当前位置:网站首页>Dpdk - tcp/udp protocol stack server implementation (II)
Dpdk - tcp/udp protocol stack server implementation (II)
2022-06-26 06:14:00 【Ah Jie's small fish pond】
List of articles
One 、 summary
stay 《DPDK——TCP/UDP The protocol stack server implements ( One )》 Has been described in TCP/UDP The framework and basic information of the simple protocol stack project , The work to be completed in this article is as follows :
- udp Package structure design , Include udp Control block structure 、 Protocol stack and application layer transport packet structure
- ARP Table processing
- UDP Socket function implementation
- UDP Package processing
Two 、UDP data structure
As shown in the figure below ,UDP The data structure of is mainly divided into two parts : Data transmission block and control block .
UDP Control blocks are created at the application layer socket Generated at the same time , It mainly includes a send queue and a receive queue , Thread synchronization variables , And related parameters , as follows :
struct localhost
{
int fd;
uint32_t localip; // ip --> mac
unsigned char localmac[RTE_ETHER_ADDR_LEN];
uint16_t localport;
unsigned char protocol;
struct rte_ring *sndbuf;
struct rte_ring *rcvbuf;
struct localhost *prev;
struct localhost *next;
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
};
The transport block acts as a protocol stack to UDP Data encapsulation of application communication ,DPDK The protocol stack receives the data sent by the network card , Encapsulate the data according to the structure of the transmission block , And send it to UDP The receive queue in the control block , The structure is as follows :
struct offload
{
uint32_t sip;
uint32_t dip;
uint16_t sport;
uint16_t dport;
int protocol;
unsigned char *data;
uint16_t length;
};
3、 ... and 、arp Table processing
In network transmission ,ARP The agreement bears “ Escorting the last kilometer of the packet ” The task of , Because after the packet arrives at the LAN ,ip Address as an unreliable identifier , Obviously, there is no guarantee that the packets will be delivered to the destination host , At this time, we need to know about the host MAC Address . The specific method is to broadcast to all devices under the same router in the LAN , The content is “ Which of you is ip by xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx My host ? Please let you know as soon as you see the news MAC Address , Your express has arrived !”
therefore , This project must also maintain a ip and mac The mapping of arp surface , In this way, packets can be sent to the other host accurately .
maintain arp The table is mainly in two places : When the protocol stack receives a network card packet, it stores ip and mac Address information ; Before the protocol stack sends packets , Inquire about arp surface , If there is no mac Address , Then broadcast first arp package .
The main functions are as follows :
int ng_arp_entry_insert(uint32_t ip, unsigned char *mac)
{
struct arp_table *pstTbl = arp_table_instance();
struct arp_entry *pstEntry = NULL;
unsigned char *pstHwaddr = NULL;
pstHwaddr = ng_get_dst_macaddr(ip);
if(pstHwaddr == NULL)
{
pstEntry = rte_malloc("arp_entry", sizeof(struct arp_entry), 0);
if (pstEntry)
{
memset(pstEntry, 0, sizeof(struct arp_entry));
pstEntry->ip = ip;
rte_memcpy(pstEntry->hwaddr, mac, RTE_ETHER_ADDR_LEN);
pstEntry->type = 0;
pthread_spin_lock(&pstTbl->spinlock);
LL_ADD(pstEntry, pstTbl->entries);
pstTbl->count ++;
pthread_spin_unlock(&pstTbl->spinlock);
}
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Four 、UDP Socket function implementation
3.1 socket function
This function is mainly used to obtain fd、 Create control block .
int nsocket(__attribute__((unused)) int domain, int type, __attribute__((unused)) int protocol)
{
int iFd;
struct localhost *pstHost;
pthread_cond_t pctCond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_mutex_t pmtMutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
iFd = get_fd_frombitmap();
if(type == SOCK_DGRAM) // udp
{
pstHost = rte_malloc("localhost", sizeof(struct localhost), 0);
if(pstHost == NULL)
{
printf("[%s][%d]: rte_malloc fail!\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
memset(pstHost, 0x00, sizeof(struct localhost));
pstHost->fd = iFd;
pstHost->protocol = IPPROTO_UDP;
pstHost->rcvbuf = rte_ring_create("recv buffer", D_RING_SIZE, rte_socket_id(), RING_F_SP_ENQ | RING_F_SC_DEQ);
if (pstHost->rcvbuf == NULL)
{
printf("[%s][%d]: rte_ring_create fail!\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
rte_free(pstHost);
return -1;
}
pstHost->sndbuf = rte_ring_create("send buffer", D_RING_SIZE, rte_socket_id(), RING_F_SP_ENQ | RING_F_SC_DEQ);
if (pstHost->sndbuf == NULL)
{
