当前位置:网站首页>[pytoch basic tutorial 31] youtubednn model analysis
[pytoch basic tutorial 31] youtubednn model analysis
2022-06-24 08:50:00 【Mountain peak evening view】
Learning summary
- youtubeDNN That is, one with softmax loss Loss function training , And the training mode is list-wise sample The classic DSSM The twin tower model .
(1) Candidate generation model : It was used Embedding MLP, Note the final multi category output layer , The prediction is that the user clicks “ Which one? ” video . Online service , You need to extract... From the output layer 【 video Embedding】, From the last floor ReLU Layers get 【 user Embedding】, Then use the nearest neighbor search ( Such as LSH etc. ) Quickly get the candidate set of a user . This can improve the efficiency of model services , You don't have to move the logic of model inference to the server , Just put the user Embedding And video Embedding Deposit in redis Feature database is OK .
(2) Sort model : It's also Embedding MLP framework , But there are more user and video feature input layers , The output layer adopts Weighted LR( Logical regression ) As an output layer ( Prediction is typical CTR), And the viewing time is used as the positive sample weight , Let the model predict the viewing time , This is closer YouTube Business goals to achieve .
(3) Efficient training model : The author draws lessons from... In machine translation Sampled Softmax Method , That is, use the importance to sample part of the video V ′ V^{\prime} V′, More details can be found in The paper : Sampling thousands of negative samples by importance ; after importance weighting The way to correct . Other solutions :
- Use other methods , To approach softmax Probability , such as : be based on noise-contrastive estimation (NCE) Methods , Be similar to word2vec in skip-gram Of negative sampling
- level softmax
List of articles
- Learning summary
- One 、YoutubeDNN Model
- Two 、 Recall model
- Four 、YouTubeDNNN The model code
- 5、 ... and 、YouTube The twin tower model
- 6、 ... and 、 model training trick
- 7、 ... and 、youtube Twin tower model code
- 8、 ... and 、Facebook The twin tower model
- Nine 、 Precautions for project implementation
- Reference
One 、YoutubeDNN Model
YouTube There are a lot of user original content , Its business model and Netflix、 Tencent in China 、 Iqiyi and other streaming media are different , The latter is a purchased or homemade film , also YouTube Huge video base , It's hard for users to find what they like . Based on the typical two-stage information retrieval dichotomy : Firstly, a depth candidate generation model is described , Then a separate depth ranking model is described .
YouTube Three challenges in video recommendation :
Large scale 、 Quick update 、 noise ( User history behavior is sparse ; A lot of data in video is unstructured ).
(1) Data scale :YouTube The number of users and video is one billion .
(2) Quick update : The recommendation system needs to respond to newly uploaded videos and users' new behaviors in time .
(3) Data noise : Due to sparsity and external factors , The historical behavior of users is difficult to predict . Most of the YouTube Video has only implicit feedback ( That is, the user's viewing behavior of the video ), Lack of explicit feedback ( That is, the user's rating of the video ).
YouTubeDNN The overall structure of ( Recall layer and sorting layer ):
The first stage , Recall layer : Filter out a small number of videos from millions of videos ; It needs to be fast ; The recall layer views according to user history 、 Search and other records for recall , To meet the user's interest in generalization .
The second stage , Sort layer : In order to more accurately recommend to users , This stage requires more complex models and features to sort .
The third stage , Offline evaluation : The evaluation indicators are precision、recall、ranking loss; Finally, do it online A/B test ( indicators : Click through rate 、 Watch time ).
A/B Testing is to randomly divide the tested object into A、B Two groups , Through the method of comparative test, the experimental conclusion is drawn . During the development of online evaluation indicators , Try to ensure that these indicators are consistent with the core indicators of online business , So as to know whether the company's business objectives have been achieved .
Two 、 Recall model
2.0 Traditional recall thinking
First calculate the price of the goods offline embedding And user's embedding, When recalled online , According to the user's embedding And all goods embedding Inner product , find topN. This traditional approach needs to solve several problems :
- Commodity embedding And the user embedding How to make sure that The same space
- user embedding And the inner product of all commodities , There are performance issues
- Such as SVD Singular value decomposition method , Enter the collaboration matrix , The characteristics are relatively single
2.1 Key points of problem modeling and training
