当前位置:网站首页>Summary of the most complete MySQL data types in history (Part 2)
Summary of the most complete MySQL data types in history (Part 2)
2022-07-25 01:12:00 【51CTO】
Then continue to sort out the above , Above we wrote about
time type , Then we'll write the date and time type date type .
date type
date Type is used when only date values are required , There is no time part , When storing, you need 3 byte .
The date format is YYYY-MM-DD. among YYYY Indicate year ,MM Represents the month ,DD Means day .
(1) With 'YYYY-MM-DD' perhaps 'YYYYMMDD' Date in string format , The value range is '1000-01-01' ~ '9999-12-3' ; For example, the input '2022-12-31' perhaps ‘20221231’, The date when the database is inserted is 2022-12-31;
(2) With ‘YY-MM-DD’ perhaps ‘YYMMDD’ Date in string format , ad locum ‘YY’ Represents the annual value of two digits . Dates with two digit year values can be confusing , Because I don't know the century .mysql Use the following rules to interpret two digit year values :‘00~69’ The annual value of the range is converted to 2000-2069,'70-99' The annual value of the range is converted to 1970~1999.
(3) With YY-MM-DD perhaps YYMMDD Date in numeric format , Similar to the front ,00~69 The annual value of the range is converted to 2000~2069,70~99 The annual value of the range is converted to 1970~1999.
(4) Use CURRENT_DATE perhaps NOW(), Insert current system date .
for instance :
Create a file called yunweijia_4 Data sheet for ;
Insert some values into the table ;
Then check the results :
Another example :
Delete data table yunweijia_4 Data in ;
Insert data into the table ;
Check the results :
Another example :
Old rules , First delete the data in the table
Insert data into table ;
Check the results :
Another example :
Delete data in table ;
Insert the current time of the system :
View results :
CURRENT_DATE Only the current date value is returned , Not including the time part ;NOW() Function returns date and time values , When saving to the database , Only the date part is retained .
datetime type
DATETIME Type is used for values that need to contain both date and time information , When storing, you need 8 byte . The date format is ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’. among ,YYYY Indicate year ,MM Represents the month ,DD Means day ,HH For hours ,MM Represents minutes ,SS For seconds . In giving DATETIME When assigning a field of type , You can insert data using either a string type or a number type , As long as meet DATETIME The date format can be .
(1) With ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ perhaps ‘YYYYMMDDHHMMSS’ Value in string format , The value range is ‘1000-01-01 00:00:00’~‘9999-12-3 23:59:59’;
(2) With ‘YY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ perhaps ‘YYMMDDHHMMSS’ Date in string format , ad locum YY Represents the annual value of two digits . Same as before ,‘00~69’ The annual value of the range is converted to ‘2000~2069’,‘70~99’ The annual value of the range is converted to ‘1970~1999’.
(3) With YYYYMMDDHHMMSS perhaps YYMMDDHHMMSS Date and time in numeric format .
TIMESTAMP type
TIMESTAMP The display format is the same as DATETIME identical , The display width is fixed at 19 Characters , The date format is YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS, When storing, you need 4 byte .TIMESTAMP The value range of column is less than DATETIME Value range of , by ‘1970-01-01 00:00:01’UTC~‘2038-01-1903:14:07’UTC. among ,UTC(Coordinated Universal Time) For world standard time , So when inserting data , Ensure that it is within the legal value range .
Be careful :
because
datetime The type and TIMESTAMP It is quite different from the above usage , So here are no more examples .
Text string type
The string type is used to store string data , In addition to storing string data , Other data can also be stored , Such as binary data of pictures and sounds .
mysql Support two types of string data : Text strings and binary strings ;
Text strings can be used for case sensitive or case insensitive string comparison , You can also search for pattern matching .
stay mysql in , The text string type refers to :
- CHAR
- VARCHAR
- TEXT
- ENUM
- SET
See the following table for details :
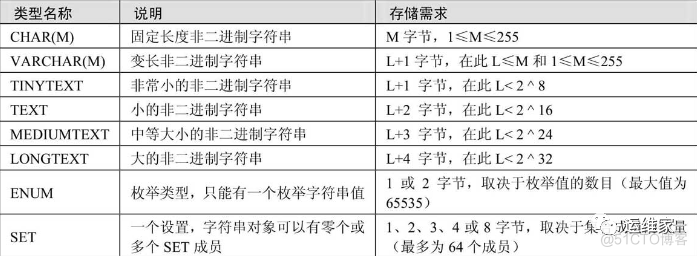
VARCHAR and TEXT The type and BLOB All are Variable length type , Its storage requirements Depends on the actual length of the column value ( Use... In the previous table L Express ), Rather than depending on the maximum possible size of the type .
for example , One VARCHAR(10) The maximum length that the column can save is 10 Character string , The actual storage needs to be the length of the string L add 1 byte ( Record the length of the string ). For characters “abcd”,L yes 4 The storage requirements are 5 byte .
CHAR and VARCHAR type
CHAR(M) Is a fixed length string , Specify the string column length when defining . Fill in the space on the right when saving , To reach the specified length .M Column length ,M The range is 0~255 Characters .
for example :CAHR(4) Defines a fixed length character string , The maximum number of characters it contains is 4. When the retrieved CHAR When the value of , The trailing space will be deleted .
VARCHAR(M) Is a variable length string ,M Indicates the maximum column length .M The range is 0~65535.VARCHAR The maximum actual length of is determined by the size of the longest line and the character set used , The actual space occupied is the actual length of the string plus 1.
for example :VARCAHR(50) Defines a maximum length of 50 String , If the inserted string is only 10 Characters , Then the actual stored string is 10 Characters and a string ending character .VARCHAR When the corresponding value is saved and retrieved, the trailing space remains .
Let's take a look at CHAR(4) and VARCHAR(4) What is the difference between storage :

