当前位置:网站首页>AVL tree of ordered table
AVL tree of ordered table
2022-07-24 22:14:00 【Harrison who likes to knock code】
Preface
The most important foundation in the database is the index , Why can indexes be built , Because the fields that can be indexed can be sorted ,( Any string can be sorted ) But we usually don't feel deeply .
How does sorting help speed up finding things in the database ?
The way of storing data in the database can really be sequential . For example, the hard disk structure in the database may have order . If the underlying data is written in order on the hard disk , Build an index tree just above the underlying data .
Search binary trees (BST)
Search Binary Tree simply add data , It's easy to find data , Therefore, the search binary tree itself can support indexing .( Add, delete, change and check all play in the tree )
But the problem is , In the worst case , This tree will degenerate into a linked list .
This leads to Balanced search Binary Tree The concept of : A tree is first guaranteed to search for binary trees , Then ensure its balance . The so-called balance : Assume that the amount of all data is N Words , The maximum height of the tree is only LogN The level of .
Why not use a hash table (O(1))? Because in reality, the operation in the database is related , Such as range query .
Balanced search Binary Tree (AVL)
The basic operation of balanced search Binary Tree , Left and right ,( Neither left nor right rotation will destroy the original search )
Where the head node goes to the left is the left rotation , The head node turns right .
left-handed
left-handed : Specify the header node first , then , The head node is inverted to the left , The right child of the head node comes up 
Right hand
Right hand : The head node is inverted to the right , The left child of the head node comes up .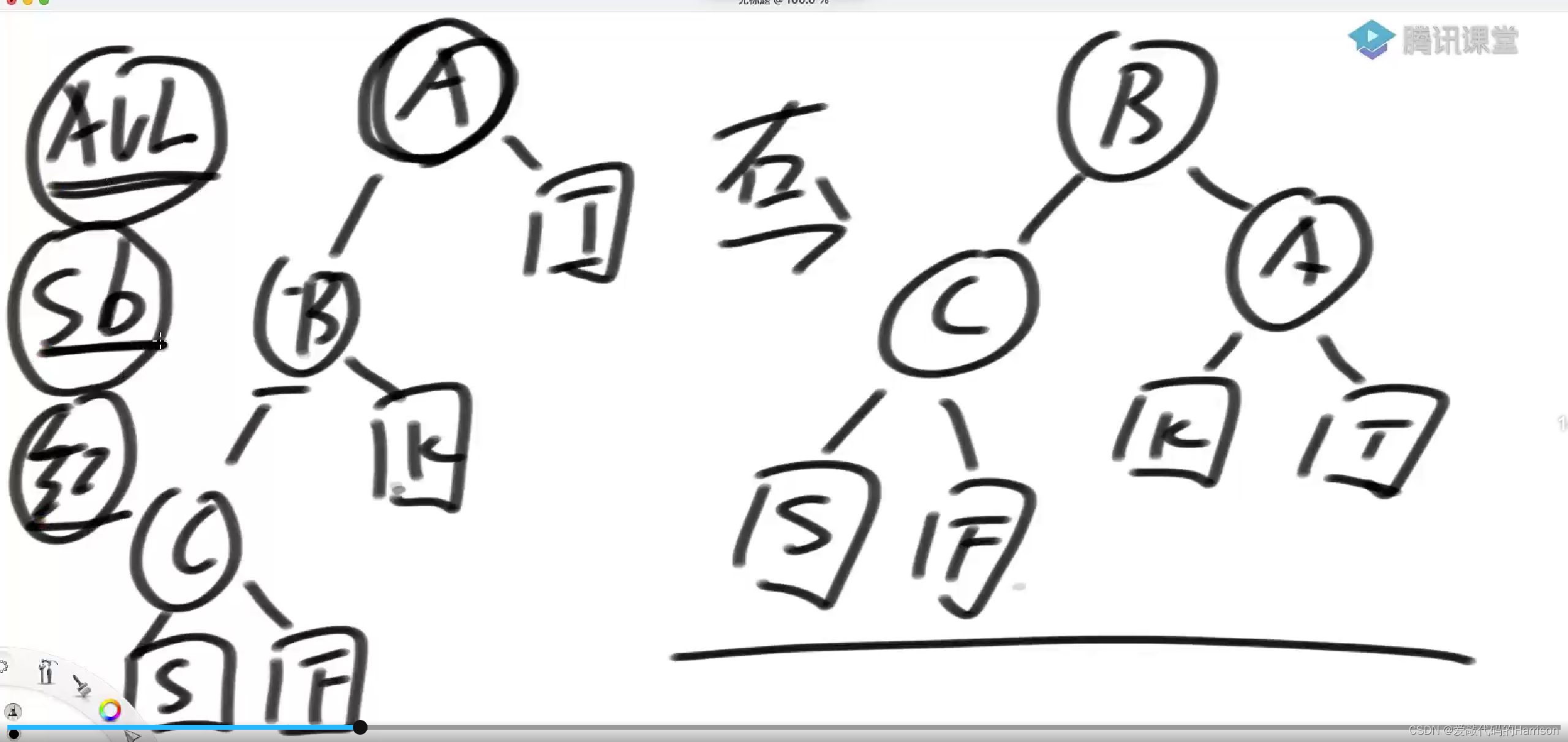
summary : There are many ways to implement the classic ordered table , such as AVL Trees ,SB Trees (size balance tree), A red-black tree, etc , But no matter what kind of balanced search Binary Tree , No matter how balance is defined , The only way for the bottom layer to balance them is left-handed and right-handed !
