当前位置:网站首页>How to refine permissions to buttons?
How to refine permissions to buttons?
2022-06-23 00:36:00 【A little rain in Jiangnan】
@[toc] Because I wrote a lot Spring Security The reason for the article , So there is always a little friend to ask brother song : How to implement button level permissions ? Some have even seen vhr My little friend also asked this question , In fact, sometimes it makes me really depressed , I just want to do TienChin project , I'll take this problem out again and carefully smooth it out with my friends .
1. Authority granularity
First of all, we all know that permissions have different granularity , stay vhr In the project , On the whole, I handle permissions based on the request address , Is this granularity coarse or fine ?
Some partners may think that the permission granularity is too coarse , The so-called fine-grained permissions should be button based .
If there are small partners who have done the development of the front and back end , There should be such experience : stay Shiro perhaps Spring Security In the frame , Some labels are provided , These tags can be used to meet certain roles or permissions , Show a button ; When a user does not have a certain role or permission , The button is automatically hidden .
But think about it , The display and hiding of buttons is just a style change made by the front page to improve the user experience , Essentially , When you click a button , Or sent a HTTP request , Then the interface for the server to process the request , Permission control is required . Since you want to control permissions on the interface , Then follow vhr What's the difference ?
Now it is popular to separate the front end from the back end , therefore Shiro perhaps Spring Security The front-end tags in are basically not used now , Instead, the user logs in successfully , Send a request to the server , Get the permissions and role information of the currently logged in user , Then according to these permissions 、 Role and other information , The front-end automatically determines whether a menu or button should be displayed or hidden , The goal is to improve the user experience , Avoid users from clicking on a button without permission . The display or hiding of the front end is just to improve the user experience , The real permission control still needs to be done by the backend .
The backend can handle permissions in the interface or business layer , Where to do it , It depends on their own projects .
therefore ,vhr The permissions , In terms of design , The granularity is not coarse , It is also fine-grained , It's just with the menu list , My friends may feel a little rough . however , The menu table can be further refined , We can continue to add new records to the menu table , New record hidden Field is true, The menu is hidden , It's just a matter of refining permissions .
As shown in the figure below, you can continue to add new access rules , Just put enabled Field set to false that will do ( So the menu won't be displayed , It is simply the configuration of permissions ).

therefore vhr The permission design of is OK Of .
When you understand vhr Permission design in , Look again. TienChin This project , Or look RuoYi-Vue This scaffold , You will find it very easy 了 .
2. Permissions on the table
First, let's look at the definition of the resource table , That is to say sys_menu.
CREATE TABLE `sys_menu` ( `menu_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ' menu ID', `menu_name` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL COMMENT ' Menu name ', `parent_id` bigint(20) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' Parent menu ID', `order_num` int(4) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' According to the order ', `path` varchar(200) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '' COMMENT ' Routing address ', `component` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Component path ', `query` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Routing parameters ', `is_frame` int(1) DEFAULT '1' COMMENT ' Whether it is an external chain (0 yes 1 no )', `is_cache` int(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' Whether the cache (0 cache 1 Don't cache )', `menu_type` char(1) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '' COMMENT ' Menu type (M Catalog C menu F Button )', `visible` char(1) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' Menu status (0 Show 1 hide )', `status` char(1) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' Menu status (0 normal 1 Discontinue use )', `perms` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Authority sign ', `icon` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '#' COMMENT ' Menu icons ', `create_by` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '' COMMENT ' The creator ', `create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Creation time ', `update_by` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '' COMMENT ' Update the ', `update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Update time ', `remark` varchar(500) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT '' COMMENT ' remarks ', PRIMARY KEY (`menu_id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3054 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci COMMENT=' Menu permission table '; In fact, many fields here are related to us vhr The project is very similar , I won't repeat , Here I mainly talk about a field with my friends , That's it menu_type.
menu_type Represents the type of a menu field , There are three types of menus , They are the directory (M)、 menu (C) And the buttons (F). The contents mentioned here , It's like we're in vhr The first level menu mentioned in , The menu is equivalent to what we are doing in vhr The secondary menu described in .
When the user logs in from the front end successfully , To dynamically load the menu , Just search M and C Type of data ,F Data of type is not a menu item , You can filter it directly when querying , adopt menu_type This field can be easily filtered out F Data of type . Guys, think about it ,F After filtering the data of type , The rest of the data is just the first level menu and the second level menu , That's not the same vhr Is it the same again !
Finally, let's talk about F Type of ,F Type is the button level permission , The execution of each button on the front end , What permissions are needed , Now define it here .
