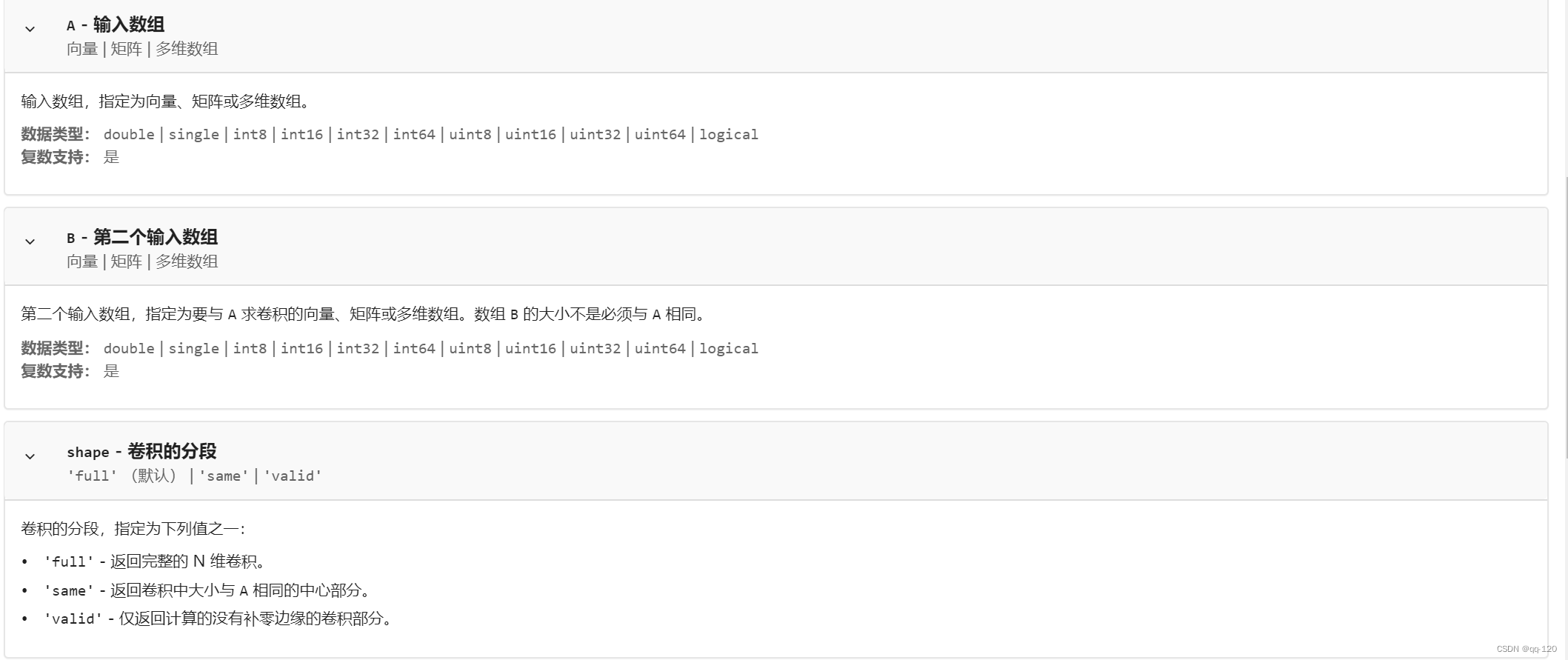
当前位置:网站首页>Make learning pointer easier (2)
Make learning pointer easier (2)
2022-06-27 12:47:00 【Xiao Zhang, China Academy of Aeronautics and Astronautics】
List of articles
Preface
In depth study of pointer ( Two )
One 、 Function pointer array
An array is a storage space for the same type of data , So we've learned about pointer arrays , You can read my last blog if you don't understand ; Make learning pointer easier ( One )
such as :int* arr[10]; // Each element of the array is int *
So we can understand the function pointer array , The first must be an array , Second, the array element type is function pointer ( Address ); Then save the address of the function in an array , This array is called the function pointer array , How to define the array of function pointers ?
int (* parr1[10])();
int * parr2 [10] ();
int ( * )() parr3[10];
Look at these three , That's a function pointer array ? The answer is :parr1 ,parr1 The first and [] combination , explain parr1 It's an array , What is the content of the array ? yes int (*)() Function pointer of type . Note that the array name should be placed in the band * In parentheses ,int ( *parr1[10])(); So the first one is the function pointer array ; Purpose of function pointer array : Transfer table ;
1.1 The purpose of the function pointer ( The use of function pointers in the last blog )
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int sub(int a, int b)
{
return a - b;
}
int mul(int a, int b)
{
return a*b;
}
int div(int a, int b)
{
return a / b;
}
int main()
{
int x, y;
int input = 1;
int ret = 0;
do
{
printf( "*************************\n" );
printf( " 1:add 2:sub \n" );
printf( " 3:mul 4:div \n" );
printf( "*************************\n" );
printf( " Please select :" );
scanf( "%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf( " Enter the operands :" );
scanf( "%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = add(x, y);
printf( "ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 2:
printf( " Enter the operands :" );
scanf( "%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = sub(x, y);
printf( "ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 3:
printf( " Enter the operands :" );
scanf( "%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = mul(x, y);
printf( "ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 4:
printf( " Enter the operands :" );
scanf( "%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = div(x, y);
printf( "ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 0:
printf(" Exit procedure \n");
breark;
default:
printf( " Wrong choice \n" );
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
Select from above 1~4 There are a lot of duplicate or very similar code , If you add more functions to the computer , You have to add a lot of code , There are a lot of the same duplicate code , We can package it into a function to implement the function, so as to avoid writing the same code repeatedly ; So each of these functions is a function , How to integrate into one function to call all function functions ?
