当前位置:网站首页>Embedded c learning notes
Embedded c learning notes
2022-06-26 01:35:00 【m0_ forty-six million three hundred and twenty-one thousand one】
Catalog
1. 2 Base number 、8 Base number 、16 The conversion of base systems
Binary representation :0B
Hexadecimal representation :0X
Hexadecimal said

2. Base conversion method

For binary to hexadecimal, a hexadecimal equals four bits of binary , adopt 8421 Code calculation
3. C Language structure
meaning
The ability to assemble multiple different data into one type ( It can contain multiple different data types )
Structure structure

Other uses of structs
Can pass typedef To define the structure , And define other parameters through this structure 
4. excent usage
extern yes C A key word in a language , Usually used before variable name or function name , The function is to explain “ This variable / Functions are defined elsewhere , To quote... Here ”,extern Most of this keyword should be in the storage type of variables
External variables ( Global variables )extern---- Global static storage
Standard definition format :extern Type name Variable name ;
effect
Use this variable in advance , Or reference variables in other files
Reference resources :extern( External variables )
5. const Usage method
effect
You can define an immutable variable , An error will be reported when there are other assignment operations ( Generally, this variable is capitalized to distinguish )
const int MaxNum = 100; // Maximum class size
const And a pointer
const int *p1;
int const *p2;
int * const p3;
In the last case , The pointer is read-only , That is to say p3 The value of itself cannot be modified ; In the first two cases , The data pointed to by the pointer is read-only , That is to say p1、p2 The value of itself can be modified ( Point to different data ), But the data they point to cannot be modified .
const And function parameters
stay C In language , Individually define const Variables have no obvious advantage , Totally usable #define Command instead of .const Usually used in function parameters , If the parameter is a pointer , To prevent modification of the data pointed to by the pointer inside the function , You can use it const To limit .
const He Fei const Type conversion
When a pointer variable str1 By const When the limit , And it's like const char *str1 This form , Indicates that the data pointed to by the pointer cannot be modified ; If you will str1 Assign a value to another one that is not const Decorated pointer variable str2, There's a risk . Because by str1 Can't modify data , And after assignment, it passes str2 Can modify the data , The meaning has changed , So the compiler doesn't advocate this behavior , Will give errors or warnings .
in other words ,const char * and char * It's a different type , Can't be const char * The data of type is assigned to char * Variable of type . But the reverse is possible , The compiler allows you to char * The data of type is assigned to const char * Variable of type .
This limitation is easy to understand ,char * The data pointed to has read and write permissions , and const char * The data pointed to has only read permission , Lowering data permissions will not cause any problems , However, increasing the authority of data may lead to danger .
C The parameters of many functions in the language standard library are const Limit , But we didn't pay attention to this problem in the previous coding process , Often non const Data of type is passed to const Type parameters , This has never caused any side effects , The reason is the above mentioned , Will not const Type conversion to const Type is allowed .
Reference resources C Language const A detailed explanation of the use of ,C Detailed definition of language constants
6. The pointer (* usage )
1. Defining a pointer requires *( as follows , Defines the pointer that should be , be called a)
2. When taking values, you need to use *( as follows , Need to use * To represent the address of the data )
3. For a defined pointer , no need * Represents the position of the pointer , Not the data 
Reference to pointer variable
printf("a=%d\n",a); // By name , Direct access to variables a Space ( Read )
printf("a=%d\n",*p); // Through the address , Indirect access to variables a Space ( Read )
*p=6;// Equivalent to a=6; Indirect access to a Corresponding space ( save )
printf("a=%d\n",*p);
Wild pointer ( Misquote )
int *pi,a; //pi uninitialized , No legal direction , by “ wild ” The pointer
*pi=3; // Runtime error ! Not right ” wild ” The space pointed to by the pointer is used for saving . This statement attempts to put 3 Deposit in “ wild ” The pointer pi In the random space referred to , Run time errors will occur .
a=*pi; // Runtime error ! Not right ” wild ” The space fetch operation pointed to by the pointer . This statement attempts to start from “ wild ” The pointer pi Fetch data from the indicated space , Then assign it to the variable a It will also generate runtime errors .
/* Quote... Correctly */
// & To get a The address of
pi=&a;// Give Way pi There is a legal point ,pi Point to a The space corresponding to the variable
*pi=3;// hold 3 Indirect deposit pi The variable pointed to a The corresponding space
The difference between pointer and multiplication
The following differences :a multiply b,1 multiply b,a Add the pointer b Value ,a Multiply by the pointer b Value 
7. Structure pointer
Just like ordinary variables , The structure pointer is the position of the represented structure , as follows :
# include <stdio.h>
# include <string.h>
struct AGE
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct STUDENT
{
char name[20]; // full name
int num; // Student number
struct AGE birthday; // Birthday
float score; // fraction
};
int main(void)
{
struct STUDENT student1; /* use struct STUDENT Structure type defines structure variables student1*/
struct STUDENT *p = NULL; /* Define a point struct STUDENT Pointer variables of struct type p*/
p = &student1; /*p Point to the structure variable student1 The first address , That is, the address of the first member */
strcpy((*p).name, " Xiao Ming "); //(*p).name Equivalent to student1.name
(*p).birthday.year = 1989;
(*p).birthday.month = 3;
(*p).birthday.day = 29;
(*p).num = 1207041;
(*p).score = 100;
printf("name : %s\n", (*p).name); //(*p).name Can not write p
printf("birthday : %d-%d-%d\n", (*p).birthday.year, (*p).birthday.month, (*p).birthday.day);
printf("num : %d\n", (*p).num);
printf("score : %.1f\n", (*p).score);
return 0;
}
It can also be useful -> To point to a special variable of a pointer , as follows :
# include <stdio.h>
# include <string.h>
struct AGE
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct STUDENT
{
char name[20]; // full name
int num; // Student number
struct AGE birthday; /* use struct AGE Structure type defines structure variables birthday, Birthday */
float score; // fraction
};
int main(void)
{
struct STUDENT student1; /* use struct STUDENT Structure type defines structure variables student1*/
struct STUDENT *p = NULL; /* Definition struct STUDENT Pointer variables of struct type p*/
p = &student1; /*p Point to the structure variable student1 The first address , That is, the address of the first item */
strcpy(p->name, " Xiao Ming ");
p->birthday.year = 1989;
p->birthday.month = 3;
p->birthday.day = 29;
p->num = 1207041;
p->score = 100;
printf("name : %s\n", p->name); //p->name Can not write p
printf("birthday : %d-%d-%d\n", p->birthday.year, p->birthday.month, p->birthday.day);
printf("num : %d\n", p->num);
printf("score : %.1f\n", p->score);
return 0;
}
Reference resources : Structure pointer description
8. Macro definition
Macro definition is a common preprocessing instruction , That is to use “ identifier ” To express “ Replace list ” The content in . The identifier is called the macro name , In the process of pretreatment , The preprocessor takes all the macro names in the source program , Replace with the contents of the replacement list in the macro definition .
There are parameter macro definitions
The format is :
#define identifier Replace list
The substitution list can be a numeric constant 、 character constants 、 String constants, etc , Therefore, a macro definition can be understood as using an identifier to represent a constant , Or symbolic constant .
Macro definition with parameters
The definition format of substitute meal macro is :
#define identifier ( Parameters 1, Parameters 2,..., Parameters n) Replace list
Reference resources Macro definition
9.Typedef
Define a new type name for the basic data type
All basic types by default can be used typedef Keyword to redefine the type nameFor custom data types ( Structure 、 Common body and enumeration type ) Define concise type names

