当前位置:网站首页>Super complete summary: how to operate files in go language
Super complete summary: how to operate files in go language
2022-07-24 08:45:00 【Golang DreamWorks】
Preface
hello , Hello everyone , I am a
asong.We all know that
UnixEverything in the world is called a document , File processing is a very common problem , So this article summarizesGoCommon ways of language operation files , The whole idea is as follows :
Go Language version :1.18
All the codes in this article have been uploaded github:https://github.com/asong2020/Golang_Dream/tree/master/code_demo/file_operate_demo
What are the operation documents
These actions are indispensable for operating a file :
create a file Open file Read the file write file Close file pack / Unpack Compress / decompression Change file permissions Delete file Moving files Rename file Empty files
So this paper summarizes some example methods for these operations for your reference ;
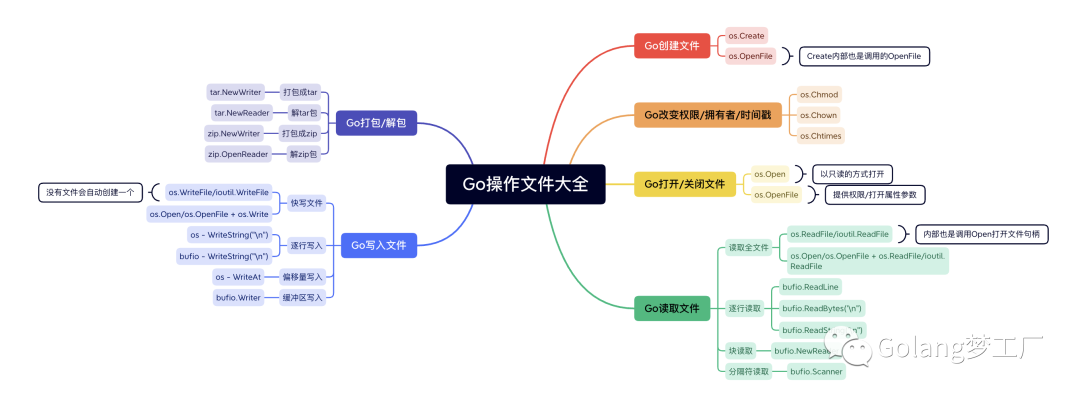
Go Libraries available for language operation files
Go The official library of languages :os、io/ioutil、bufio It covers all scenarios of file operation ,
os Provides a pair of files IO Directly called method ,bufio Provide methods for buffer operation files ,io/ioutil Also available on file IO Directly called method , however Go Language in Go1.16 The version has been deprecated io/ioutil library , This io/ioutil A package is a collection of things that are not clearly defined and difficult to understand . All functions provided by this package have been moved to other packages , therefore io/ioutil The methods of operating files in io Libraries have the same meaning , We will use it in the future ioutil The method in is that you can find the corresponding method in other packages through annotations .
Basic operation of file
Here I put create a file 、 Open file 、 Close file 、 Changing file permissions is classified as the basic operation of files , Direct use of basic operations of files os Methods in the Library , Because we need to do IO operation , Let's look at the following example :
import (
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
// create a file
f, err := os.Create("asong.txt")
if err != nil{
log.Fatalf("create file failed err=%s\n", err)
}
// Get file information
fileInfo, err := f.Stat()
if err != nil{
log.Fatalf("get file info failed err=%s\n", err)
}
log.Printf("File Name is %s\n", fileInfo.Name())
log.Printf("File Permissions is %s\n", fileInfo.Mode())
log.Printf("File ModTime is %s\n", fileInfo.ModTime())
// Change file permissions
err = f.Chmod(0777)
if err != nil{
log.Fatalf("chmod file failed err=%s\n", err)
}
// Change the owner
err = f.Chown(os.Getuid(), os.Getgid())
if err != nil{
log.Fatalf("chown file failed err=%s\n", err)
}
// Get the file information again Verify that the changes are correct
fileInfo, err = f.Stat()
if err != nil{
log.Fatalf("get file info second failed err=%s\n", err)
}
log.Printf("File change Permissions is %s\n", fileInfo.Mode())
// Close file
err = f.Close()
if err != nil{
log.Fatalf("close file failed err=%s\n", err)
}
// Delete file
err = os.Remove("asong.txt")
if err != nil{
log.Fatalf("remove file failed err=%s\n", err)
}
}
Writing documents
Write a file
os/ioutil Packages are provided WriteFile Method can quickly handle the creation / Open file / Writing data / Close file , An example is as follows :
func writeAll(filename string) error {
err := os.WriteFile("asong.txt", []byte("Hi asong\n"), 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
Write file by line
os、buffo There is no way to write data by row , So we can call os.WriteString、bufio.WriteString The method is to add line breaks to the data , Let's look at an example :
import (
"bufio"
"log"
"os"
)
// Direct manipulation IO
func writeLine(filename string) error {
data := []string{
"asong",
"test",
"123",
}
f, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
if err != nil{
return err
}
for _, line := range data{
_,err := f.WriteString(line + "\n")
if err != nil{
return err
}
}
f.Close()
return nil
}
// Write using cache
func writeLine2(filename string) error {
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Create... For this file buffered writer
bufferedWriter := bufio.NewWriter(file)
for i:=0; i < 2; i++{
// Write a string to buffer
bytesWritten, err := bufferedWriter.WriteString(
"asong How handsome \n",
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
log.Printf("Bytes written: %d\n", bytesWritten)
}
// Write memory buffer To hard disk
err = bufferedWriter.Flush()
if err != nil{
return err
}
file.Close()
return nil
}
Offset write
In some scenarios, we want to write data according to the given offset , have access to os Medium writeAt Method , Examples are as follows :
import "os"
func writeAt(filename string) error {
data := []byte{
0x41, // A
0x73, // s
0x20, // space
0x20, // space
0x67, // g
}
f, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
if err != nil{
return err
}
_, err = f.Write(data)
if err != nil{
return err
}
replaceSplace := []byte{
0x6F, // o
0x6E, // n
}
_, err = f.WriteAt(replaceSplace, 2)
if err != nil{
return err
}
f.Close()
return nil
}
Cache write
os The methods in the library are direct to files IO operation , Frequent IO Operation will increase CPU Interrupt frequency of , So we can use memory cache to reduce IO operation , Use memory cache before writing section to hard disk , When the capacity of the memory buffer reaches a certain value, the memory data is written buffer To hard disk ,bufio This is how to show a library , Let's take an example to see how to use :
import (
"bufio"
"log"
"os"
)
func writeBuffer(filename string) error {
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Create... For this file buffered writer
bufferedWriter := bufio.NewWriter(file)
// Write a string to buffer
bytesWritten, err := bufferedWriter.WriteString(
"asong How handsome \n",
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
log.Printf("Bytes written: %d\n", bytesWritten)
// Check the number of bytes in the cache
unflushedBufferSize := bufferedWriter.Buffered()
log.Printf("Bytes buffered: %d\n", unflushedBufferSize)
// How many bytes are still available ( Unused cache size )
bytesAvailable := bufferedWriter.Available()
if err != nil {
return err
}
log.Printf("Available buffer: %d\n", bytesAvailable)
// Write memory buffer To hard disk
err = bufferedWriter.Flush()
if err != nil{
return err
}
file.Close()
return nil
}
Reading documents
Read the full file
There are two ways we can read the whole file :
os、io/ioutilProvided inreadFileMethod can read the full text quicklyio/ioutilProvided inReadAllMethod can read the full text after opening the file handle ;
import (
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"os"
)
func readAll(filename string) error {
data, err := os.ReadFile(filename)
if err != nil {
return err
}
log.Printf("read %s content is %s", filename, data)
return nil
}
func ReadAll2(filename string) error {
file, err := os.Open("asong.txt")
