当前位置:网站首页>Keras深度学习实战(12)——面部特征点检测
Keras深度学习实战(12)——面部特征点检测
2022-06-27 16:18:00 【盼小辉丶】
Keras深度学习实战(12)——面部特征点检测
0. 前言
在计算机视觉中,面部关键点(也称为面部特征点)的定位通常是许多面部分析方法和算法中的关键步骤。在本节中,我们将训练卷积神经网络来检测面部的关键点,即左右眼,鼻子和嘴巴的四个坐标的边界。以下是两个绘制了面部关键点的示例图片:

如上图所示,检测到的关键点此图中被绘制为点。在人脸图像上共检测 68 个关键点,其中面部关键点包括:嘴,右眉,左眉,右眼,左眼,鼻子,下巴。在本文中,我们将基于预训练 VGG16 架构提取图像特征,然后微调模型检测图像中人物面部关键点。
1. 数据集和模型分析
1.1 数据集分析
对于关键点检测任务,我们所使用的数据集可以从 Github 中下载,数据集中标注了中图片的人物面部的关键点。在此任务中,输入数据是需要在其上检测关键点的图像,输出数据是图像中人物面部关键点的 x 和 y 坐标。
在构建模型前,首先将数据集下载至本地,查看数据集中标记的面部关键点信息,文件路径为 P1_Facial_Keypoints/data/training_frames_keypoints.csv:

检查此数据集中的面部关键点信息,可以看到,文件中共有 137 列,其中第一列是图像的名称,其余 136 列代表相应图像中 68 个面部关键点的 x 和 y 坐标值。
1.2 模型分析
接下来,继续分析此任务以及我们将使用的模型架构:
- 根据关键点检测任务,下载数据集
- 将图像调整为可以用于网络输入的形状
- 调整图像大小时,需要确保同时修改关键点,以便它们可以对应于已调整大小后的图像
- 使用预训练的
VGG16模型提取输入图像特征 - 创建面部关键点检测任务的输入和输出数组,其中输入数组是通过
VGG16模型处理后的图像特征,而输出数组是修改后的面部关键点位置坐标 - 最后,训练模型以减少面部预测关键点与实际关键点之间的绝对平均误差值
2. 面部特征点检测
本节中,我们将编程实现上一节中所分析的面部关键点检测模型。
导入相关库、数据集,并实例化预训练的 `VGG16模型:
import pandas as pd
import cv2
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
from keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input
from keras.applications import vgg16
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
data = pd.read_csv('P1_Facial_Keypoints/data/training_frames_keypoints.csv')
vgg16_model = vgg16.VGG16(include_top=False, weights='imagenet',input_shape=(224,224,3))
预处理数据集,包括:提取图像、调整图像尺寸、获得 VGG16 提取到的图像特征,并将根据缩放图像修改的面部关键点位置作为输出。
初始化用于创建输出和输出的列表:
x = []
x_img = []
y = []
循环构建图像文件名,并读取图像:
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
img_path = 'P1_Facial_Keypoints/data/training/' + data.iloc[i,0]
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
捕获面部关键点值并进行存储,然后调整图像大小,以满足模型输入形状,并预处理图像,以便可以将其传递给 VGG16 模型并提取特征::
kp = deepcopy(data.iloc[i,1:].tolist())
kp_x = (np.array(kp[0::2])/img.shape[1]).tolist()
kp_y = (np.array(kp[1::2])/img.shape[0]).tolist()
kp2 = kp_x +kp_y
img = cv2.resize(img, (224, 224))
preprocess_img = preprocess_input(img.reshape(1,224,224,3))
vgg16_img = vgg16_model.predict(preprocess_img)
将输入和输出值追加到相应的列表中:
x_img.append(img)
x.append(vgg16_img)
y.append(kp2)
创建输入和输出数组:
x = np.array(x)
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], x.shape[2], x.shape[3], x.shape[4])
y = np.array(y)
建立并编译模型
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense, Dropout
model_fine_tuning = Sequential()
model_fine_tuning.add(Conv2D(512, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu',input_shape=(x.shape[1],x.shape[2],x.shape[3])))
model_fine_tuning.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model_fine_tuning.add(Flatten())
model_fine_tuning.add(Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model_fine_tuning.add(Dropout(0.5))
model_fine_tuning.add(Dense(y.shape[1], activation='sigmoid'))
model_fine_tuning.summary()
输出用于检测面部关键点的微调模型简要信息如下:
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 5, 5, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) (None, 2, 2, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten (Flatten) (None, 2048) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 512) 1049088
_________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 136) 69768
=================================================================
Total params: 3,478,664
Trainable params: 3,478,664
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
最后,编译并拟合模型:
model_fine_tuning.compile(loss='mean_absolute_error',optimizer='adam')
history = model_fine_tuning.fit(x/np.max(x), y,
epochs=10,
batch_size=32,
verbose=1,
validation_split = 0.1)
需要注意的是,我们将输入数组除以输入数组的最大值,以缩放输入数据集,而 validation_split 可选参数用于在没有提供验证集的时候,按一定比例(此处为 10% )从训练集中取出一部分训练数据作为测试集。训练和测试损失随 epoch 增加的变化情况如下:
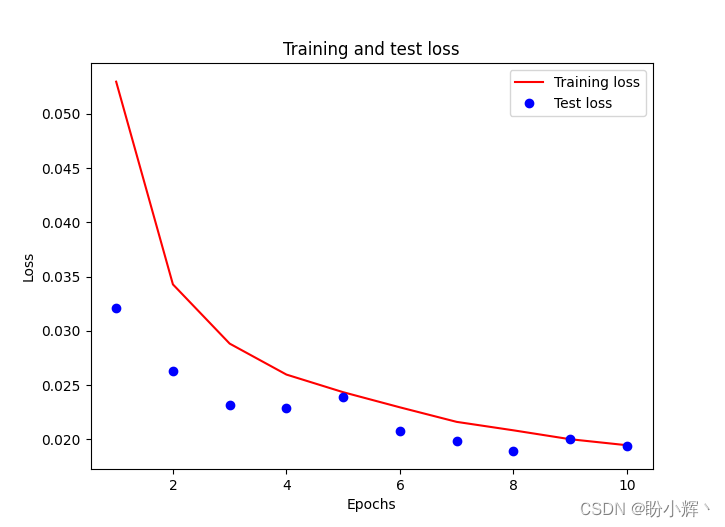
3. 模型测试
预测测试图像。在下面的代码中,我们预测输入数组中倒数第 6 和第 7 个图像,由于 validation_split 为 0.1,训练时模型并未见到这 2 张图像,可以用于衡量训练后的模型性能。我们确保将图像通过 preprocess_input 方法进行预处理,然后通过 vgg16_model 提取图像特征,最后将 vgg16_model 的输出传递给构建的 model_fine_tuning :
test_img_input = preprocess_input(x_img[-7].reshape(1,224,224,3))
pred = model_fine_tuning.predict(vgg16_model.predict(test_img_input/np.max(test_img_input)))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.title('Original image')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(x_img[-7], cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.subplot(222)
plt.title('Image with facial keypoints')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(x_img[-7], cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
kp = pred.flatten()
plt.scatter(kp[0:68]*224, kp[68:]*224)
test_img_input = preprocess_input(x_img[-6].reshape(1,224,224,3))
pred = model_fine_tuning.predict(vgg16_model.predict(test_img_input/np.max(test_img_input)))
plt.subplot(223)
plt.title('Original image')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(x_img[-6], cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.subplot(224)
plt.title('Image with facial keypoints')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(x_img[-6], cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
kp = pred.flatten()
plt.scatter(kp[0:68]*224, kp[68:]*224)
plt.show()
先前对测试图像的预测可以如下所示,我们可以看到,在测试图像上可以非常准确地检测到图片中人物的面部关键点。