AVL Trees ( The most demanding balance )
Why would there be AVL Trees , because AVL The balance of the tree will make it more efficient to play addition, deletion, modification and query on the tree !!!
AVL The balance of the tree : Any node ,| The maximum height of the left tree - The maximum height of the right tree | < 2
It's easy to search a binary tree and add nodes , But deleting nodes is not so easy , stay coding It takes a lot of work on .
Searching binary tree is one of the most troublesome cases to delete nodes , The node to be deleted has a left tree , There are also right trees . You can replace... With the leftmost node on the right tree of the node to be deleted , You can also replace with the rightmost node on the left tree . The following describes how to replace with the leftmost on the right tree .
Here's the picture , The node to be deleted is X, find X Node the leftmost node in the right tree a, Cover X. such , The searchability of both sides has not been destroyed . Because in the first class search Binary Tree ,a The node is the distance X The node nearest and larger than it , This is the property of searching binary tree .

The above describes how to delete the search Binary Tree , Of course , It's easy to add and check .AVL Trees , The addition of , Deleting and searching are the same as searching a binary tree , Just after these operations ,AVL Trees have their own balance supplement .
AVL The balance of the tree
damage AVL Four types of tree balance
that AVL How trees adjust their balance ? And destruction AVL The type of balance .AVL There are four types of tree breaking balance ( It has nothing to do with left and right rotation ):
Here are AVL A situation in which the balance of a tree is partially destroyed
- LL type
- LR type
- RR type
- RL type
LL Type violation
encounter LL Type violation , One right spin will restore balance , encounter RR type , Just do a left-handed rotation .
LR Type violation
encounter LR Type violation , Here's the picture , The height of the right tree is relatively small , The height of the left tree is relatively large , And it is because the height of the right tree of the left tree is relatively large , To destroy the balance of .
How to adjust , Find a way to make Grandson replaces grandpa , That is to say, let C Replace A.
First step : In order to B Make a left rotation on the whole tree of the head node , Give Way C Take a step up first .
The second step : In order to A Make a right rotation for the whole tree of the head node , Give Way C Come to the head completely .
RR Type violation
RR type : Just do a left-handed rotation 
RL Type violation
RL type : Find a way to get your grandson to the top , in other words C Node replacement A.(C It's sun )
First step : Start with B Play a right spin for the whole tree at the head node
The second step : In order to A Play a left spin for the whole tree at the head node
In extreme cases
But there is an extreme case , Both belong to LL Violation type , It belongs to LR Violation type .
The tree in the picture above , After deleting the node on the right , It breaks the balance , And both LL, again LR.
both LL again LR, Directly in accordance with the LL Type standard to adjust , Direct right rotation . That's right. !
Counterexample , both LL type , again LR type ( The figure below A The height of the whole left tree is 7, The height of the whole right tree is 5) according to LR It is wrong to adjust according to the type standard .