if err != nil {
return err
}
content, err := ioutil.ReadAll(file)
log.Printf("read %s content is %s\n", filename, content)
file.Close()
return nil
}
Read line by line
os Provided in the library Read The method is to read by byte length , If we want to read the file by line, we need to cooperate bufio Use it together ,bufio Three methods are provided in ReadLine、ReadBytes("\n")、ReadString("\n") Data can be read by row , I use ReadBytes("\n") Let's write an example :
func readLine(filename string) error {
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_RDONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
bufferedReader := bufio.NewReader(file)
for {
// ReadLine is a low-level line-reading primitive. Most callers should use
// ReadBytes('\n') or ReadString('\n') instead or use a Scanner.
lineBytes, err := bufferedReader.ReadBytes('\n')
bufferedReader.ReadLine()
line := strings.TrimSpace(string(lineBytes))
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
return err
}
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
log.Printf("readline %s every line data is %s\n", filename, line)
}
file.Close()
return nil
}
Read the file by block
In some scenarios, we want to read files by byte length , At this time, we can do the following :
osLibraryReadMethodosLibrary cooperationbufio.NewReadercallReadMethodosLibrary cooperationioLibraryReadFull、ReadAtLeastMethod
// use bufio.NewReader
func readByte(filename string) error {
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_RDONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// establish Reader
r := bufio.NewReader(file)
// Each read 2 Bytes
buf := make([]byte, 2)
for {
n, err := r.Read(buf)
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
return err
}
if n == 0 {
break
}
log.Printf("writeByte %s every read 2 byte is %s\n", filename, string(buf[:n]))
}
file.Close()
return nil
}
// use os
func readByte2(filename string) error{
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_RDONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Each read 2 Bytes
buf := make([]byte, 2)
for {
n, err := file.Read(buf)
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
return err
}
if n == 0 {
break
}
log.Printf("writeByte %s every read 2 byte is %s\n", filename, string(buf[:n]))
}
file.Close()
return nil
}
// use os and io.ReadAtLeast
func readByte3(filename string) error{
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_RDONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Each read 2 Bytes
buf := make([]byte, 2)
for {
n, err := io.ReadAtLeast(file, buf, 0)
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
return err
}
if n == 0 {
break
}
log.Printf("writeByte %s every read 2 byte is %s\n", filename, string(buf[:n]))
}
file.Close()
return nil
}
Separator read
bufio The package provides Scanner Scanner module , Its main function is to divide the data flow into marks and remove the spaces between them , He supports us to customize Split Function as a separator function , The delimiter can not be a simple byte or character , We can customize the separator function , Implement the separation rule in the separation function and how much the pointer moves , What data is returned , If not customized Split function , Then the default ScanLines As a separator function , That is, use newline as separator ,bufio The default method is also provided in ScanRunes、ScanWrods, Now let's use SacnWrods Method write an example , Get text separated by spaces :
func readScanner(filename string) error {
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_RDONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return err
}
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(file)
// Can be customized Split Function as a separator function
// ScanWords yes scanner The built-in separator function is used to find text words separated by spaces
scanner.Split(bufio.ScanWords)
for {
success := scanner.Scan()
if success == false {
// An error or EOF Is to return Error
err = scanner.Err()
if err == nil {
log.Println("Scan completed and reached EOF")
break
} else {
return err
}
}
// Get data ,Bytes() perhaps Text()
log.Printf("readScanner get data is %s", scanner.Text())
}
file.Close()
return nil
}
pack / Unpack
Go Linguistic archive The package provides tar、zip Two kinds of packaging / Unpacking method , Here we use zip The packaging / Unpacking is an example :
zip Unpacking example :
import (
"archive/zip"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
// Open a zip archive for reading.
r, err := zip.OpenReader("asong.zip")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer r.Close()
// Iterate through the files in the archive,
// printing some of their contents.
for _, f := range r.File {
fmt.Printf("Contents of %s:\n", f.Name)
rc, err := f.Open()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
_, err = io.CopyN(os.Stdout, rc, 68)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
rc.Close()
}
}
zip Packaging example :
func writerZip() {
// Create archive
zipPath := "out.zip"
zipFile, err := os.Create(zipPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create a new zip archive.
w := zip.NewWriter(zipFile)
// Add some files to the archive.
var files = []struct {
Name, Body string
}{
{"asong.txt", "This archive contains some text files."},
{"todo.txt", "Get animal handling licence.\nWrite more examples."},
}
for _, file := range files {
f, err := w.Create(file.Name)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
_, err = f.Write([]byte(file.Body))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
// Make sure to check the error on Close.
err = w.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
summary
In the final analysis, this article is an introduction os、io、bufio How do these packages manipulate files , because Go Language operation provides too many methods , Through this article, I will introduce them all , It can be easily used as a document query , If you ask what is the best way to operate files , I can't answer you , It needs to be analyzed according to specific scenarios , If you know all these methods , Writing a benchmark Just compare it , Practice is the only test of truth .
All the codes in this article have been uploaded github:https://github.com/asong2020/Golang_Dream/tree/master/code_demo/file_operate_demo
All right. , This is the end of the article , I am a asong, See you next time .
Created a reader exchange group , Welcome to join the group , Learn and communicate together . Entry mode : Official account acquisition . More information on study, please go to the official account .
边栏推荐
- 阻塞队列BlockingQueue 源码解析(ArrayBQ和LinkedBQ)
- Wargames NATAS (16-19) problem solving essays
- Porting boa server on imx6ull
- Treap
- [Shangshui Shuo series] final rad New Literacies
- 超全总结:Go语言如何操作文件
- Shell script backup mongodb database
- Hack the box - File Inclusion module detailed Chinese tutorial
- How RPC callers implement asynchronous calls: completable future
- 3、 Midway interface security certification
猜你喜欢