Let me give you a simple example :

When you need to show User management This menu , need system:user:list This authority , When you need to click The user to change When you push this button , You need to system:user:edit This authority .
Other related tables are basically the same as vhr It's all the same , Users have user tables sys_user, Roles have role tables sys_role, The tables associated with users and roles are sys_user_role, The tables associated with resources and roles are sys_role_menu.
When the user logs in successfully , The back end will provide an interface , Return all the roles and permissions of the current user to the front end :
- Query the role idea : According to the user id, Go first
sys_user_roleRoles are found in the table id, Then according to the role id Go tosys_roleThe corresponding role is found in the table ( This description is for your convenience , In fact, a multi table joint query is sufficient ). - Query permission idea : According to the user id, Go first
sys_user_roleRoles are found in the table id, Then according to the role id Go tosys_roleThe corresponding role is found in the table , Then take the character id Go tosys_role_menuThe corresponding... Is found in the tablemenu_id, According tomenu_idGo tosys_menuThe corresponding... Is found in the table menu The permissions ( This description is for your convenience , In fact, a multi table joint query is sufficient ).
After the front end has user permissions and roles , You can decide whether to display a menu or a button .
3. Backend permission judgment
Let me talk about this first TienChin How to do it in the project ( namely RuoYi Implementation scheme of scaffold ), And again vhr Make a comparison .
stay TienChin In a project, permissions are controlled through annotations , The access rights of interfaces are marked by annotations , For example, the following :
@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('system:menu:add')")@PostMappingpublic AjaxResult add(@Validated @RequestBody SysMenu menu) { // Omit }/** * Modify the menu */@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('system:menu:edit')")@PutMappingpublic AjaxResult edit(@Validated @RequestBody SysMenu menu) { // Omit }/** * Delete menu */@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('system:menu:remove')")@DeleteMapping("/{menuId}")public AjaxResult remove(@PathVariable("menuId") Long menuId) { // Omit } What permissions are required for each interface , It's all through @PreAuthorize Annotation to achieve , How this annotation works , Brother song also wrote two articles before :
- You want to control your permissions , These eight notes you must know !
- Spring Security Is the permission annotation in magic ?
I understand these two articles , I understand the above annotation , I won't repeat it here .
But in the final analysis, there is still a little bit of this way of writing “ Hard encoding ”, Because what permissions are required to access which interface , Fixed in the code , If the direct relationship between interface and permission can be saved to the database , Then users can when they need it , Flexible modification at any time , Beauty is not true !
stay vhr In the project , Brother song used Spring Security Custom in FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource and AccessDecisionManager The dynamic control authority of the server is realized . This specific implementation idea was also shared with you in the previous article , Portal :Spring Security Dynamic permission implementation scheme !, I won't repeat it here .
relatively speaking ,vhr The implementation scheme in is more flexible , Because the relationship between interfaces and permissions can be configured . But how to say ? It's like RuoYi-Vue In fact, hard coding is not impossible , After all, the mapping relationship between interfaces and permissions is still a little obvious “ major ” some , Ordinary users may not know how to configure , The system provides this function , So most of them are for professionals like programmers , So do programmers really need this feature ? I think it is still necessary to analyze the situation in detail .
All in all , Small partners can combine the actual situation of their own projects , To determine whether the mapping relationship between interfaces and permissions needs dynamic management , If you need dynamic management , Then you can follow vhr The scheme in , If you don't need dynamic management , Then follow RuoYi-Vue The way in the scaffold .
How to set the user's permissions ? Let's talk about this topic today .
4. Roles and authorities
First, let's look at roles and permissions , How to design roles and permissions , In fact, there are many very mature theories , The most common is RBAC 了 .
4.1 RBAC brief introduction
RBAC(Role-based access control) Is a role-based access control (Role-based access control,RBAC), It is a relatively new and widely used permission control mechanism , This mechanism does not directly grant permissions to users , It's about giving authority to roles .
RBAC The permission model classifies users by role , Through the role of the user to determine whether the user has the operation authority on a resource .RBAC Simplify the management of users and permissions , It associates users with roles 、 Roles are associated with permissions 、 Permissions are associated with resources , This mode makes user authorization management very simple and easy to maintain .
4.2 RBAC The proposed
jurisdiction 、 Characters these things , In the early 1970 Relevant applications can be found in commercial computer programs in the s , But the early process was relatively simple , And there is no definite 、 General purpose 、 A recognized rights management model .
Ferraiolo and Kuhn Two big men in 1992 A universal role-based access control model was proposed in ( It seems that this model is older than SongGe ), For the first time RBAC The permission model is used to replace the traditional MAC and DAC Two permission control schemes , And that's it RBAC The related concepts in .