The example above is based on LL The model is correct after adjustment .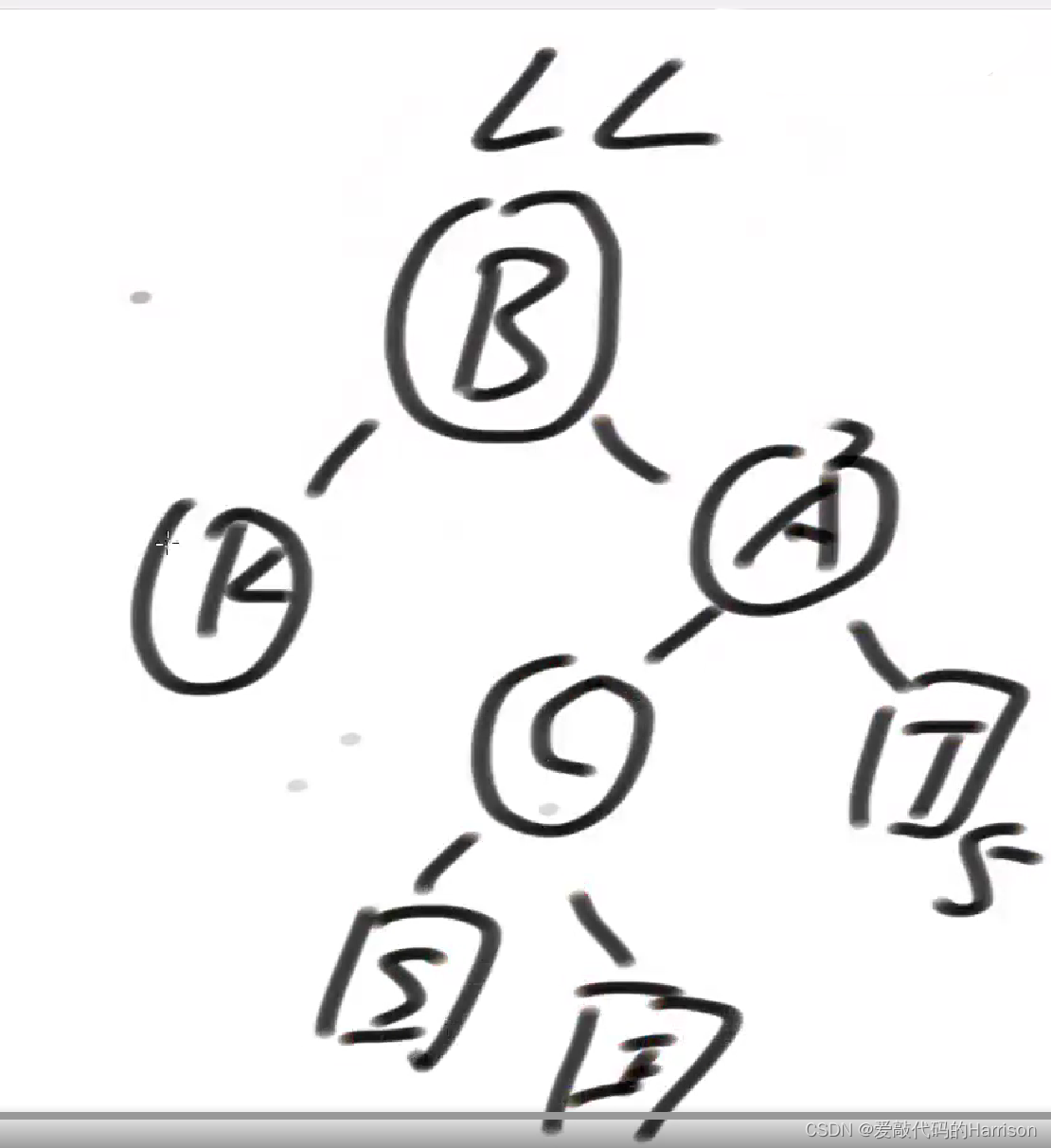
But according to LR Type adjustment is wrong . Although the following example (S Is the height of 5) That's right. , But if S Is the height of 4 Words , Still undermines the balance .