Larave uses sanctum for API authentication

Scatter chart - date

M-dao creates a one-stop Dao platform, allowing hundreds of millions of players to join Dao space

阻塞队列BlockingQueue 源码解析(ArrayBQ和LinkedBQ)

使用Go语言开发eBPF程序
Wargames NATAS (0-10) problem solving essay

【一起上水硕系列】EE feedback 详解

Route interceptor

2022.7.11全盘题解
![[Sheung Shui Shuo series] EE feedback details](/img/19/5a80d5ef80d75be74b7ce08d6df058.png)
[Sheung Shui Shuo series] EE feedback details
随机推荐
Wargames NATAS (0-10) problem solving essay
Mysql database advanced
Hack the box - Web requests module detailed Chinese tutorial
Move protocol global health declaration, step into Web3 in sports
Rocky基础-Shell脚本基础知识
Crypto giants all in metauniverse, and platofarm may break through
What is the difference between domestic "rocket heart" artificial heart and different artificial heart?
Protocol buffer learning notes
Okaleido tiger NFT is about to log in to binance NFT platform, and the era of NFT rights and interests is about to start
Shanghai issued a document to support the entry of NFT cultural exchange: the trend of digital collections has arrived!
[emotion] what is "excellent"
Kotlin learning note 1 - variables, functions
SQL problem summary
基于FPGA的VGA字符显示
Php+spool to realize the shell client of web version
Dao race track is booming. What are the advantages of m-dao?
Learn the rxjs operator
面试官:哥们Go语言的读写锁了解多少?
Xiaobai learns oauth2
T-SQL query statement