当前位置:网站首页>QT下assimp库的模型加载
QT下assimp库的模型加载
2022-07-23 18:45:00 【Elsa的迷弟】
Assimp库概述
一个非常流行的模型导入库是Assimp,它是Open Asset Import Library(开放的资产导入库)的缩写。Assimp能够导入很多种不同的模型文件格式(并也能够导出部分的格式),它会将所有的模型数据加载至Assimp的通用数据结构中。当Assimp加载完模型之后,我们就能够从Assimp的数据结构中提取我们所需的所有数据了。由于Assimp的数据结构保持不变,不论导入的是什么种类的文件格式,它都能够将我们从这些不同的文件格式中抽象出来,用同一种方式访问我们需要的数据。
当使用Assimp导入一个模型的时候,它通常会将整个模型加载进一个场景(Scene)对象,它会包含导入的模型/场景中的所有数据。Assimp会将场景载入为一系列的节点(Node),每个节点包含了场景对象中所储存数据的索引,每个节点都可以有任意数量的子节点。Assimp数据结构的(简化)模型如下:
文章目录
加载模型
void Model::loadModel(const QString& path)
{
Assimp::Importer importer;
const aiScene *scene=importer.ReadFile(path.toLatin1(),
aiProcess_Triangulate |
aiProcess_GenSmoothNormals |
aiProcess_FlipUVs |
aiProcess_CalcTangentSpace);
if(!scene || scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE || !scene->mRootNode)
{
qDebug() << "ERROR::ASSIMP:: " << importer.GetErrorString() << endl;
return;
}
int index=path.lastIndexOf('/');
rootPath=path.left(index);
processNode(scene->mRootNode,scene);
processMaterials(scene);
}
class Assimp::Importer
CPP-API:Importer类形成了一个到Open Asset Import Library功能的c++接口。
创建该类的一个对象,并调用ReadFile()来导入文件。如果导入成功,函数返回一个指向导入数据的指针。数据保留对象的属性,用于只读访问。导入的数据将与Importer对象一起被销毁。如果导入失败,ReadFile()返回一个nullptr指针。在这种情况下,您可以通过调用GetErrorString()来检索人类可读的错误描述。可以使用单个Importer实例多次调用ReadFile()。实际上,构造Importer对象涉及到相当多的分配,可能会花费一些时间,所以最好尽可能频繁地重用它们。
如果你需要Importer做自定义文件处理来访问文件,实现IOSystem和IOStream,并在调用ReadFile()之前调用SetIOHandler()来提供一个自定义IOSystem实现的实例。如果不指定定制IO处理程序,则将使用使用标准c++ IO逻辑的默认处理程序。
注意:
一个Importer实例不是线程安全的。如果使用多个线程进行加载,每个线程都应该维护自己的Importer实例。
ReadFile
const aiScene *ReadFile(const char *pFile, unsigned int pFlags)
读取给定文件,如果成功则返回文件内容。
如果调用成功,文件的内容将作为指向一个aiScene对象的指针返回。返回的数据是只读的,导入器对象保留数据的所有权,并将在销毁时销毁数据。如果导入失败,返回nullptr。可以通过调用GetErrorString()来检索人类可读的错误描述。之前的场景将在这次调用中被删除。
return:
指向导入数据的指针,如果导入失败则为nullptr。指向场景的指针仍然属于Importer实例。使用GetOrphanedScene()来获得它的所有权。
Note:
Assimp能够自动确定文件的文件格式。
Parameters:pFile:待导入文件的路径和文件名。pFlags:导入成功后可选执行的后期处理步骤。提供aiPostProcessSteps标志的按位组合。如果你希望首先检查导入的场景以调整你的后处理设置,可以考虑使用ApplyPostProcessing()。
ApplyPostProcessing
constaiScene *ApplyPostProcessing(unsigned int pFlags)
应用后处理到一个已经导入的场景。
这严格等效于调用具有相同标志的ReadFile()。但是,你可以使用这个单独的函数来检查导入的场景,以微调你的后期处理设置。
pFlags
pFlags为导入成功后执行的可选后处理步骤,是一些后期处理(Post-processing)的选项,可在官网找到具体的信息。
例如:
- aiProcess_Triangulate,我们告诉Assimp,如果模型不是(全部)由三角形组成,它需要将模型所有的图元形状变换为三角形。
- aiProcess_FlipUVs将在处理的时候翻转y轴的纹理坐标
- aiProcess_GenNormals:如果模型不包含法向量的话,就为每个顶点创建法线。
- aiProcess_SplitLargeMeshes:将比较大的网格分割成更小的子网格,如果你的渲染有最大顶点数限制,只能渲染较小的网格,那么它会非常有用。
- aiProcess_OptimizeMeshes:和上个选项相反,它会将多个小网格拼接为一个大的网格,减少绘制调用从而进行优化。
处理导入的模型