If S Height is 4, according to LL Type standard adjustment , Still right , according to LR Adjustment is wrong !!!, You can draw it yourself .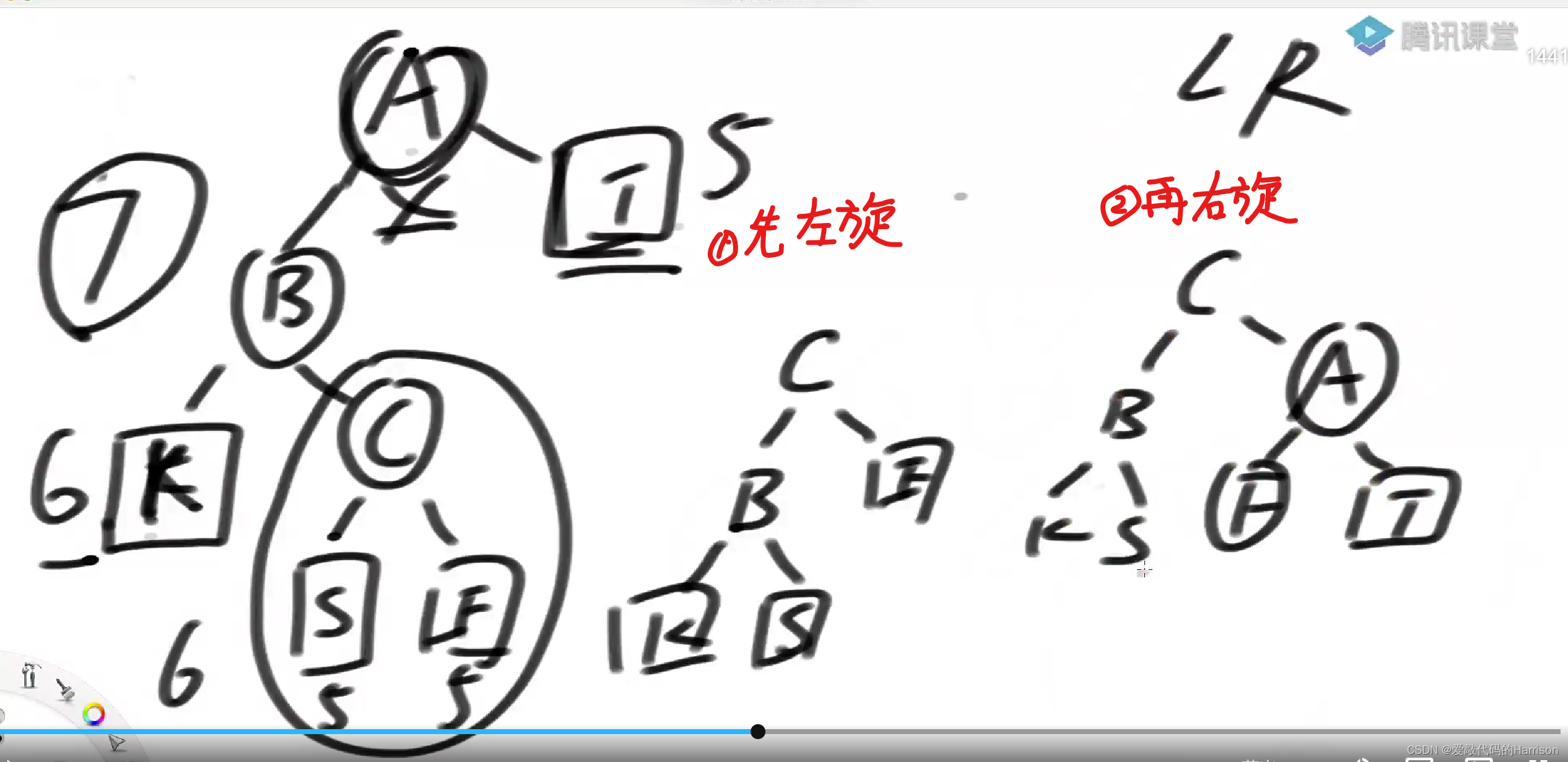
Empathy , There will also be RL Type violations and are RR Type violation . But it won't happen LL type , again RR type .
AVL The adjustment cost of the tree
The adjustment cost of the above four types of violations is very small ,O(1).
that AVL After adding a node to the tree , How to adjust it ? After joining a node , Check every node along the way , See what type of violation it belongs to . Including added nodes .
If AVL The maximum height of the tree before joining the node is LogN, Then add a node , Even up, all nodes should check whether they violate the rules , Because there's only LogN Nodes , The adjustment cost of each node is O(1); therefore ,AVL The cost of adjusting the balance of trees is O(LogN)
AVL In the tree , The factor that keeps the balance is the height of the tree h, So every time the relative position of nodes is adjusted , Update the balance factor h. If the balance factor of other trees is different , Do the same , For example, red and black trees ,SB Trees, etc , Subsequent articles will talk about .
Add
An ordered list follows AVL The relationship between trees
If you compare an ordered table to an interface , that AVL A tree is a concrete class , And what can realize the ordered table is SB Trees , Red and black trees , Jump watch ,234 Trees ,B Trees ,B+ Trees …, The time complexity of their implementation of ordered tables is O(LogN), The difference is that the specific implementation details are different .