void computer(int (*cmp)(int x,int y)){
printf( " Enter the operands :" );
scanf( "%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = cmp(x, y);
printf( "ret = %d\n", ret);
}
I think this function can solve the problem , below switch Statement to call this function directly , Just transfer the function function , One thing to note is that the return value must match , Parameters are of the same type , Here are two int Parameters of type , The return value is int type , Such a function can be passed to perform operations !!! This is a function pointer ;
1.2 Purpose of function pointer array
Or the big code above , Use a function pointer array to apply , Use arrays for those function functions , See how the code implements
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int sub(int a, int b)
{
return a - b;
}
int mul(int a, int b)
{
return a*b;
}
int div(int a, int b)
{
return a / b;
}
int main()
{
int x, y;
int input = 1;
int ret = 0;
int(*p[5])(int x, int y) = {
0, add, sub, mul, div }; // Transfer table
while (input)
{
printf( "*************************\n" );
printf( " 1:add 2:sub \n" );
printf( " 3:mul 4:div \n" );
printf( "*************************\n" );
printf( " Please select :" );
scanf( "%d", &input);
if ((input <= 4 && input >= 1))
{
printf( " Enter the operands :" );
scanf( "%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = (*p[input])(x, y);
}
else
printf( " Incorrect input \n" );
printf( "ret = %d\n", ret);
}
return 0;
}
Do not use the dereference when calling * Symbols are OK , direct p [input]) ( x , y ); This is a use of our function pointer array , Also called transfer table ;
Two , A pointer to an array of function pointers
This is the pointer , Then it saves the address of the function pointer array , This is just to understand , Know how to write , Just understand it ;
void test(const char* str)
{
printf(“%s\n”, str);
}
int main()
{
// A function pointer pfun
void ( * pfun )( const char * ) = test;
// An array of function pointers pfunArr
void ( * pfunArr[5] )( const char * str);
pfunArr[0] = test;
// Pointer to function array pfunArr The pointer to ppfunArr
void ( * ( * ppfunArr)[5] ) (const char * ) = &pfunArr;
return 0;
}
3、 ... and , Callback function
A callback function is a function called through a function pointer . If you put a pointer to a function ( Address ) Pass as a parameter to another
function , When this pointer is used to call the function it points to , Let's just say this is a callback function . The callback function is not controlled by this function
The implementer of directly calls , It's called by another party when a particular event or condition occurs , Used to enter the event or condition
Row response .
That is, we do not call this function directly , Instead, pass the function address , Call this function through the function pointer in another function , Would it be easier to understand ? We qsort A library function is a typical callback function ;
#include <stdio.h>
//qosrt The user of the function has to implement a comparison function
int int_cmp(const void * p1, const void * p2)
{
return (*( int *)p1 - *(int *) p2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 6, 8, 0 };
int i = 0;
qsort(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), sizeof (int), int_cmp);
for (i = 0; i< sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); i++)
{
printf( "%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Let's simulate the implementation qsort Library function , I have written an article about simulation implementation before qsort Function blog can see ;
qsort Simulation and implementation of library functions
summary
There is also a long topic analysis blog on the interview questions , Then the pointer series blog will come to an end for the time being ;
边栏推荐
- 全球最快下载工具 XDM
- mysql学习1:安装mysql
- Thymeleaf的配置
- mybaitis生成器详解
- A brief talk on cordola tree
- Uniapp drop-down layer selection box effect demo (sorting)
- [fans' welfare] today, I'd like to introduce a method to collect money for nothing - convertible bonds. I personally verified that each person can earn 1500 yuan a year
- yml的配置
- Dm8: Dameng database - lock timeout
- TCP 流控问题两则
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Convn-n dimensional convolution
uniapp下拉弹层选择框效果demo(整理)
mybaitis生成器详解
消息队列的使用
C语言 函数指针与回调函数
Uni app sends request instructions using the escook / request miniprogram plug-in
Microservice splitting
uni-app 使用escook/request-miniprogram插件发请求说明
Mit6.031 software construction7 reading notesdesigning specifications
解开C语言的秘密《关键字》(第六期)
Minimum editing distance (linear DP writing method)
Pycharm in Chinese
如何下载带有超链接的图片
行业洞察 | 新零售业态下,品牌电商应如何重塑增长?
关闭windows defender安全中心的方法
亚马逊测评掉评、留不上评是怎么回事呢?要如何应对?
Threejs' ambient light + point light + parallel light + spherical light and Hepler understanding + shadow ()
LeetCode_ Fast power_ Recursion_ Medium_ 50.Pow(x, n)
Private dry goods sharing: how to implement platform in Enterprise Architecture
Detailed configuration of log4j
![[on Nacos] get started quickly](/img/cc/af4ab640952b880595a89f66688ff5.jpg)