Ferraiolo,Cugini and Kuhn On 1995 It's been expanded in 1992 Permission model proposed in . The main function of this model is that all access is through roles , A role is essentially a collection of permissions , And all users can only obtain permissions through roles . Within the organization , The role is relatively stable , There are many users and permissions , And may change rapidly . therefore , Controlling permissions through roles can simplify the management and inspection of access control .
here we are 1996 year ,Sandhu,Coyne,Feinstein and Youman Officially put forward RBAC Model , The model refines RBAC, Based on this theory, the RBAC0-RBAC3 Four different models .
today , Most information technology providers have RBAC Into their product line , In addition to regular enterprise applications ,RBAC It is also widely used in medical treatment 、 Defense and other fields .
At present, online about RBAC SongGe only finds theoretical things in English , Interested partners can have a look , The address is :
If the friends have Chinese Information Links , Welcome to note .
4.3 RBAC Three principles
- Minimum permissions : The permissions configured for a role are the minimum set of permissions it needs to complete a task .
- Separation of responsibilities : Accomplish tasks jointly through mutually independent and mutually exclusive roles .
- Data abstraction : Through the abstraction of authority ,RBAC The level of data abstraction supported is similar to RBAC Implementation details of .
4.4 RBAC Model classification
Speaking of RBAC, We have to start with its model classification .
4.4.1 RBAC0
RBAC0 Is the simplest user 、 role 、 The permissions model .RBAC0 yes RBAC The core part of the permission model , Other models are built on this basis .
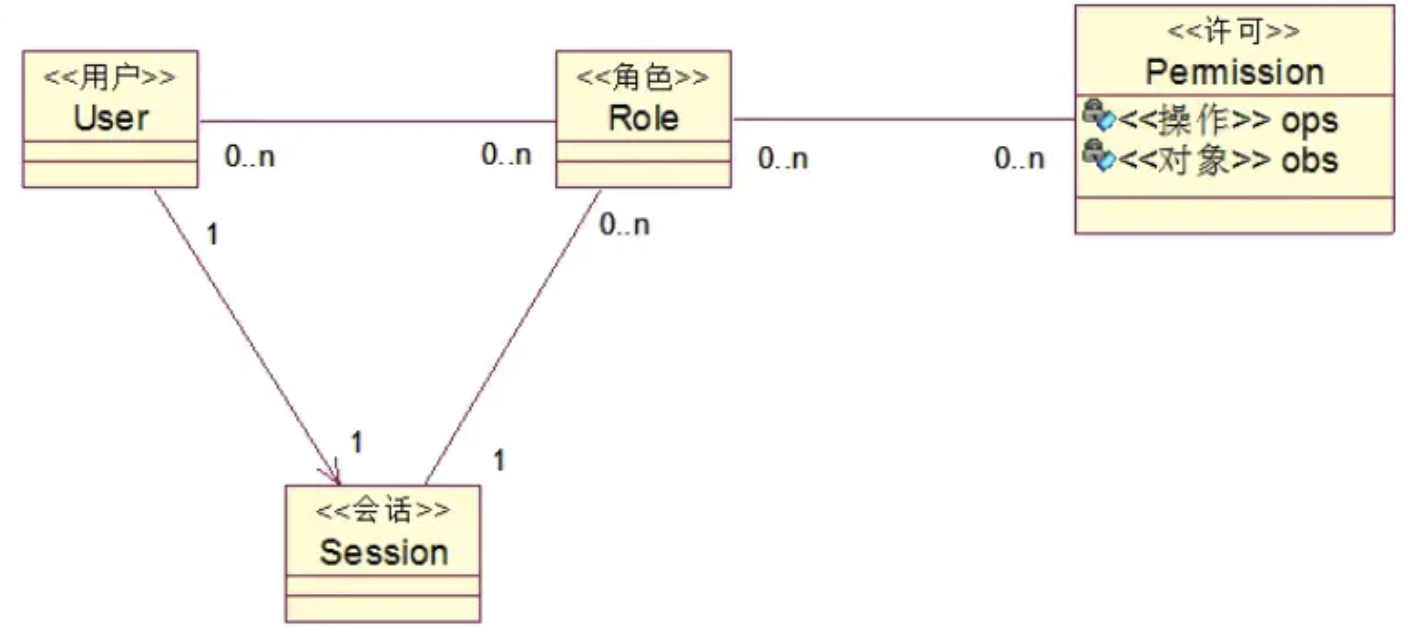
stay RBAC0 in , A user can have multiple roles , A role can have multiple permissions , The permissions of the end user are the combination of the permissions of the roles that the user has .