In the recall phase ,YouTube Consider the recommendation problem as a large-scale multi classification problem softmax problem , Defined as based on a specific user U U U And its context C C C, stay t t t moment , The video library V V V The video specified in w t w_t wt It is divided into i i i The probability of a class : P ( w t = i ∣ U , C ) = e v i u ∑ j ∈ V e v j u P\left(w_{t}=i \mid U, C\right)=\frac{e^{v_{i} u}}{\sum_{j \in V} e^{v_{j} u}} P(wt=i∣U,C)=∑j∈Vevjueviu
among :
- u ∈ R N u \in \mathbb{R}^{N} u∈RN It is the high dimension of the user in the context embedding;
- v j ∈ R N v_{j} \in \mathbb{R}^{N} vj∈RN It's for each candidate video embedding
- v j u v_j u vju It's No j j j A video of embedding
Summary : Given the user's historical behavior and context , Learn from users embedding, Then input softmax, Generate candidate set results of recall layer .training Many classification ,serving Nearest neighbor .
(1) Training : Multiple classification problem
- youtubeDNN That is, one with softmax loss Loss function training , And the training mode is list-wise sample The classic DSSM The twin tower model .
- The training is a multi classification problem , Using negative sampling softmax loss(1 just ,k negative )
(2)embedding Generate
- Only user The characteristics and user tower , But no item tower
- user embedding:user Real time feature user The result of the tower
- item embedding:softmax layer (
Dense(dim, N)+softmax) Weight matrices
(3) Use example age
example age: Eliminate the impact of sample time bias
- Training : Use the last moment of training concentration time - sample log Time of birth
- forecast : Set to 0, Make sure the prediction is made at the last moment of training
2.2 Recall layer model architecture
The candidate set generation model for video recall is shown in the following figure , In fact, it is also a two tower model in essence :
Look at the network from the bottom up :
(1) Input layer
input features :
(1) User history of watching video embedding vector , It needs to be done mean pooling.
(2) Search term embedding vector .
(3) User geographic features and user device features : They are all discrete features , May adopt embedding Method or directly use one-hot Fang ( When the discrete dimension is small ).
YouTube Is the use of user viewing sequences and search sequences , Through something like Item2vec Pre training generation .
The feature vector also includes the geographic location of the user Embedding、 Age 、 Gender and other characteristics .
【 Be careful 】 The characteristic of sample age ,YouTube Not only the original eigenvalues are used , The squared eigenvalues are also used as a new feature input model . The operation is In order to mine the nonlinear characteristics of features .
The treatment of continuous features is not limited to square , Others such as prescription 、Log、 Exponential and other operations can be used to mine the nonlinear characteristics of features .
(4)example age: One thing to pay attention to in the video recommendation system , Users prefer to watch new videos , However, the machine learning model is based on historical viewing video records , So this is a little contrary to the original intention , So a feature is constructed in this paper example age, It can be understood as the age of the video : The initial value is set to 0, As time goes on , The age at which the video was recorded . After adding, the experiment shows that the effect is obvious :
(5) Characteristics of population attributes : Provide a priori , Make reasonable recommendations for new users ( Cold start ), That is, the geographical area and use of users
(2)ReLU layer
take (1) Features in concat Layer connection , Then input to the third floor ReLU Training in neural networks .
Use the common tower design , The bottom floor is the widest , Up, halve the number of neurons in each layer , until Softmax The input layer is 256 dimension (1024ReLU->512ReLU->256ReLU).
(3)softmax layer
Based on specific users U U U And its context C C C, stay t t t moment , The video library V V V The video specified in w t w_t wt It is divided into i i i The probability of a class : P ( w t = i ∣ U , C ) = e v i u ∑ j ∈ V e v j u P\left(w_{t}=i \mid U, C\right)=\frac{e^{v_{i} u}}{\sum_{j \in V} e^{v_{j} u}} P(wt=i∣U,C)=∑j∈Vevjueviu
among :
- u ∈ R N u \in \mathbb{R}^{N} u∈RN It is the high dimension of the user in the context embedding;
- v j ∈ R N v_{j} \in \mathbb{R}^{N} vj∈RN It's for each candidate video embedding
- v j u v_j u vju It's No j j j A video of embedding
(4) Output layer
Three layers ReLU After network ,YouTube Here is the use of softmax As an output layer , Note that the output layer here does not estimate the click through rate , It is Predict which video users will click . Dimensions of the output layer and video ID Of embedding The vector dimensions are the same , Finally, we get the user vector u.
Through the learning of the network structure , Finally, you can get all the video embedding vector V, Dimension for pool_size × k, among :
pool_sizeThe size of the video resource for the training set ,- k by embedding Dimensions .
- You can also get the output vector of all users u, The dimension of each user vector is k, And video embedding The vector dimensions are consistent .