void Model::processNode(aiNode *node,const aiScene *scene)
{
for(unsigned int i=0;i<node->mNumMeshes;i++)
{
aiMesh* mesh=scene->mMeshes[node->mMeshes[i]];
matrialMeshesMap[mesh->mMaterialIndex].push_back(meshes.size());
meshes.push_back(processMesh(mesh));
}
for(unsigned int i=0;i<node->mNumChildren;i++)
{
processNode(node->mChildren[i],scene);
}
}
aiScene
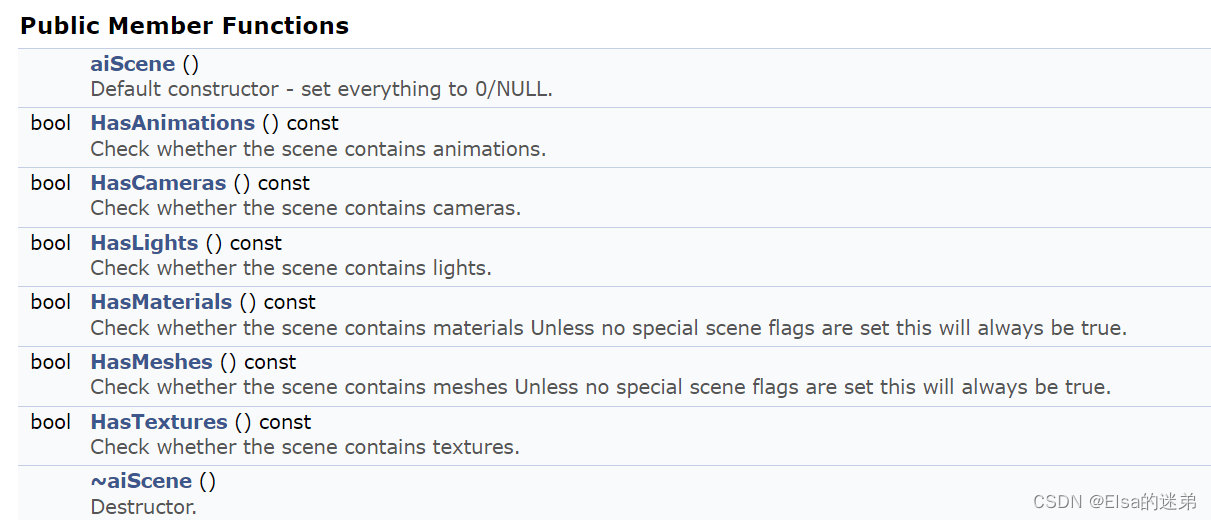