Why is relational database declining today , Then came the popularity of horizontally extensible databases , Consistency hash database . Stay until the following articles continue to understand
Finally, attach the full code ~
package com.harrison.class25;
/** * @author Harrison * @create 2022-04-03-10:46 * @motto looking for him for thousand times in the crowd , Suddenly look back , The man was in the dim light . */
public class Code01_AVLTreeMap {
/* because AVL Trees are used in ordered tables , So we must ask for its key Comparable There is no way to compare , You don't have to talk about the order table */
public static class AVLNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
// AVL The specific nodes in the are encapsulated
public K k;
public V v;
// The node pointing to the left child and the right child
public AVLNode<K, V> l;
public AVLNode<K, V> r;
// AVL The balance factor in the tree : Height ( The whole tree AVL The height of the tree )
public int h;
public AVLNode(K key, V value) {
k = key;
v = value;
h = 1;
}
}
/* use AVL An ordered table implemented by a tree */
public static class AVLTreeMpa<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
public AVLNode root;// The root node of the whole tree
public int size;// Added key The number of
public AVLTreeMpa() {
root = null;
size = 0;
}
// in the light of cur Node the whole tree to play right-handed
private AVLNode<K, V> rightRotate(AVLNode<K, V> cur) {
// Remember first cur The left child , Because right-handed is cur To the right
AVLNode<K, V> left = cur.l;
// Then the left child's right tree hangs on mine (cur) Left side
cur.l = left.r;
// Left child's right take over cur
left.r=cur;
// adjustment cur and left Height
// And must first adjust cur And then adjust the height left
// Because the right-handed back head node is left 了
cur.h = Math.max((cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0), (cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0)) + 1;
left.h = Math.max((left.l != null ? left.l.h : 0), (left.r != null ? left.r.h : 0)) + 1;
return left;
}
private AVLNode<K,V> leftRotate(AVLNode<K,V> cur){
AVLNode<K,V> right=cur.r;
cur.r=right.l;
right.l=cur;
cur.h = Math.max((cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0), (cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0)) + 1;
right.h = Math.max((right.l != null ? right.l.h : 0), (right.r != null ? right.r.h : 0)) + 1;
return right;
}
/* Search the binary tree without repeating key Just say search Binary Tree , Its subtext is every key Is not the same */
// In order to cur On the whole subtree for the head , Add records , And return the head node of the whole tree to
// add() Method will not encounter the same key
public AVLNode<K,V> add(AVLNode<K,V> cur,K key,V value){
if(cur==null){
return new AVLNode<K,V>(key,value);
}else{
if(key.compareTo(cur.k)<0){
// There may be a head change
cur.l=add(cur.l,key,value);
}else{
cur.r=add(cur.r,key,value);
}
}
cur.h = Math.max((cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0), (cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0)) + 1;
// The above is just to search the added nodes of binary tree
// After adding the completion point , Adjust the balance
return maintain(cur);
}
// stay cur On this tree , Delete key The node represented by
// return cur The new head of the tree
private AVLNode<K,V> delete(AVLNode<K,V> cur,K key){
if(key.compareTo(cur.k)>0){
cur.r=delete(cur.r,key);
}else if(key.compareTo(cur.k)<0){
cur.l=delete(cur.l,key);
}else{
if(cur.l==null && cur.r==null){
cur=null;
}else if(cur.l==null && cur.r!=null){
cur=cur.r;
}else if(cur.l!=null && cur.r==null){
cur=cur.l;
}else{
// Find the leftmost node on the right tree
AVLNode<K,V> des=cur.r;
while (des.l!=null){
des=des.l;
}
/* First tune one in the right tree delete() Method , After deleting the leftmost node , Complete the balance adjustment of the right tree , Then get the leftmost node , Replace the node to be deleted , Then check the balance up one by one */
cur.r=delete(cur.r,des.k);
des.l=cur.l;
des.r=cur.r;
cur=des;
}
}
if (cur != null) {
cur.h = Math.max(cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0, cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0) + 1;
}
// Every time a node is deleted, the balance will be checked up , So the recursive function will call itself many times , Check your balance every time
return maintain(cur);
}
private AVLNode<K,V> maintain(AVLNode<K,V> cur){