There are two issues to note in the output layer :
problem 1:【 Using video ID As a prediction label】
In the model service , If each recommendation request needs to be run end-to-end model( Process the candidate set ), because model The number of parameters is huge , So the inference process is also expensive . In order to improve the efficiency of model service , After the output layer does this , You can get users and videos embedding, And pre stored in the online feature database , Finally through embedding Nearest neighbor search method ( Such as local sensitive hash LSH etc. ) matching .
problem 2:【embedding The birth of 】
(1) video embedding
Video vector softmax The parameters of a layer are essentially a m × n Matrix , among :
- m It refers to the last layer of red ReLU The dimension of layers m
- n Refers to the total number of categories , That is to say YouTube The total number of all videos n.
- video Embedding This is this. m x n The column vectors of a dimensional matrix .( In this way Embedding The generating method is actually the same as word2vec The generation method of Chinese word vector is the same )
(2) user embedding vector
because input All feature vectors are user related features , Such as using a user's u The eigenvector is used as the model input, The last layer ReLU Layer of output Can be used as the user's embedding vector .
2.3 Heterogeneous Signals
Heterogeneous signals .
Use deep learning as a generalization of matrix decomposition , Advantage lies in , Any continuous and classified features can be easily added to the model . Searching history is handled in a similar way to viewing history , Each query is marked as unigram and bigrams, And each tag is embedded . After averaging , The user's tokenized embedded query represents a summary of intensive search history .
Demographic characteristics are important for providing a priori information , Therefore, it is recommended for new users ( Cold start ) Act reasonably . The user's geographic areas and devices are embedded and connected . Simple binary and continuous features ( Such as the user's gender , Login status and age ) Normalize to [0, 1] The actual value of is directly input into the network .
2.4 Sample selection and context selection
Positive and negative samples and context selection .
In supervised learning , The most important thing is to choose label, This also determines the upper limit of the model effect :
Use a wider range of data sources : Not just training with data from recommended scenarios , Data for other scenarios, such as search, also need to be used , This can also provide some information for the recommended scenario explore.
Generate a fixed number of training samples for each user : One we found in practice practical lessons, If the maximum number of samples is fixed for each user , Treat every user equally , avoid loss By minority active user domanate, Can significantly improve the online effect .
Discard sequence information : What we are trying to achieve is to remove the sequence information , Watch videos of the past / History Search query Of embedding Vector weighted average . This is counterintuitive , The possible reason is that the model does not model negative feedback well .
Asymmetric co browsing (asymmetric co-watch) problem : So-called asymmetric co-watch It refers to users browsing videos , It's always sequential , Start looking at some of the more popular , Gradually find subdivided videos . The following figure shows (a) yes hled-out The way , Use context information to estimate a video in the middle ; chart (b) yes predicting next watch The way , Using the above information , Estimate the next video you're browsing . We found that figure (b) The way online A/B test Better performance in . But in fact , Traditional collaborative filtering algorithm , Are implicit sampling graphs (a) Of held-out The way , Ignoring asymmetric browsing patterns .

