当前位置:网站首页>Network security algorithm
Network security algorithm
2022-06-25 18:13:00 【[email protected]】
List of articles
1. Shared key encryption
- Both encryption and decryption use the same key
- Also known as symmetric encryption
Data transfer process :
- A Prepare to B send data
- To prevent eavesdropping ,A Use the key to encrypt the data before sending it to B
- B After receiving the encrypted data, decrypt the data with the same key
The problem is :
- If A and B No direct communication , You need to transfer the key through the future , If the key is X hacking ,X You can crack the ciphertext
2. Public key encryption
- Encryption and decryption use different keys
- The encryption is called public key
- The decryption is called private key
Data transfer process :
- A Prepare to B send data
- Receiving party B Generate public and private keys , And send the public key to A
- A Use B The sent public key encrypts the data
- A Send encrypted data to B,B Then decrypt the ciphertext with the private key
- Even if there is something like “ Symmetric encryption ” Problems caused by process sending , That is, the key sent through the network is eavesdropped , But the public key is sent here , Even if it is eavesdropped, the data cannot be cracked
The problem is :
- Public key encryption has the problem of public key reliability
- A Prepare to B send data
- Receiving party B Generate public and private keys , And send the public key to A
- In the key from B->A In the process of ,X The public key of the transmission process is replaced by its own public key , take X The public key of is sent to A
- A Use X To encrypt data and send it to B
- X Eavesdropping A Data sent , Because the data is generated by X Public key encryption , therefore X You can use your own private key to decrypt , So it's cracked , meanwhile X Use B After encrypting the data with the public key of, send it to B, such B Will not be aware that the data has been eavesdropping
- Solving this problem requires digital certificates
1. There is a problem with the shared key that the key cannot be transferred securely
2. Public key encryption has the problem of slow encryption and decryption
3. Mixed encryption
- Encrypt the data with a symmetric key
- Use public key encryption for the key
4. Message authentication code
- The message authentication code can detect whether the message has been tampered
- Using shared key encryption
- A When sending a message ,A Use ciphertext and key to generate a value , Send values and ciphertext together
- B When receiving a message , The ciphertext and key are also used to generate a numerical value , Judge the value and A Whether the values sent are the same , If not, the data is tampered with
The problem is :
A、B Both sides can encrypt the message and calculate the verification code , It is impossible to prove that the original message is A What is generated is still B Generated
5. digital signature
- In public key encryption , Encryption uses a public key P, Decryption uses a private key S, Anyone can use a public key to encrypt data , Only the person holding the private key can decrypt
- The method of digital signature is the opposite of that of domain public key
- sender A Ready to send messages , Public and private keys ( Public key encryption is the recipient B Prepare the public and private keys )
- A Send the public key to B
- A Use the private key to encrypt a summary of the data ( The abstract can be used as hash Function generation ), The encrypted digest is the digital signature
- A Send the encrypted data together with the digital signature to B
- B After receiving the data and digital signature , Decrypt the digital signature with the public key to get the abstract 1, Decrypt the message with the public key to get the plaintext , use hash The function processes the plaintext to get the digest 2, Comparison summary 1 And summary 2 You can judge whether the message has been tampered with 、 By A send out 、 Prevention of hindsight denial
The problem is :
After using data signature B Will believe that the sender of the message is A, But it could actually be X Pretending to be A
The reason is that public key encryption cannot confirm who the key is made by
6. digital certificate
- Neither public key encryption nor digital signature can guarantee that the public key actually comes from the sender of the information , therefore , Even if the public key is maliciously replaced by a third party , Nor will the recipient notice
- A Now send the public and private keys to B
- A You need to go to the certification center first CA Apply for a certificate , Proof public key P It's your own.
- authentication center CA Kept in A The public and private keys of
- CA authentication A Information ( mailbox 、 Id card ), Confirmation is A My information , authentication center CA Use your own private key , according to A Data and public key to generate digital signature , meanwhile CA Also saved A Information and digital signature
- B Received A After sending the message and digital signature , use CA Public key decryption A Digital signature of , obtain A Information and public key
- If in the process X counterfeit A Send public key and digital signature ,B Use CA The decrypted information of the public key does not conform to A Information about
版权声明
本文为[[email protected]]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/02/202202190532337685.html
边栏推荐
- 观察者模式之通用消息发布与订阅
- Mobile heterogeneous computing technology - GPU OpenCL programming (basic)
- SDN系统方法 | 10. SDN的未来
- Qinheng ch583 USB custom hid debugging record
- 图标丢失,URL附带JESSSIONID的什么来的?
- 158_ Model_ Power Bi uses DAX + SVG to open up almost all possibilities for making business charts
- 十大证券公司哪个佣金最低 办理开户安全吗
- The icon is missing. What does the URL come from with the jesssionid?
- 力扣每日一题-第27天-561.数组拆分Ⅰ
- SQL Server实时备份库要求
猜你喜欢

Encryption trend: Fashion advances to the meta universe
![存在重复元素III[利用排序后的有序性进行剪枝]](/img/26/5c3632a64945ea3409f8240ef5b18a.png)
存在重复元素III[利用排序后的有序性进行剪枝]

How to judge whether you are suitable for software testing
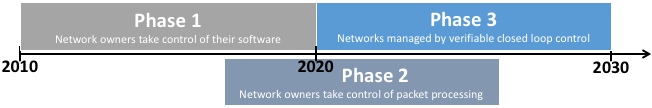
SDN system method | 10 The future of SDN

【日常记录】——对BigDecimal除法运算时遇到的Bug

移动端异构运算技术 - GPU OpenCL 编程(基础篇)

158_模型_Power BI 使用 DAX + SVG 打通制作商业图表几乎所有可能

Centos7 installing redis 7.0.2

揭秘GES超大规模图计算引擎HyG:图切分
近来开发的一款简单易用的图可视化工具
随机推荐
Accumulation of some common knowledge points
How to open a stock account? Is it safe to open a securities account
IET出席2022世界科技社团发展与治理论坛 为构建国际科技共同体献言献策
MVDR beam MATLAB, MVDR beam forming matlab[easy to understand]
Interrupt operation: abortcontroller learning notes
Operating steps for installing CUDA in win10 (continuous improvement)
What is an operator?
What is the ranking of the top ten securities companies? Is it safe to open a mobile account?
Computing architecture of microblog comments
沁恒CH583 USB 自定义HID调试记录
Find the longest substring length satisfying the condition
Intelligent dialog 01 redis installation
篇4:win10安装MingW64
深度学习网路模型
QT generate random numbers (random strings) within the specified range
Bert's summary of me
Redis趋势—NVM内存
HMS core machine learning service realizes simultaneous interpretation, supports Chinese-English translation and multiple voice broadcast
Vscode automatically generates ifndef define ENDIF of header file
为什么在变频器场合需要安科瑞的电力有源滤波器?