if(cur==null){
return null;
}
int leftHeight=cur!=null?cur.l.h:0;
int rightHeiht=cur.r!=null?cur.r.h:0;
if(Math.abs(leftHeight-rightHeiht)>1){
if(leftHeight>rightHeiht){
int leftLeftHeight = cur.l != null && cur.l.l != null ? cur.l.l.h : 0;
int leftRightHeight = cur.l != null && cur.l.r != null ? cur.l.r.h : 0;
if(leftLeftHeight>leftRightHeight){
// Equal to why you put it here , Because since LL type , again LR type , according to LL Type standard to adjust the balance
cur=rightRotate(cur);
}else{
cur.l=leftRotate(cur.l);
cur=rightRotate(cur);
}
}else{
int rightLeftHeight = cur.r != null && cur.r.l != null ? cur.r.l.h : 0;
int rightRightHeight = cur.r != null && cur.r.r != null ? cur.r.r.h : 0;
if(rightLeftHeight>=rightRightHeight){
// Empathy , If both RR type , again RL type , according to RR Type standard to adjust the balance
cur=leftRotate(cur);
}else{
cur.r=rightRotate(cur.r);
cur=leftRotate(cur);
}
}
}
return cur;
}
private AVLNode<K, V> findLastIndex(K key) {
AVLNode<K, V> pre = root;
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
pre = cur;
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) == 0) {
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
cur = cur.l;
} else {
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return pre;
}
private AVLNode<K, V> findLastNoSmallIndex(K key) {
AVLNode<K, V> ans = null;
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) == 0) {
ans = cur;
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
ans = cur;
cur = cur.l;
} else {
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return ans;
}
private AVLNode<K, V> findLastNoBigIndex(K key) {
AVLNode<K, V> ans = null;
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) == 0) {
ans = cur;
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
cur = cur.l;
} else {
ans = cur;
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return ans;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return false;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
return lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.k) == 0 ? true : false;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.k) == 0) {
lastNode.v = value;
} else {
size++;
root = add(root, key, value);
}
}
public void remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return;
}
if (containsKey(key)) {
size--;
root = delete(root, key);
}
}
public V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.k) == 0) {
return lastNode.v;
}
return null;
}
public K firstKey() {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur.l != null) {
cur = cur.l;
}
return cur.k;
}
public K lastKey() {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur.r != null) {
cur = cur.r;
}
return cur.k;
}
public K floorKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNoBigNode = findLastNoBigIndex(key);
return lastNoBigNode == null ? null : lastNoBigNode.k;
}
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNoSmallNode = findLastNoSmallIndex(key);
return lastNoSmallNode == null ? null : lastNoSmallNode.k;
}
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
![[icml2022] climate change and machine learning: opportunities, challenges and considerations, 121 ppt](/img/be/6a3f53070c2ffc9610a77d4e910f91.png)
[icml2022] climate change and machine learning: opportunities, challenges and considerations, 121 ppt

由斐波那契数列引述到矩阵快速幂技巧

数据库之-元数据 DatabaseMetaData 初学

工程项目管理软件排名
Application programming of communication heartbeat signal for communication abnormality judgment

实现redis哨兵,模拟master故障场景

C# 使用SQLite
Gradle 学习 ----Gradle 进阶说明

大咖对话:品牌扎堆数藏赛道,下半场的机遇、挑战在哪里?
SVM - for linear separability (Part 2)
随机推荐
Glidemodule appglidemodule and generated API details
Esp32485 air temperature and humidity test
Leetcode 102. sequence traversal of binary tree
ESP32C3 LED PWM使用和ESP32差异说明
Get the solution to the slow running speed of Mengxin Xiaobai computer! ٩ ( ‘ ω‘ )و get! ٩ ( ‘ ω‘ )و
One click compilation and installation of redis6.2.4
[postgraduate entrance examination vocabulary training camp] day 12 - native, separate, figure, contribution, categories, assessment, propose
Available parameters of ansible Playbook
PCL点云处理之移动最小二乘拟合实验(六十二)
使用frp实现内网穿透
Web3 security go + security
数据库之-元数据 DatabaseMetaData 初学
Gradle learning set integration
【ICML2022】气候变化与机器学习:机遇、挑战与考虑,121页ppt
《ArchSummit:珍爱微服务底层框架演进》
由斐波那契数列引述到矩阵快速幂技巧
图结构的实现,从点到边再到图
leetcode:不可能得到的最短骰子序列【思维题 + 分组思想】
Cell专刊|AI在蛋白结构、精准医疗、抗体疗法[综述]等的应用与未来预测
大咖对话:品牌扎堆数藏赛道,下半场的机遇、挑战在哪里?