Define concise type names for arrays
typedef int INT_ARRAY_100[100];
INT_ARRAY_100 arr;
- Define concise names for pointers
typedef char* PCHAR;
PCHAR pa;
Reference resources typedef
10. Conditional compilation
Conditional compilation means that the preprocessor compiles instructions according to conditions , Conditionally select part of the source code as the output , Send it to the compiler to compile . It's mainly for selective operation , Prevent macros from replacing content ( Such as documents, etc ) The repetition of contains . The common conditional compilation instructions are shown in the table .
| Conditional compilation instructions | explain |
|---|---|
| #if | If the condition is true , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #elif | If the previous condition is false , And the condition is true , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #else | If the previous conditions are all false , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #endif | End the corresponding conditional compilation instructions |
| #ifdef | If the macro has been defined , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #ifndef | If the macro is not defined , Then perform the corresponding operation |
11. Memory operations
One 、malloc/calloc
malloc and calloc Can allocate memory areas , but malloc Only one memory area can be requested at a time ,calloc You can apply for multiple memory areas at a time . in addition calloc The allocated memory area will be initially converted into 0,malloc No initialization .
Two 、 malloc/calloc
free Can be released by malloc or calloc Memory allocated by the memory allocation function . When the program is large , You may have to dynamically allocate memory multiple times during , If not released in time , The program will take up a lot of memory .
3、 ... and 、 memset
memset hold buffer Before the memory area referred to count Bytes set to a character ASCLL value . Generally used to give an array , String and other types of assignment .
Four 、 memcpy
memcpy Will be able to src The memory area referred to is copied count Byte to dest The memory area referred to . If count Than src The number of bytes is large ,strcpy Can copy ’/0’ After that . it is to be noted that dest and src Don't overlap .
memcpy Just copy memory space , Do not deal with spatial overlap .
边栏推荐
- FIFO code implemented in C language
- MOS管防倒灌电路设计及其过程分析
- 2022安徽省安全员C证考试练习题模拟考试平台操作
- Data analysis slicer, PivotTable and PivotChart (necessary in the workplace)
- CityJSON
- Zhihuijia - full furniture function
- 原生DOM与虚拟DOM
- QT cmake pure C code calls the system console to input scanf and Chinese output garbled code
- 填鸭数据即时收集解决方案资源
- 2022资料员-通用基础(资料员)考试模拟100题及在线模拟考试
猜你喜欢