printf("[%s][%d]: rte_ring_create fail!\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
rte_ring_free(pstHost->rcvbuf);
rte_free(pstHost);
return -1;
}
rte_memcpy(&pstHost->cond, &pctCond, sizeof(pthread_cond_t));
rte_memcpy(&pstHost->mutex, &pmtMutex, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
LL_ADD(pstHost, g_pstHost);
}
return iFd;
}
3.2 bind function
bind The task of the function is to put ip And port information bound to socket Function to create a control block structure .
int nbind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, __attribute__((unused)) socklen_t addrlen)
{
void *info = NULL;
info = get_hostinfo_fromfd(sockfd);
if(info == NULL)
return -1;
struct localhost *pstHostInfo = (struct localhost *)info;
if(pstHostInfo->protocol == IPPROTO_UDP)
{
const struct sockaddr_in *pstAddr = (const struct sockaddr_in *)addr;
pstHostInfo->localport = pstAddr->sin_port;
rte_memcpy(&pstHostInfo->localip, &pstAddr->sin_addr.s_addr, sizeof(uint32_t));
rte_memcpy(pstHostInfo->localmac, &g_stCpuMac, RTE_ETHER_ADDR_LEN);
}
return 0;
}
3.3 recvfrom function
The current implementation of recvfrom The function is blocking , Using conditional variables + The mutex waits for the data in the receive queue to arrive .
ssize_t nrecvfrom(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, __attribute__((unused)) int flags,
struct sockaddr *src_addr, __attribute__((unused)) socklen_t *addrlen)
{
struct localhost *pstHostInfo = NULL;
struct offload *pstOffLoad = NULL;
struct sockaddr_in *pstAddr = NULL;
unsigned char *pucPtr = NULL;
int iLen = 0;
int iRet = -1;
pstHostInfo = (struct localhost *)get_hostinfo_fromfd(sockfd);
if(pstHostInfo == NULL)
return -1;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pstHostInfo->mutex);
while((iRet = rte_ring_mc_dequeue(pstHostInfo->rcvbuf, (void**)&pstOffLoad)) < 0)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&pstHostInfo->cond, &pstHostInfo->mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pstHostInfo->mutex);
pstAddr = (struct sockaddr_in *)src_addr;
pstAddr->sin_port = pstOffLoad->sport;
rte_memcpy(&pstAddr->sin_addr.s_addr, &pstOffLoad->sip, sizeof(uint32_t));
if(len < pstOffLoad->length)
{
rte_memcpy(buf, pstOffLoad->data, len);
pucPtr = rte_malloc("unsigned char *", pstOffLoad->length - len, 0);
rte_memcpy(pucPtr, pstOffLoad->data + len, pstOffLoad->length - len);
pstOffLoad->length -= len;
rte_free(pstOffLoad->data);
pstOffLoad->data = pucPtr;
rte_ring_mp_enqueue(pstHostInfo->rcvbuf, pstOffLoad);
return len;
}
iLen = pstOffLoad->length;
rte_memcpy(buf, pstOffLoad->data, pstOffLoad->length);
rte_free(pstOffLoad->data);
rte_free(pstOffLoad);
return iLen;
}
3.4 sendto function
sento The function encapsulates the data to be sent into a transmission block , Put it in the send queue , Send the protocol stack to the network card .
ssize_t nsendto(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, __attribute__((unused)) int flags,
const struct sockaddr *dest_addr, __attribute__((unused)) socklen_t addrlen)
{
struct localhost *pstHostInfo = NULL;
struct offload *pstOffLoad = NULL;
const struct sockaddr_in *pstAddr = (const struct sockaddr_in *)dest_addr;
pstHostInfo = (struct localhost *)get_hostinfo_fromfd(sockfd);
if(pstHostInfo == NULL)
return -1;
pstOffLoad = rte_malloc("offload", sizeof(struct offload), 0);
if (pstOffLoad == NULL)
return -1;
pstOffLoad->dip = pstAddr->sin_addr.s_addr;
pstOffLoad->dport = pstAddr->sin_port;
pstOffLoad->sip = pstHostInfo->localip;
pstOffLoad->sport = pstHostInfo->localport;
pstOffLoad->length = len;
/* struct in_addr addr; addr.s_addr = pstOffLoad->dip; printf("nsendto ---> src: %s:%d \n", inet_ntoa(addr), ntohs(pstOffLoad->dport)); */
pstOffLoad->data = rte_malloc("unsigned char *", len, 0);
if (pstOffLoad->data == NULL) {
rte_free(pstOffLoad);
return -1;
}
rte_memcpy(pstOffLoad->data, buf, len);
rte_ring_mp_enqueue(pstHostInfo->sndbuf, pstOffLoad);
return len;
}
3.5 close function
close The function releases the created control block .
int nclose(int fd)
{
void *info = NULL;
info = (struct localhost *)get_hostinfo_fromfd(fd);
if(info == NULL)
return -1;
struct localhost *pstHostInfo = (struct localhost *)info;
if(pstHostInfo->protocol == IPPROTO_UDP)
{
LL_REMOVE(pstHostInfo, g_pstHost);
if (pstHostInfo->rcvbuf)
rte_ring_free(pstHostInfo->rcvbuf);
if (pstHostInfo->sndbuf)
rte_ring_free(pstHostInfo->sndbuf);
rte_free(pstHostInfo);
set_fd_frombitmap(fd);
}
return 0;
}
5、 ... and 、UDP Package processing
5.1 Protocol stack receive
The protocol stack always receives packets from the network card , We need to filter out the required protocol data , This is mainly through the network layer IP Data header to analyze , The code is as follows :