2.5 Experiments with Features and Depth

Four 、YouTubeDNNN The model code
import torch
from ...basic.layers import MLP, EmbeddingLayer
class YoutubeDNN(torch.nn.Module):
"""The match model mentioned in `Deep Neural Networks for YouTube Recommendations` paper. It's a DSSM match model trained by global softmax loss on list-wise samples. Note in origin paper, it's without item dnn tower and train item embedding directly. Args: user_features (list[Feature Class]): training by the user tower module. item_features (list[Feature Class]): training by the embedding table, it's the item id feature. neg_item_feature (list[Feature Class]): training by the embedding table, it's the negative items id feature. user_params (dict): the params of the User Tower module, keys include:`{"dims":list, "activation":str, "dropout":float, "output_layer":bool`}. sim_func (str): similarity function, includes `["cosine", "dot"]`, default to "cosine". temperature (float): temperature factor for similarity score, default to 1.0. """
def __init__(self, user_features, item_features, neg_item_feature, user_params, sim_func="cosine", temperature=1.0):
super().__init__()
self.user_features = user_features
self.item_features = item_features
self.neg_item_feature = neg_item_feature
self.sim_func = sim_func
self.temperature = temperature
self.user_dims = sum([fea.embed_dim for fea in user_features])
self.embedding = EmbeddingLayer(user_features + item_features)
self.user_mlp = MLP(self.user_dims, output_layer=False, **user_params)
self.mode = None
def forward(self, x):
user_embedding = self.user_tower(x)
item_embedding = self.item_tower(x)
if self.mode == "user":
return user_embedding
if self.mode == "item":
return item_embedding
if self.sim_func == "cosine":
y = torch.cosine_similarity(user_embedding, item_embedding, dim=-1) #[batch_size, 1+n_neg_items, embed_dim]
elif self.sim_func == "dot":
y = torch.mul(user_embedding, item_embedding).sum(dim=1)
else:
raise ValueError("similarity function only support %s, but got %s" % (["cosine", "dot"], self.sim_func))
y = y / self.temperature
return y
def user_tower(self, x):
if self.mode == "item":
return None
input_user = self.embedding(x, self.user_features, squeeze_dim=True) #[batch_size, num_features*deep_dims]
user_embedding = self.user_mlp(input_user).unsqueeze(1) #[batch_size, 1, embed_dim]
if self.mode == "user":
return user_embedding.squeeze(1) #inference embedding mode -> [batch_size, embed_dim]
return user_embedding
def item_tower(self, x):
if self.mode == "user":
return None
pos_embedding = self.embedding(x, self.item_features, squeeze_dim=False) #[batch_size, 1, embed_dim]
if self.mode == "item": #inference embedding mode
return pos_embedding.squeeze(1) #[batch_size, embed_dim]
neg_embeddings = self.embedding(x, self.neg_item_feature,
squeeze_dim=False).squeeze(1) #[batch_size, n_neg_items, embed_dim]
return torch.cat((pos_embedding, neg_embeddings), dim=1) #[batch_size, 1+n_neg_items, embed_dim]
Engineering problems : Global negative sampling
5、 ... and 、YouTube The twin tower model

The paper :Sampling-Bias-Corrected Neural Modeling for Large Corpus Item Recommendations,2019(2016 Version of the upgrade )


6、 ... and 、 model training trick
6.1 In-Batch Negative sampling ( Correction )
6.2 Cosine similarity to find similarity
Equivalent to : Why add L2 norm

6.3 temperature coefficient
temperature coefficient
review :torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss = LogSoftmax + NLLLoss( Please refer to the official documents ).
(1) Loss function in multi classification scenario :
The distribution and API
Law 1 : The determination of each category is regarded as a binary classification problem . Using cross entropy .
To solve the problem of inhibition , Do not output the probability of each category , And each probability is greater than 0 And the sum of probability is 1 Conditions .( Second, we output the distribution , Find one and use 1 Subtract it , Although multi classification can be the same , But in the end 1 Subtract all other probability calculations , It's a bit troublesome to build the calculation diagram ).
Only one of the two terms of cross entropy in the previous two classifications can be 0.