主要参数
unsigned int aiScene:: mFlags
AI_SCENE_FLAGS_XXX标志的任意组合。
缺省情况下,该值为0,没有设置标志。大多数应用程序都希望拒绝所有设置了AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE位的场景。
if(...||scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE||...){
...
}
表示当scene->mFlags 包含这一项时。
struct aiNode
mRootNode,aiNode->mChildren[i]都是aiNode类型
共有成员
C_STRUCT aiNode ** mChildren
此节点的子节点。如果mNumChildren为0则为nullptr。unsigned int * mMeshes
此节点的网格。aiString mName
节点名称。unsigned int mNumChildren
此节点的子节点数。unsigned int mNumMeshes
此节点的网格数。aiNode * mParent
父节点。aiMatrix4x4 mTransformation
相对于节点父节点的转换。
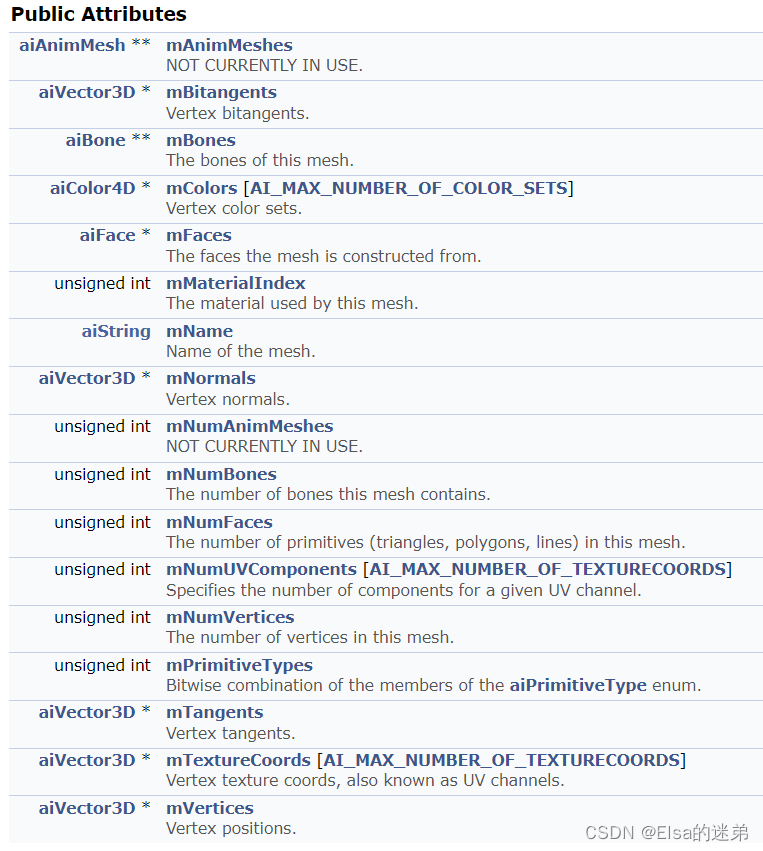
aiMesh** mMeshes
一个网格表示一个几何或模型和一个材料。
网格包含:
- 名称(
aiString mName) - 顶点(
aiVector3D * mVertices)顶点数量(unsigned int mNumVertices) - 法线(
aiVector3D * mNormals) - 切线,双切线(
aiVector3D * mTangents,aiVector3D * mBitangents) - 面(
aiFace * mFaces)面数量(unsigned int mNumFaces)【面组成网络】 - 材质下标(
unsigned int mMaterialIndex)【一个mesh只有一个材质】 - 骨骼(
aiBone ** mBones)骨骼数量(unsigned int mNumBones) - 顶点颜色集(
aiColor4D * mColors [AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_COLOR_SETS]) - 顶点纹理坐标,也称为UV通道。(
aiVector3D * mTextureCoords [AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_TEXTURECOORDS]) - UV通道组件数量(
unsigned int mNumUVComponents [AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_TEXTURECOORDS])

