当前位置:网站首页>Mathematical modeling -- integer programming
Mathematical modeling -- integer programming
2022-06-25 17:15:00 【Herding cattle】
Catalog
Integer programming model solution
Integer linear programming model
Basic concepts
The programming problem in which some or all of the decision variables must be rounded off is called Integer programming .
Pure integer programming : All decision variables are integers ; mixed integer programming : Some of the decision variables are integer values , The other part is not an integer ;0-1 Integer programming : The decision variable can only take 0 or 1 Integer programming of .
Integer linear programming model ( Some or all decision variables in a linear programming model are integers ) General form :

Sometimes , Or by introducing 0-1 Variables linearize some specific nonlinear constraints . If there is m Two mutually exclusive constraints , That is, only one condition can work at a time , Then introduce m individual 0-1 Variable :

And a sufficiently large normal number M, Then the following group m+1 The three constraints meet the above requirements :

Integer programming model solution
Integer linear programming model
For example, solve the following integer programming :

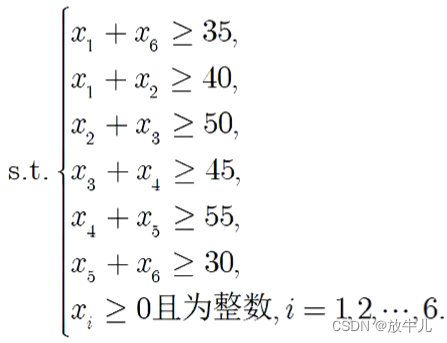
clc,clear
prob = optimproblem;
x = optimvar('x',6,'Type','integer','LowerBound',0);
prob.Objective = sum(x);
con = optimconstr(6); % Create an empty optimization constraint array
a = [35,40,50,45,55,30];
con(1) = x(1)+x(6) >= 35;
for i = 1:5
con(i+1) = x(i)+x(i+1) >= a(i+1);
end
prob.Constraints.con = con;
[sol,fval,flag] = solve(prob);
sol.x,fvalans =
35
5
45
0
55
0
fval =140
You can also make it up like this :

Monte Carlo solution
Monte Carlo method is also called computer simulation method , It is similar to being in a square area with a known area , Find the area of the irregular figure surrounded by it , Sprinkle a large number of beans , According to the number of beans , Find the area .
unifrnd(A,B)% Generated by A and B Specify the upper and lower endpoints [A,B] A continuous and uniformly distributed random array R.
R = unifrnd(A,B,m,n,...)
R = unifrnd(A,B,[m,n,...])% return m*n*... Array
rng(1)%1 As a random number seed , For consistency comparison .
rng('shuffle')% Provide seeds for the random number generator based on the current time .
tic% Timing begins
toc% End of the timing
B = all(A)% If A It's two-dimensional , The number of columns is n, be B For one 1*n Matrix . If A The elements of a column in are all true , be B The corresponding element in is 1. If A It's three-dimensional , be B Columns of 、 Number of pages and A identical ,B The number of lines is 1. The case that is higher than three dimensions can be analogized .
For example, solving nonlinear integer programming :x All are integers

clc,clear
rng(0);
p0 = 0;
n = 10^6;
tic;
for i = 1:n
x = randi([0,99],1,5);
[f,g] = mente(x);
if all(g <= 0)
if p0 <f
x0 = x;p0 = f;
end
end
end
x0,p0,toc
function [f,g] = mente(x)
f = x(1)^2+x(2)^2+3*x(3)^2+4*x(4)^2+2*x(5)^2-8*x(1)-2*x(2)...
-3*x(3)-x(4)-2*x(5);
g = [sum(x)-400
x(1)+2*x(2)+2*x(3)+x(4)+6*x(5)-800
2*x(1)+x(2)+6*x(3)-200
x(3)+x(4)+5*x(5)-200];
endx0 =
46 98 1 99 3
p0 =50273
after 0.927967 second .
Genetic algorithm

fun It's the objective function ( Only the minimum value ),nvars Represents the number of variables ,A、b Linear inequality constraint ,Aeq、beq Linear equal sign constraint ,lb、ub Represents upper and lower bounds ,nonlcon Represents a nonlinear constraint ,intcon Indicate which variables are integer variables ,options Used to indicate other optimization settings .
Also use the example above :
clc,clear
f = @(x) x(1)^2+x(2)^2+3*x(3)^2+4*x(4)^2+2*x(5)^2-8*x(1)-2*x(2)...
-3*x(3)-x(4)-2*x(5);
A = [1,1,1,1,1;
1,2,2,1,6;
2,1,6,0,0;
0,0,1,1,5];
b = [400;800;200;200];
[x,fvdisc] = ga(@(x)-f(x),5,A,b,[],[],zeros(1,5),99*ones(1,5),[],[1:5])@(x)-f(x) Indicates that another anonymous function is defined -f(x)
x =
50 99 0 99 20
fvdisc =-51568
other
The process of solving practical problems is : Problem analysis 、 The model assumes 、 Symbol description 、 model .
MATLAB The middle line is too long to use "..." To wrap
边栏推荐
- Xshell connecting VMware virtual machines
- 【Matlab】数据统计分析
- tasklet api使用
- The role of the project manager in the project
- Sword finger offer II 025 Adding two numbers in a linked list
- Home office earned me C | community essay
- Design and arrangement of DDIA data intensive application system
- 剑指 Offer II 025. 链表中的两数相加
- 宝藏又小众的国画3d材质贴图素材网站分享
- 微信公众号服务器配置
猜你喜欢

PLSQL storage function SQL programming

SnakeYAML配置文件解析器

App测试和Web测试的区别

足下教育日精进自动提交

巴比特 | 元宇宙每日荐读:三位手握“价值千万”藏品的玩家,揭秘数字藏品市场“三大套路”...

LSF如何看job预留slot是否合理?

单例模式应用
![[black apple] Lenovo Savior y70002019pg0](/img/9c/7a94aa911dd0c6b94ba192bc2687e6.png)
[black apple] Lenovo Savior y70002019pg0

2022-06-17 advanced network engineering (IX) is-is- principle, NSAP, net, area division, network type, and overhead value

Create a new ar fashion experience with cheese and sugar beans
随机推荐
Ten thousand volumes - list of Dali wa
Uncover ges super large scale graph computing engine hyg: Graph Segmentation
Next.js 热更新 Markdown 文件变更
Cache architecture scheme of ten million level shopping cart system
n-queens problem
The role of the project manager in the project
How do components communicate
[micro service sentinel] overview of flow control rules | detailed explanation of flow control mode for source | < direct link >
剑指 Offer II 012. 左右两边子数组的和相等
TCP chat + transfer file server server socket v2.8 - fix 4 known problems
芝士糖豆打造AR潮玩新体验
记一次基于PHP学生管理系统的开发
[proficient in high concurrency] deeply understand the basics of assembly language
Differences between et al and etc
N皇后问题
Sword finger offer 50 First character that appears only once
Redis系列——概述day1-1
A development of student management system based on PHP
WPF开发随笔收录-心电图曲线绘制
Pytorch official document learning record