We can see from the comparison results in the above figure ,CHAR(4) The fixed length is defined as 4 The column of , No matter how long the stored data is , The space occupied is 4 Bytes ;VARCHAR(4) The number of bytes occupied by the defined column is the actual length plus 1;
But the query is different , We can look at it through the following example ;
for instance :
Create a file called yunweijia_5 Data sheet for ;
Insert some data into this data table ;
Check the results :
There's a problem here , The document above describes ,char The space will be deleted when saving ,varchar The space at the end will be reserved , But from the perspective of its own practice , Whether it's char still varchar Have deleted the space at the end .
TEXT type
TEXT Column holds non binary strings , Such as the content of the article 、 Comments, etc .
When saving or querying TEXT Column value , Do not delete trailing spaces .
Text Types are divided into 4 Kind of :
For the rest, go to VX official account “ Operation and maintenance home ” , reply “196” see .
------ “ Operation and maintenance home ” , reply “196” ------
------ “ Operation and maintenance home ” , reply “196” ------
------ “ Operation and maintenance home ” , reply “196” ------
Weifang operation and Maintenance Engineer Recruitment , The development prospect of hardware operation and maintenance engineers , Personal planning of operation and maintenance engineer , Shenzhen Sunshine rain dew operation and maintenance engineer , Public institutions recruit operation and maintenance engineers ;
Qianxin operation and Maintenance Engineer Interview , Sany Heavy Industry system operation and maintenance engineer , Operation and maintenance engineer interview questions , Operation and maintenance engineer of Environmental Engineering ;
What direction do operation and maintenance engineers have , Hangzhou operation and maintenance engineer recruits Ali , Bridge operation and maintenance engineer , Desktop operation and maintenance engineer training plan .
边栏推荐
- Redis管道技术/分区
- [development tutorial 10] crazy shell · open source Bluetooth smart health watch OTA image production and download technical documents
- Free personal virtual machine - AWS free EC2 package
- Educational events
- UXDB在不知道明文密码的情况下重置密码
- Visual studio code installation package download slow & Installation & environment configuration & new one-stop explanation
- SAP Spartacus - progressive web applications, progressive web applications
- Pytorch structure reparameterization repvggblock
- ASP rs.open SQL, Conn, what does 3, 1 stand for in 3,1?
- If in ython__ name__ == ‘__ main__‘: Function and principle of
猜你喜欢
![[29. DFS depth is preferred]](/img/f1/f0c4302a1f7c14c206ff0bdf2eed5c.png)
[29. DFS depth is preferred]

Tool use of rookie tutorial -- View subclass (implementation class) class diagram in idea

MySQL Basics (concepts, common instructions)

Pads copper laying

7.14 - daily question - 408

7.16 - daily question - 408

C recursively obtains all files under the folder and binds them to the treeview control

Moonpdflib Preview PDF usage record
Unity slider slider development
![[C + + primer notes] Chapter 6 functions](/img/9a/b79e7c3013678038420faee329d6b6.jpg)
[C + + primer notes] Chapter 6 functions
随机推荐
Latex notes
Pursue and kill "wallet Assassin" all over the network
Dynamic kubernetes cluster capacity expansion of airbnb
[29. DFS depth is preferred]
[basic usage of STL]
Worthington cytochrome c digestion study carboxypeptidase B scheme
Related knowledge of paging
如何创建索引
Redis管道技术/分区
Fabric. JS centered element
Wireshark packet capturing and rapid packet location skills
[25. Hash table]
After burning up 130 billion yuan in ten years, vertical e-commerce will eventually enter the dust of history
ROS manipulator movelt learning notes 3 | kinect360 camera (V1) related configuration
Volley7 – networkdispatcher obtains data from the network [easy to understand]
Educational codeforces round 89 (rated for Div. 2) ABC problem solution
How to implement a state machine?
第四章 驱动子系统开发
Install scoop and lux (formerly Annie)
Unity panel control