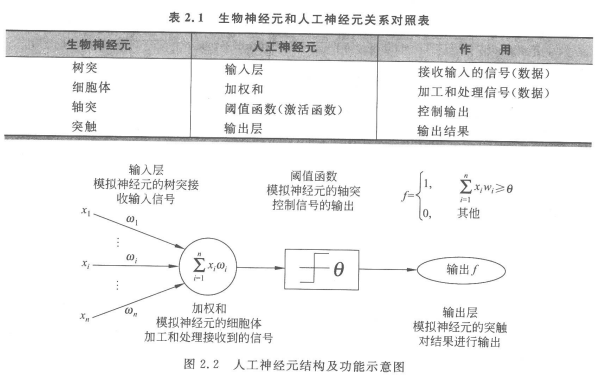
From the figure, we can get a rough idea of how artificial neurons imitate biological neurons to work :

5. Research progress of neural networks

6. Typical structure of neural network
There are many different models of artificial neural networks , You can usually press the following 5 Principles categorize .·
- According to the network structure , There are forward networks and feedback networks .
- Distinguish according to the learning style , There are supervised learning networks and unsupervised learning networks .
- Distinguish according to network performance , There are continuous and discrete networks , Stochastic and deterministic networks .· Distinguish according to synaptic properties , There are first-order linear correlation networks and higher-order nonlinear correlation networks .
- According to the hierarchical simulation of biological nervous system , There is a neural hierarchy model , Combined model ﹑ Network hierarchy model ﹑ Hierarchical model and intelligent model of nervous system .
6.1 Single layer perceptron network
The single-layer perceptron was first used , It is also the simplest neural network structure , It consists of one or more linear threshold units .

Because this network structure is relatively simple , Therefore, the ability is also very limited , Generally, it is less used .
6.2 Feedforward network
The signal of feedforward network is transmitted unidirectionally from input layer to output layer .
The neurons in each layer are only connected to the neurons in the previous layer , Only accept the information transmitted from the previous layer .
It is a widely used neural network model , Because its structure is not too complex , Learning and adjusting programs are also easier to operate , And because of the multi-layer network structure , Its ability to solve problems has also been significantly strengthened , Basically, it can meet the use requirements .

6.3 Feedforward inner interconnection network
This network structure is still a feedforward network from the outside , But there are some internal nodes interconnected in the layer .

6.4 Feedback network

This network structure also establishes another relationship between input and output , The output layer of the network has a feedback loop to the input layer as an input of the input layer , The network itself is feedforward .
The input layer of this neural network not only receives external input signals , At the same time, it receives the output signal of the network itself . The output feedback signal may be the original output signal , It can also be a converted output signal ; It can be the output signal at this time , It can also be an output signal after a certain delay .
Such networks are often used for system control 、 Real time signal processing and other occasions that need to be adjusted according to the current state of the system .
6.5 Full Internet

Fully interconnected network is a network between all neurons all There are mutual connections .
Such as Hopfiled and Boltgmann Networks are of this type .
7. Learning algorithm of neural network

7.1 Learning methods
- Supervised learning Supervised learning : It has characteristics (feature) And labels (label) Of , Even if there is no label , The machine can also use the relationship between features and labels , Judge the label .
- Unsupervised learning Unsupervised learning : Only features , No label .
- Semi-Supervised learning Semi-supervised learning : Data used , Part of it is marked , And most of them are unmarked . Compared with supervised learning , The cost of semi supervised learning is lower , But it can achieve high accuracy .
- Reinforcement learning Reinforcement learning : Reinforcement learning also uses unlabeled data , But there are some ways to know whether you are getting closer or farther away from the correct answer ( Reward and punishment function ).
7.2 Learning rule
Hebb Learning rule : The simple understanding is , If the processing unit receives an input from another processing unit , And if both units are highly active , At this time, the connection weight between the two units will be strengthened .
Hebb Learning rules is a learning method without guidance , It only changes the weight according to the activation level between neuronal connections , Therefore, this method is also called correlation learning or parallel learning .
Delta(δ \deltaδ) Learning rule :Delta Rules are the most commonly used learning rules , The key point is to change the connection weight between units to reduce the error between the actual output and the expected output of the system .
This rule is also called Widrow-Hoff Learning rule , First, in the Adaline Apply... In the model , It can also be called Minimum mean square deviation rule .
BP The learning algorithm of network is called BP Algorithm , Is in Delta Developed on the basis of rules , It can learn effectively on multi-layer network .
Gradient descent learning rule : The key point of gradient descent learning rule is in the learning process , Keep the gradient of the error curve down .
The error curve may have a local minimum , When learning online , Try to get rid of the local minimum of the error , And reach the real minimum error .
At present, many algorithms to reduce the value of loss function use the learning rule of gradient descent . There are many categories of gradient descent , Those who are interested can find out by themselves .
Kohonen Learning rule : The rule is made by Teuvo Kohonen Based on the study of biological system learning , Only for networks that do not train under guidance .
Backward propagation learning rules : Back propagation (Back Propagation,BP) Study , It is a widely used neural network learning rule .
Probabilistic learning rules : From statistical mechanics 、 Starting from the standard of steady-state energy in molecular thermodynamics and probability theory , The way of learning neural network is called probabilistic learning .
The error curve may have a local minimum , When learning online , Try to get rid of the local minimum of the error , And reach the real minimum error .
Competitive learning rules : Competitive learning belongs to unsupervised learning . This learning method uses excitatory connections between neurons in different layers and the same excitatory connections between neurons close to each other in the same layer , But the nerve which is far away has no inhibitory connection .
The essence of competitive learning rules is that high-level neurons in neural networks compete to identify the input patterns of low-level neurons .
8. BP neural network