aiMaterial** mMaterials
材料的数据结构。
材料数据使用键值结构存储。单个键值对被称为“材料属性”。c++用户应该使用aiMaterial提供的成员函数来处理材质属性,C用户必须坚持使用aiMaterialGetXXX家族的未绑定函数。标准库定义了一组标准键(AI_MATKEY_XXX)。
获取特定纹理类型的纹理数量。
unsigned int GetTextureCount (aiTextureType type) const
enum aiTextureType
aiTextureType_NONE,aiTextureType_DIFFUSE,aiTextureType_SPECULAR,aiTextureType_AMBIENT,aiTextureType_EMISSIVE(自发光纹理),aiTextureType_HEIGHT(凹凸贴图),aiTextureType_NORMALS(法线贴图),aiTextureType_SHININESS (材质的光泽度),aiTextureType_OPACITY (像素不透明度),aiTextureType_DISPLACEMENT (位移贴图),aiTextureType_LIGHTMAP (灯光贴图纹理,又名环境遮挡),aiTextureType_REFLECTION 反射结构。
包含完美的镜子反射的颜色。很少使用,几乎从不用于实时应用程序。aiTextureType_UNKNOWN 未知的纹理。
一个纹理引用不符合上面的任何定义被认为是“未知的”。它仍然被导入,但是被排除在任何进一步的后处理之外。
从材料中获得与特定纹理槽相关的所有参数。
aiReturn GetTexture ( aiTextureType type,
unsigned int index,
aiString *path,
aiTextureMapping *mapping=NULL,
unsigned int *uvindex=NULL,
float *blend=NULL,
aiTextureOp *op=NULL,
aiTextureMapMode *mapmode=NULL
) const
通过type和index可以获取特定的纹理,返回值为path路径,
参数:
- mapping 纹理映射。允许NULL作为值。
- uvindex 接收纹理的UV索引。NULL是一个有效值。
- blend 接收纹理的混合因子,NULL是一个有效值。
- op 接收当前纹理和前一个纹理之间要执行的纹理操作。允许NULL作为值。
- mapmode 接收用于纹理的映射模式。参数可以是NULL,
但如果它是一个有效的指针,它必须指向一个数组的3个aiTextureMapMode
(一个为每个轴:UVW顺序(=XYZ))。
示例:
texCount=scene->mMaterials[i]->GetTextureCount(aiTextureType_DIFFUSE);
if(texCount>0)
{
scene->mMaterials[i]->GetTexture(aiTextureType_DIFFUSE,0,&texturePath);
textureId=findTextureIndex(&texturePath);//findTextureIndex为自定义函数
mat.diffuseTexture=textureId;
}
返回的texturePath为文件名称,因此在使用QImage image=QImage(path).mirrored(false,false);时path要将根目录和文件名称相加。
类似于
QString texPath=QString("%1/%2").arg(rootPath).arg(texturePath->C_Str());
或
QImage data(directory.filePath(str.C_Str()));
获取颜色信息
aiColor3D color;
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_COLOR_AMBIENT,color);
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_COLOR_DIFFUSE,color);
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_COLOR_SPECULAR,color);
获取光泽度信息
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_SHININESS,mat.shininess);

边栏推荐
- Principe de l'énergie et méthode variationnelle note 19: principe de l'énergie résiduelle minimale + principe du travail possible
- 2022/7/22 训练日志
- 【AR学习】-- 二、 环境搭建
- [Luogu p6656] [LOJ 173] [template] runs (string) (Lyndon string)
- Attack and defense world web question Fakebook
- Leetcode 151. invert words in strings
- Energy principle and variational method note 18: virtual force principle
- Powercli imports licensekey to esxi
- Redux求和案例详解版教程
- Home NAS server (3) | SSD cache acceleration mechanical hard disk
猜你喜欢

solidworkd学习笔记:草图几何关系及编辑

AtCoder B - Pizza
![Atcoder regular contest 144 [VP record]](/img/8c/bcffb95cb709087103bb79b8a358d1.png)
Atcoder regular contest 144 [VP record]

Energy principle and variational method note 12: minimum potential energy principle

Energy principle and variational method note 15: solution of differential element method
web安全入门-ssh测试与防御

能量原理与变分法笔记19:最小余能原理+可能功原理

Leetcode 152. product maximum subarray (brute force cracking can actually pass!)

Powercli management VMware vCenter batch deployment export import

AtCoder——Subtree K-th Max
随机推荐
[unity project practice] entrustment
Leetcode 238. 除自身以外数组的乘积
能量原理与变分法笔记18:虚力原理
Uncover the working principle of solid state disk
Energy principle and variational method note 18: virtual force principle
Powercli imports licensekey to esxi
Compiler llvm MLIR introductions llvm backend instruction
2022/7/21 training summary
Detailed writing process of impala
Codeforces round 809 (Div. 2) [VP record]
【Unity项目实践】委托
Energy principle and variational method note 19: minimum complementary energy principle + possible work principle
Attack and defense world web question Fakebook
【面试:并发篇22多线程:ReentrantLock】
AtCoder B - Pizza
Solutions to SecureCRT garbled code problem [easy to understand]
[激光器原理与应用-8]: 激光器电路的电磁兼容性EMC设计
Typescript新数据类型Symbol的使用
The full text of Li Hongzhang's deathbed poem
[development experience] development project trample pit collection [continuous update]