从查询数据库性能优化谈到redis缓存-谈一谈缓存的穿透、雪崩、击穿

Design and process analysis of anti backflow circuit for MOS transistor

数组中的第K个最大元素

Remote incremental synchronization artifact Rsync
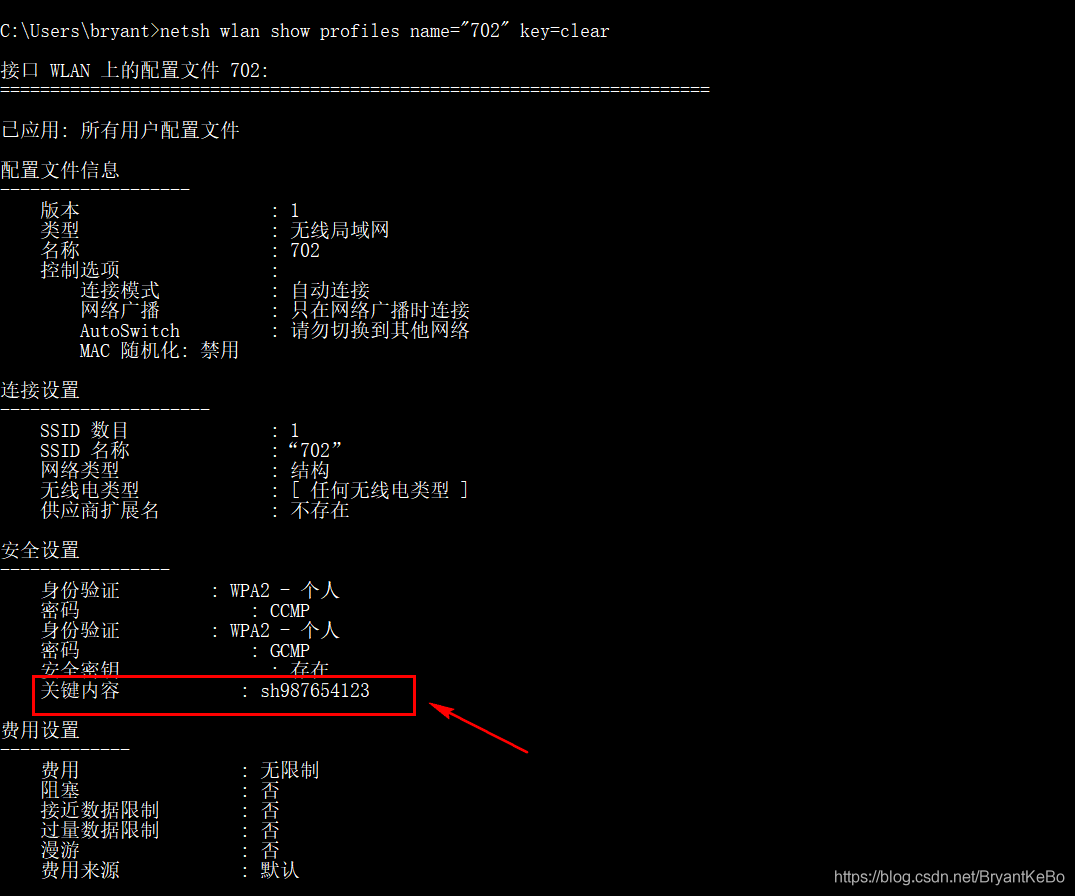
通过电脑获取WIFI密码(只能连接过的WiFi)

MySQL图书借阅系统项目数据库建库表语句(组合主键、外键设置)

--都市修炼手册之SQL-- 第一章 基础复习

Return value is object type method call equals()

Redis strings command

FIFO code implemented in C language
随机推荐
JSON实例(一)
剑指 Offer II 096. 字符串交织
Technical foreword - metauniverse
Essence and thoughts of 30 lectures on product thinking
WIN10系统C盘清理策略
如何有效地推广产品
Web信息收集,互联网上的裸奔者
Solution to MySQL error code 2003
Oracle database complete uninstallation steps (no screenshot)
15 `bs object Node name Node name String` get nested node content
Laravel basic course routing and MVC - routing
Development and monitoring of fusion experiment pulse power supply by LabVIEW
2021-1-15 摸魚做的筆記Ctrl+c /v來的
Etcd database source code analysis cluster communication initialization
JSON instance (I)
Nacos registry
Enlightenment Q & A
Computer network knowledge summary (interview)
LabVIEW开发监控聚变实验脉冲电源
Is it safe to open a fund account? Are there any risks?