小结
面部关键点的定位通常是许多面部分析方法和算法中的关键步骤。在本节中,我们介绍了如何通过训练卷积神经网络来检测面部的关键点,首先通过预训练模型提取特征,然后利用微调模型预测图像中人物的面部关键点。
系列链接
Keras深度学习实战(1)——神经网络基础与模型训练过程详解
Keras深度学习实战(2)——使用Keras构建神经网络
Keras深度学习实战(3)——神经网络性能优化技术
Keras深度学习实战(4)——深度学习中常用激活函数和损失函数详解
Keras深度学习实战(5)——批归一化详解
Keras深度学习实战(6)——深度学习过拟合问题及解决方法
Keras深度学习实战(7)——卷积神经网络详解与实现
Keras深度学习实战(8)——使用数据增强提高神经网络性能
Keras深度学习实战(9)——卷积神经网络的局限性
Keras深度学习实战(10)——迁移学习
Keras深度学习实战(11)——可视化神经网络中间层输出
边栏推荐
- How to arrange digital collections on online platforms such as reading and Chinese online? Will "read/write-to-earn" products be launched in the future?
- [JS reverse hundreds of examples] I love to solve 2022 Spring Festival problems and receive red envelopes
- Space calculation of information and innovation industry in 2022
- TDengine 连接器上线 Google Data Studio 应用商店
- Asemi rectifier bridge kbp310 function pin diagram
- 为什么要从 OpenTSDB 迁移到 TDengine
- 如何使用物联网低代码平台进行画面管理?
- Good news - British software 2022 has obtained 10 invention patents!
- All you want to know about large screen visualization is here
- (5) SPI application design and simulation verification 3 - verification code implementation
猜你喜欢
Using WebDAV instead of 445 port file share

数据同步工具 DataX 已经正式支持读写 TDengine

Allocate aligned heap space

VSCode 建议你启用 gopls,它到底是个什么东东?

Wechat applet association search

Redis installation

Industry university cooperation cooperates to educate people, and Kirin software cooperates with Nankai University to complete the practical course of software testing and maintenance

TP5 generates the most detailed two-dimensional code tp6 (also available)

推荐几个开源的物联网平台

使用 WebDAV 替代445端口文件共享
随机推荐
【ELT.ZIP】OpenHarmony啃论文俱乐部—见证文件压缩系统EROFS
PostgreSQL数据库WAL——资源管理器RMGR
ansible环境安装及数据恢复
Wanzhou gold industry: what knowledge points do you need to master to invest in precious metals?
新产品新人事新服务,英菲尼迪继续深耕中国未来可期!
How to rewrite tdengine code from 0 to 1 with vscode in "technical class"
Simple anti shake for wechat applet
Explain the distributed computing of Apache skywalking OAP in detail
JXL export Excel
广汽三菱全新欧蓝德首次国内亮相于年内上市 产品力全面焕新
How to create a login interface
国产数据库认证考试指南汇总(2022年6月16日更新)
Market status and development prospect of 4-butyl resorcinol used in skin care industry in the world in 2022
TDengine在数控机床监控中的应用
About binary
Using WebDAV instead of 445 port file share
Contest3182 - the 39th individual training match for 2021 freshmen_ C: [string] ISBN number
为什么要从 OpenTSDB 迁移到 TDengine
Push NFT out of the regulatory dilemma, and BSN launched NFT supporting infrastructure network
Shardingsphere sharding proxy actual combat scenario