8.1 The basic idea
BP Neural network is also called : Feedforward neural network with backward propagation learning (Back Propagation Feed-forward Neural Network,BPFNN/BPNN), It is one of the most widely used neural networks .
stay BPNN in , Backward propagation is a learning algorithm , Embodied in BPNN Training process of , This process needs teacher guidance ; Feedforward network is a kind of structure , Embodied in BPNN The network structure of .
Back propagation algorithm through iterative processing , Constantly adjust the weight of the network connecting neurons , The error between the final output result and the expected result is minimized .
BPNN It is a typical neural network , It is widely used in various classification systems , It also includes two stages of training and use . Because the training phase is BPNN The basis and premise for putting into use , The use phase itself is a very simple process , That is, give input ,BPNN Will calculate according to the trained parameters , Get the output .
8.2 Algorithm flow

In fact, this is essentially similar to the principle of perceptron .
Steps are as follows :


8.3 give an example




That's all for Yangyang , It's my first time to learn , Please advise , If you have questions, just comment or chat privately , When you see it, you will reply , First of all , I don't know when I will go online , Sometimes I don't come here once a week . Ha ha ha !
边栏推荐
- 支持在 Kubernetes 运行,添加多种连接器,SeaTunnel 2.1.2 版本正式发布!
- Storage structure of graph (adjacency matrix)
- Simple integration of client go gin 11 delete
- Nestjs 集成 config module 与 nacos 实现配置化统一
- 阿波罗使用注意事项
- 元宇宙中的云计算,提升你的数字体验
- Teach you how to create SSM project structure in idea
- 同花顺开户选哪家券商比较好?手机开户安全么?
- 模拟串口UART的实现
- 【深入理解TcaplusDB技术】TcaplusDB 表管理——重建表
猜你喜欢
![[in depth understanding of tcaplus DB technology] getting started tcaplus SQL driver](/img/2b/3ab5e247ac103728b4d3579c3c5468.png)
[in depth understanding of tcaplus DB technology] getting started tcaplus SQL driver

一文搞懂 MySQL 中 like 的索引情况

【毕业季】走一步看一步?一个自动化er对大学四年的思考

ROS从入门到精通(八) 常用传感器与消息数据

一个支持IPFS的电子邮件——SKIFF
![[deeply understand tcapulusdb knowledge base] common problems in deploying tcapulusdb local](/img/2b/3ab5e247ac103728b4d3579c3c5468.png)
[deeply understand tcapulusdb knowledge base] common problems in deploying tcapulusdb local

采用QTest进行数据集测试-性能测试-GUI测试

3个月自学自动化测试,薪资从4.5K到15K,鬼知道我经历了什么?

#夏日挑战赛# 【FFH】从零开始的鸿蒙机器学习之旅-NLP情感分析

软件上线前为什么要做性能测试?软件性能测试机构怎么找
随机推荐
critical path
Zabbix学习笔记(三十七)
【Proteus仿真】NE555延时电路
Bubble sort, select sort, direct insert sort
带超时的recv函数
iVX无代码挑战五秒游戏制作
经典面试题:一个页面从输入url到呈现过程
[deeply understand tcapulusdb technology] how to start tcapulusdb process
【深入理解TcaplusDB技术】TcaplusDB 表管理——删除表
Which securities firm is better to choose for opening an account in flush? Is it safe to open a mobile account?
Hash table (hash table)
Matlab calling API
一张图解码 OpenCloudOS 社区开放日
Fibonacci search (golden section)
智能計算之神經網絡(BP)介紹
手把手教你IDEA创建SSM项目结构
An IPFs enabled email - skiff
运用span-method巧妙实现多层table数据的行合并
R语言数据预处理、把类型变量转化为因子变量,把数据集转化为h2o格式、数据集划分(训练集、测试集、验证集)
一个支持IPFS的电子邮件——SKIFF