当前位置:网站首页>Learning records of numpy Library
Learning records of numpy Library
2022-06-27 13:37:00 【Rat human decline】
Catalog
Horizontal and vertical operation
3、Adding, removing, and sorting elements
5、convert array( such as A one-dimensional To A two-dimensional )
To qualify elements in a sequence
reverse an array Take the opposite
Multidimensional sequence flat
Transposing( Transposition ) and reshaping a matrix
10、Working with mathematical formulas
1、array
what is array
An array is a central data structure of the NumPy library.
An array is a grid of values and it contains information about the raw data, how to locate an element, and how to interpret an element.( Like learning pytorch)
import numpy as np
import torch
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
print(a)
print(a.dtype)
print(a.shape)
''''
In NumPy, dimensions are called axes.
[[ 1 2 3 4]
[ 5 6 7 8]
[ 9 10 11 12]]
This matrix can be said to be ,3 Row four column
It can also be said that
The first axis has a length of 3 and the second axis has a length of 4.
'''
print(a[0])narray
N-dimensional array
The NumPy ndarray class is used to represent both matrices( matrix ) and vectors( vector ).
vector: an array with a single dimension
matrix: an array with two dimensions
tensor( tensor ): 3-D or higher dimensional array
2、create a basic array
import numpy as np
import torch
a = np.zeros(2)
print(a)
a = np.ones(2)
print(a)
a = np.arange(4) #an array with a range of elements
print(a)
b = np.arange(1,8,3) #start end step
print(b)
a = np.linspace(0, 10, num=5) # branch 5 branch Linear increase
print(a)
a = np.ones(2, dtype=np.int64) #specify the type
print(a)Horizontal and vertical operation
Horizontal and vertical merge
import numpy as np
a1 = np.array([[1, 1],
[2, 2]])
a2= np.array([[3, 3],
[4, 4]])
a_h = np.hstack((a1,a2)) # level
print(a_h)
a_v = np.vstack((a1,a2)) #vertical vertical
print(a_v)Split horizontally and vertically
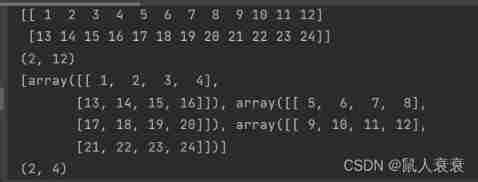
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,25).reshape(2,12)
print(a)
print(a.shape)
'''
Return a list
return 3 individual array
Every array Of shape (2*4) 4 = 12/3, The original 12 Column
'''
a_hsp = np.hsplit(a, 3)
print(a_hsp)
print(a_hsp[0].shape)
3、Adding, removing, and sorting elements
Sort
import numpy as np
import torch
arr = np.array([2, 1, 5, 3, 7, 4, 6, 8])
print(arr)
arr_sort = np.sort(arr)
print(arr_sort)
print(arr)

It can be seen that , Sorting does not change the elements of the original sequence

such as
import numpy as np
import torch
'''
Returns the index of the elements of an ordered sequence
'''
x = np.array([3, 1, 2])
index = np.argsort(x)
print(index) #3-0,1-1,2-2, The index returned 1,2,0concatenate Connect
import numpy as np
import torch
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
b = np.array([5, 6, 7, 8])
c = np.concatenate((a, b))
print(c)
x = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(x) # 2*2
y = np.array([[5, 6]])
z = np.concatenate((x, y), axis=0) # Same number of columns Connect
print(z)
x = np.array([[1, 2, 3]])
print(x) # 2*2
y = np.array([[5, 6]])
z = np.concatenate((x, y), axis=1) # The same number of lines Connect
print(z)4、shape of array
get the shape of array
'''
The three-dimensional array 3x2x4
'''
array_example = np.array([[[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]],
[[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]],
[[0 ,1 ,2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]]])
print(array_example)
print(array_example.ndim) # Print dimension
print(array_example.shape)
print(array_example.size) # Total number of print elements reshape
import numpy as np
'''
The three-dimensional array 3x2x4
'''
array_example = np.array([[[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]],
[[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]],
[[0 ,1 ,2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]]])
print(array_example)
array_example1 = np.reshape(array_example,newshape=(3,4,2),order='C')
print(array_example1.shape)
print(array_example1)
5、convert array( such as A one-dimensional To A two-dimensional )
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
print(a)
print(a.shape)
a2 = a[np.newaxis, :] #np.newaxis will increase the dimensions of your array
print(a2)
print(a2.shape)
a3 = np.expand_dims(a, axis=1) # expand dim Expand dimensions
print(a3)
print(a3.shape)
6、index of array
index

import numpy as np
data = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(data[1])
print(data[1:])
print(data[-2:])To qualify elements in a sequence

import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1 , 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
# Establish a conditional discriminant
five_blow = (a <= 5)
print(a[five_blow])
divisible_by_2 = (a % 2 == 0)
print(a[divisible_by_2])
c = a[(a > 2) & (a < 11)]
print(c)return boolean values

import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1 , 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
five_up = (a > 5) | (a == 5)
print(five_up)7、Basic array operations
Basic operation
addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and more
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2])
b = np.ones(2,dtype=int)
print(a)
print(b)
c = a + b
print(c)
c1 = a - b
print(c1)
c2 = a * b
print(c2)
c3 = a // a
print(c3)Sum up Find the maximum value
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2])
print(a.max())
print(a.min())
print(a.sum())reverse an array Take the opposite
A one-dimensional
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
reversed_arr = np.flip(arr)
print(reversed_arr)Multidimensional

import numpy as np
arr_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
arr_2d_re = np.flip(arr_2d,axis=0) # Press That's ok Take the opposite
print(arr_2d_re)
arr_2d_re1 = np.flip(arr_2d,axis=1) # Press That's ok Take the opposite
print(arr_2d_re1)
arr_2d_re2 = np.flip(arr_2d)
print(arr_2d_re2) 