(1)NLLLoss The function evaluates to the following red box :
(2) You can use it directly torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss( Include the following red box calculations in ). Note that on the right is the unique hot coding vector generated by the category .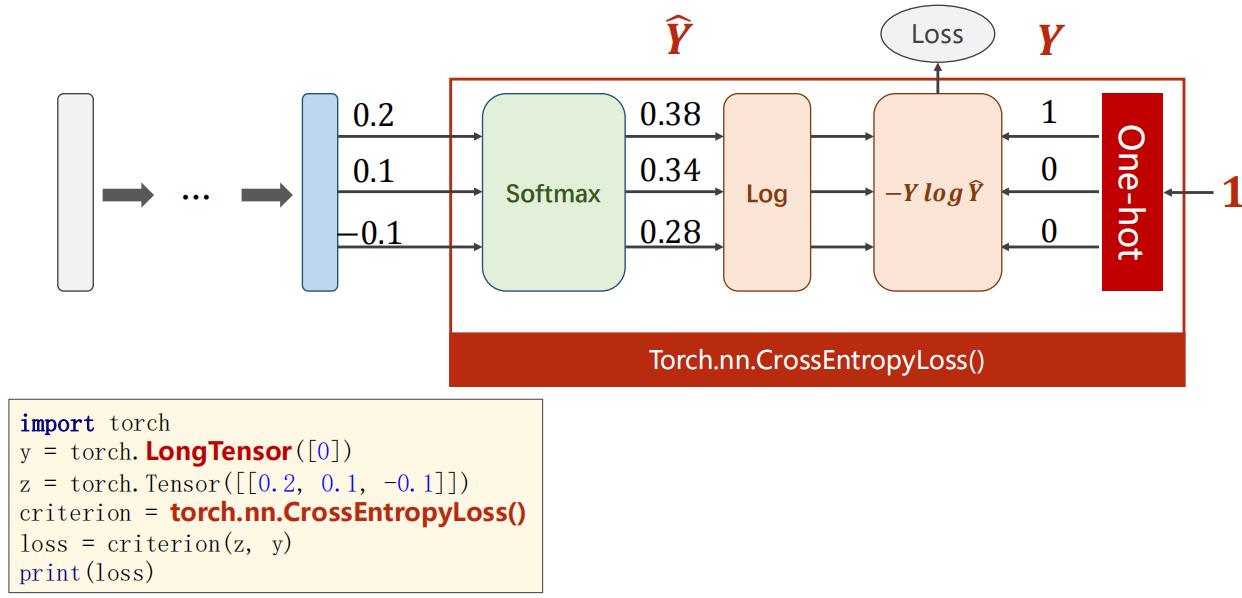
Cross entropy , The last layer of network does not need to be activated , Because at the end of Torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss Activation functions have been included softmax.
(1) Cross entropy handwritten version
import numpy as np
y = np.array([1, 0, 0])
z = np.array([0.2, 0.1, -0.1])
y_predict = np.exp(z) / np.exp(z).sum()
loss = (- y * np.log(y_predict)).sum()
print(loss)
# 0.9729189131256584
(2) Cross entropy pytorch chestnuts 
Cross entropy loss and NLL The difference between losses ( Read the document ):
- https://pytorch.org/doc s/stable/nn.html#crossentropyloss
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#nllloss
- Understand why :CrossEntropyLoss <==> LogSoftmax + NLLLoss
(2) A scene of chestnuts
scene : use List wise How to train ,1 A positive sample ,3 Negative samples ,cosine Similarity as a measure of the training process .
Suppose the current model perfectly predicts a training data , That is, output logits by ( 1 , − 1 , − 1 , − 1 ) (1,-1,-1,-1) (1,−1,−1,−1), be loss It should be very, very small . But at this time, if CrossEntropyLoss, Got Loss yes :
− log ( exp ( 1 ) / ( exp ( 1 ) + exp ( − 1 ) ∗ 3 ) ) = 0.341 -\log (\exp (1) /(\exp (1)+\exp (-1) * 3))=0.341 −log(exp(1)/(exp(1)+exp(−1)∗3))=0.341
But at this time, if you are right logits Divide by the last temperature coefficient temperature = 0.2 =0.2 =0.2, namely logits by ( 5 , − 5 , − 5 (5,-5,-5 (5,−5,−5, -5), after CrossEntropyLoss, Got Loss yes :
− log ( exp ( 5 ) / ( exp ( 5 ) + exp ( − 5 ) ∗ 3 ) ) = 0.016 -\log (\exp (5) /(\exp (5)+\exp (-5) * 3))=0.016 −log(exp(5)/(exp(5)+exp(−5)∗3))=0.016
This will result in a negligible Loss 了 . Yes logits Except the last one temperature The role of is to expand logits The upper and lower bounds of each element in , Pull back softmax The sensitive range of the operation . Generally in the industry L2 Norm And temperature Use it with .
7、 ... and 、youtube Twin tower model code
8、 ... and 、Facebook The twin tower model