int pkt_process(void *arg)
{
struct rte_mempool *pstMbufPool;
int iRxNum;
int i;
struct rte_mbuf *pstMbuf[32];
struct rte_ether_hdr *pstEthHdr;
struct rte_ipv4_hdr *pstIpHdr;
pstMbufPool = (struct rte_mempool *)arg;
while(1)
{
iRxNum = rte_ring_mc_dequeue_burst(g_pstRingIns->pstInRing, (void**)pstMbuf, D_BURST_SIZE, NULL);
if(iRxNum <= 0)
continue;
for(i = 0; i < iRxNum; ++i)
{
pstEthHdr = rte_pktmbuf_mtod_offset(pstMbuf[i], struct rte_ether_hdr *, 0);
if (pstEthHdr->ether_type == rte_cpu_to_be_16(RTE_ETHER_TYPE_IPV4)) //IPv4: 0800
{
pstIpHdr = (struct rte_ipv4_hdr *)(pstEthHdr + 1);
// Maintain a arp surface
ng_arp_entry_insert(pstIpHdr->src_addr, pstEthHdr->s_addr.addr_bytes);
if(pstIpHdr->next_proto_id == IPPROTO_UDP) // udp
{
// udp process
udp_process(pstMbuf[i]);
}
else if(pstIpHdr->next_proto_id == IPPROTO_TCP) // tcp
{
printf("tcp_process ---\n");
tcp_process(pstMbuf[i]);
}
}
}
// to send
udp_out(pstMbufPool);
tcp_out(pstMbufPool);
}
return 0;
}
among , about UDP Packet specific , If the application layer has created a control block , The protocol stack is mainly composed of data , Then it is sent to the receiving queue in the control block , And notify blocking at recvfrom Function in the application layer .
int udp_process(struct rte_mbuf *pstUdpMbuf)
{
struct rte_ipv4_hdr *pstIpHdr;
struct rte_udp_hdr *pstUdpHdr;
struct localhost *pstHost;
struct offload *pstOffLoad;
pstIpHdr = rte_pktmbuf_mtod_offset(pstUdpMbuf, struct rte_ipv4_hdr *, sizeof(struct rte_ether_hdr));
pstUdpHdr = (struct rte_udp_hdr *)(pstIpHdr + 1);
struct in_addr addr;
addr.s_addr = pstIpHdr->src_addr;
printf("udp_process ---> src: %s:%d \n", inet_ntoa(addr), ntohs(pstUdpHdr->src_port));
pstHost = get_hostinfo_fromip_port(pstIpHdr->dst_addr, pstUdpHdr->dst_port, pstIpHdr->next_proto_id);
if (pstHost == NULL)
{
rte_pktmbuf_free(pstUdpMbuf);
return -3;
}
pstOffLoad = rte_malloc("offload", sizeof(struct offload), 0);
if (pstOffLoad == NULL)
{
rte_pktmbuf_free(pstUdpMbuf);
return -1;
}
pstOffLoad->dip = pstIpHdr->dst_addr;
pstOffLoad->sip = pstIpHdr->src_addr;
pstOffLoad->sport = pstUdpHdr->src_port;
pstOffLoad->dport = pstUdpHdr->dst_port;
pstOffLoad->protocol = IPPROTO_UDP;
pstOffLoad->length = ntohs(pstUdpHdr->dgram_len);
pstOffLoad->data = rte_malloc("unsigned char*", pstOffLoad->length - sizeof(struct rte_udp_hdr), 0);
if (pstOffLoad->data == NULL)
{
rte_pktmbuf_free(pstUdpMbuf);
rte_free(pstOffLoad);
return -2;
}
rte_memcpy(pstOffLoad->data, (unsigned char *)(pstUdpHdr+1), pstOffLoad->length - sizeof(struct rte_udp_hdr));
rte_ring_mp_enqueue(pstHost->rcvbuf, pstOffLoad); // recv buffer
pthread_mutex_lock(&pstHost->mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&pstHost->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pstHost->mutex);
rte_pktmbuf_free(pstUdpMbuf);
return 0;
}
5.2 Protocol stack sending
The protocol stack traverses the application layer control block , If there is data in the send queue , The task of the protocol stack is to accurately send to the network card , This includes broadcasting arp package 、 Assembly standard UDP Data packets , The code is as follows :
int udp_out(struct rte_mempool *pstMbufPool)
{
struct localhost *pstHost;
for(pstHost = g_pstHost; pstHost != NULL; pstHost = pstHost->next)
{
struct offload *pstOffLoad = NULL;
int iSendCnt = rte_ring_mc_dequeue(pstHost->sndbuf, (void **)&pstOffLoad);
if(iSendCnt < 0)
continue;
struct in_addr addr;
addr.s_addr = pstOffLoad->dip;
printf("udp_out ---> src: %s:%d \n", inet_ntoa(addr), ntohs(pstOffLoad->dport));
unsigned char *dstmac = ng_get_dst_macaddr(pstOffLoad->dip); // Query the opposite end mac Address
if (dstmac == NULL) // First broadcast a message arp The package determines the opposite end mac Address
{
struct rte_mbuf *pstArpbuf = ng_send_arp(pstMbufPool, RTE_ARP_OP_REQUEST, g_aucDefaultArpMac,
pstOffLoad->sip, pstOffLoad->dip);
rte_ring_mp_enqueue_burst(g_pstRingIns->pstOutRing, (void **)&pstArpbuf, 1, NULL);
rte_ring_mp_enqueue(pstHost->sndbuf, pstOffLoad); // To take out udp Data is written to the queue again
}
else
{
struct rte_mbuf *pstUdpbuf = ng_udp_pkt(pstMbufPool, pstOffLoad->sip, pstOffLoad->dip,
pstOffLoad->sport, pstOffLoad->dport, pstHost->localmac,
dstmac, pstOffLoad->data, pstOffLoad->length);
rte_ring_mp_enqueue_burst(g_pstRingIns->pstOutRing, (void **)&pstUdpbuf, 1, NULL);
if (pstOffLoad->data != NULL)
rte_free(pstOffLoad->data);
rte_free(pstOffLoad);
}
}
return 0;
}
5.3 Project address and related articles
Project address :https://github.com/hjlogzw/DPDK-TCP-UDP_Protocol_Stack
DPDK——TCP/UDP The protocol stack server implements ( One )
Background server
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Vs2022 offline installation package download and activation