Specifies that the row and column are negated
import numpy as np
arr_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
arr_2d[1] = np.flip(arr_2d[1]) # The second line Take the opposite
print(arr_2d)
arr_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
arr_2d[:,1] = np.flip(arr_2d[:,1]) # Second column Take the opposite
print(arr_2d) 

Multidimensional sequence flat
Reshaping and flattening multidimensional arrays
import numpy as np
arr_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
a_flat = arr_2d.flatten()
print(a_flat)![]()
import numpy as np
arr_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
a_flat = arr_2d.flatten()
print(a_flat)
'''
To the original array No impact
'''
a_flat[0] = 99
print(arr_2d)
print(a_flat)
'''
use ravel, the changes you make to the new array
will affect the parent array.
Flattened And with the original array There is a direct impact
'''
a_flat2 = arr_2d.ravel()
print(a_flat2)
a_flat2[0] = 99
print(a_flat2)
print(arr_2d)8、matrices matrix
Create a matrix


import numpy as np
matrix = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(matrix)
print(matrix[0,1])
print(matrix[1:2])
print(matrix[1:2,1]) 
import numpy as np
matrix = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(matrix)
print(matrix.max())
print(matrix.min())
print(matrix.sum())
print(matrix.max(axis=0)) # Maximum value per column
print(matrix.max(axis=1)) # The maximum value of each line 
Matrix addition
import numpy as np
data = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
ones = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 1]])
sumArray = data + ones
print(sumArray)

broadcast - expand
use its broadcast rules for the operation.

It will be automatically replenished
import numpy as np
data = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
ones_row = np.array([[1, 1]])
sumArray = data + ones_row
print(sumArray) 
Random number matrix
import numpy as np
rng = np.random.default_rng(0)
n = rng.random((2,3))
print(n)Create a larger than 1, Less than 5 Of 2*4 Matrix
import numpy as np
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
n = rng.integers(5,size=(2,4))
print(n)
Transposing( Transposition ) and reshaping a matrix
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(arr)
arr1 = arr.reshape(3,2)
print(arr1)
# The transpose of the matrix , The two methods
arr2 = arr.transpose()
print(arr2)
arr3 = arr.T
print(arr3)9、unique items and count
A one-dimensional
Return non repeating elements And its index
import numpy as np
a = np.array([11, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 12, 13, 11, 14, 18, 19, 20])
unique_values, indices_list = np.unique(a, return_index=True)
print(unique_values)
print(indices_list)
Return non repeating elements And its Number of element repetitions
import numpy as np
a = np.array([11, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 12, 13, 11, 14, 18, 19, 20])
unique_values, occurrence_count = np.unique(a, return_counts=True)
print(unique_values)
print(occurrence_count) 
Multidimensional
import numpy as np
a_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12], [1, 2, 3, 4]])
print(a_2d.shape)
unique_rows, indices, occurrence_count \
= np.unique( a_2d, axis=0, return_counts=True, return_index=True)
print(unique_rows) # Returns a unique row vector
print(indices) # That's ok Corresponding coordinate
print(occurrence_count) # That's ok The emergence of frequency 
10、Working with mathematical formulas




11、 and pandas and Matplotlib


边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
OpenHGNN发布0.3版本

CMOS level circuit analysis

今日睡眠质量记录78分

基于SSM实现招聘网站

IJCAI 2022 | greatly improve the effect of zero sample learning method with one line of code. Nanjing Institute of Technology & Oxford proposed the plug and play classifier module
![[acwing] explanation of the 57th weekly competition](/img/ef/be89606b0e7fffac08280db0a73781.gif)
[acwing] explanation of the 57th weekly competition

关于接口测试自动化的总结与思考
Record number of visits yesterday

阿胖的操作记录

深入理解位运算
随机推荐
scrapy
[dynamic programming] - Knapsack Problem
Prometheus 2.26.0 new features
Cool in summer
Teach you how to build a permanent personal server!
【动态规划】—— 背包问题
buuctf misc 百里挑一
On the complexity of software development and the way to improve its efficiency
crane:字典项与关联数据处理的新思路
基于SSM实现招聘网站
[WUSTCTF2020]girlfriend
命令行编辑器 sed 基础用法总结
MySQL index and its classification
快讯:华为启动鸿蒙开发者大赛;腾讯会议发布“万室如意”计划
同花顺能开户炒股吗?安全吗?
万物互联时代到来,锐捷发布场景化无线零漫游方案
以前国产手机高傲定价扬言消费者爱买不买,现在猛降两千求售
Openhgnn releases version 0.3
全球芯片市场或陷入停滞,中国芯片逆势扩张加速提升自给率
微服务如何拆分