Nine 、 Precautions for project implementation
9.1 Negative sample construction summary

9.2 Recall and sorting are different

9.3 Other twin tower models and future developments


Reference
[1] SysRec2016 | Deep Neural Networks for YouTube Recommendations
[2] borrow Youtube The paper , Talk about the eight quintessence of the twin tower model
[3] Sampling-Bias-Corrected Neural Modeling for Large Corpus Item Recommendations,2019(2016 Version of the upgrade )
[4] YouTube Intensive reading of two tower model paper with sampling correction
[5] https://github.com/datawhalechina/torch-rechub/tree/main/torch_rechub/models/matching
[6] The twin towers :https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Tt4y1W7qE?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=3d707248207c841de4a64a0ffce83324
[7] youtube Two towers :https://datawhalechina.github.io/fun-rec/#/ch02/ch2.1/ch2.1.2/YoutubeTwoTower
[8] Shallow dream deepmatch Code reappearance :https://github.com/shenweichen/AlgoNotes
[9] Youtube Double tower model is recommended ——SBCNM
[10] Recall model YoutubeDNN, DSSM
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

为什么ping不通,而traceroute却可以通

One article explains in detail | those things about growth

【NOI模拟赛】给国与时光鸡(构造)

À propos de ETL il suffit de lire cet article, trois minutes pour vous faire comprendre ce qu'est ETL

什么是图神经网络?图神经网络有什么用?

MySQL | 视图《康师傅MySQL从入门到高级》笔记

pymysql 向MySQL 插入数据无故报错

MySQL 因字符集问题插入中文数据时提示代码 :1366
![打印出来的对象是[object object],解决方法](/img/fc/9199e26b827a1c6304fcd250f2301e.png)
打印出来的对象是[object object],解决方法

MySQL | 存储《康师傅MySQL从入门到高级》笔记
随机推荐
“不平凡的代理初始值设定不受支持”,出现的原因及解决方法
【PyTorch基础教程30】DSSM双塔模型代码解析
À propos de ETL il suffit de lire cet article, trois minutes pour vous faire comprendre ce qu'est ETL
2022 spring recruitment interview summary
Win11 blank when using VIM to view content in cmder
饼状统计图,带有标注线,都可以自行设定其多种参数选项
mysql写的代码数据 增删查改等等
一文详解|增长那些事儿
数据中台:民生银行的数据中台实践方案
【团队管理】测试团队绩效管理的25点小建议
OpenCV每日函数 结构分析和形状描述符(7) 寻找多边形(轮廓)/旋转矩形交集
更改SSH端口号
Xtrabackup for data backup
图片工具
Introduction to data platform
Change SSH port number
数据中台:数据治理概述
JS to find and update the specified value in the object through the key
数据中台:中台架构及概述
K8S部署高可用postgresql集群 —— 筑梦之路