Younger sister Juan takes you to learn JDBC -- two days' Sprint Day2
![Selective search for object recognition paper notes [image object segmentation]](/img/cf/d3b08d41083f37c164b26a96b989c9.png)
Selective search for object recognition paper notes [image object segmentation]
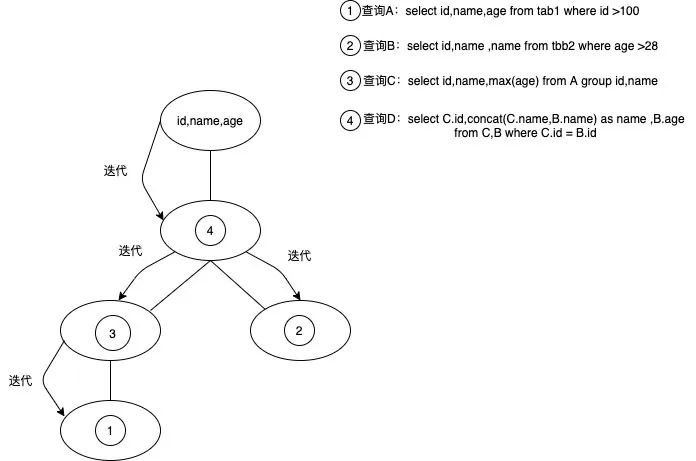
【Spark】Spark SQL 字段血缘如何实现

Logstash - logstash sends an alarm email to email

Cython入门

Thinking and summary of technical ability

Basic construction of SSM framework

Underlying principle of MySQL index

Logstash——Logstash向Email发送告警邮件
随机推荐
Definition of Halcon hand eye calibration
Work accumulation - problems encountered in using ThreadLocal in web requests
Import / export function implementation
Household accounting procedures (the second edition includes a cycle)
Data visualization practice: Experimental Report
Ppt template crawler case
ES6的搭配环境
Print bit information of numbers
numpy.exp()
跨域的五种解决方案
GoF23—原型模式
【群内问题学期汇总】初学者的部分参考问题
Machine learning 05: nonlinear support vector machines
numpy.tile()
COW读写复制机制在Linux,Redis ,文件系统中的应用
tf. nn. top_ k()
05. basic data type - Dict
numpy. log
Application of cow read / write replication mechanism in Linux, redis and file systems
事务与消息语义