4.4.2 RBAC1
RBAC1 It is in RABC0 Role inheritance is introduced on the basis of , Let the role have a parent-child relationship .

In the previous articles in this series , Brother song has also introduced to you many times Spring Security Character inheritance in .
4.4.3 RBAC2
RBAC2 Also in RBAC0 On the basis of expansion , The static responsibility separation and dynamic responsibility separation are introduced .

Understand the separation of duties , We have to understand that roles are mutually exclusive .
In the actual project , Some roles are mutually exclusive , Antagonistic , For example, the role of finance cannot be held concurrently with other roles , Otherwise, I will make my own reimbursement and approve it myself , Isn't it true that !
This problem can be solved by separating responsibilities :
Static separation of duties
Restrictions are made in the setting phase . For example, the same user cannot be granted mutually exclusive roles , Users can only have a limited number of roles , Users should have low-level permissions before obtaining high-level permissions .
Dynamic separation of duties
Limit during the operation phase . For example, under the same user at runtime 5 You can only have two characters at the same time 2 Role activation, etc .
4.4.4 RBAC3
take RBAC1 and RBAC2 Combine , Formed RBAC3.

4.5 Expand
Many permission models we see everyday are in RBAC Based on .
For example, we can see the concept of user group in some systems , Is to group users , Users have both their own roles and grouped roles .
We TienChin Permissions in scaffolds used in the project , It is basically based on RBAC From this permission model .
5. Table design
Let's see RuoYi-Vue Follow the user in the scaffold 、 Role and permission related tables .
The following tables are mainly involved here :
sys_user: This is the user table .sys_role: This is the role table .sys_user_role: This is the user role association table .sys_menu: This is the menu , It can also be understood as a resource table .sys_role_menu: This is the resource role association table .
Through the user's id, You can go to sys_user_role The user's role can be found in the table id, Then according to the role id, Go to sys_role_menu The resources that can be operated by this role are queried in the table id, Then according to the resources id, Go to sys_menu The corresponding resource is found in the table , This is basically the same process .
that Java What to do in the code ?
6. Code implementation
So we define one Java class SysUser, This is the same as that in the database sys_user The table corresponds to , Let's see UserDetailsService The concrete realization of :
@Servicepublic class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserDetailsServiceImpl.class); @Autowired private ISysUserService userService; @Autowired private SysPermissionService permissionService; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { SysUser user = userService.selectUserByUserName(username); if (StringUtils.isNull(user)) { log.info(" The logged in user :{} non-existent .", username); throw new ServiceException(" The logged in user :" + username + " non-existent "); } else if (UserStatus.DELETED.getCode().equals(user.getDelFlag())) { log.info(" The logged in user :{} have been deleted .", username); throw new ServiceException(" I'm sorry , Your account number :" + username + " have been deleted "); } else if (UserStatus.DISABLE.getCode().equals(user.getStatus())) { log.info(" The logged in user :{} Has been disabled .", username); throw new ServiceException(" I'm sorry , Your account number :" + username + " deactivated "); } return createLoginUser(user); } public UserDetails createLoginUser(SysUser user) { return new LoginUser(user.getUserId(), user.getDeptId(), user, permissionService.getMenuPermission(user)); }}What you can find from the database is SysUser object , Then the object is slightly modified , Transform it into a LoginUser object , This LoginUser It is UserDetails Implementation class of interface , The key information of the currently logged in user is saved inside .
Creating LoginUser When the object , There is one permissionService.getMenuPermission Method is used to query the user's permissions , According to the current user's id, Query the user's role , Then according to the user role , Query the user's permission , in addition , If the current user's role is admin, Then set the user role to *:*:*, This is a hard coded .
Let's see LoginUser The design of the :
public class LoginUser implements UserDetails { /** * Permission list */ private Set<string> permissions; /** * User information */ private SysUser user; public LoginUser(Long userId, Long deptId, SysUser user, Set<string> permissions) { this.userId = userId; this.deptId = deptId; this.user = user; this.permissions = permissions; } @JSONField(serialize = false) @Override public String getPassword() { return user.getPassword(); } @Override public String getUsername() { return user.getUserName(); } /** * Whether the account has not expired , Expiration cannot be verified */ @JSONField(serialize = false) @Override public boolean isAccountNonExpired() { return true; } /** * Specifies whether the user unlocks , Locked user cannot authenticate * * @return */ @JSONField(serialize = false) @Override public boolean isAccountNonLocked() { return true; } /** * Indicates whether the user's credentials have expired ( password ), Expired credentials prevent authentication * * @return */ @JSONField(serialize = false) @Override public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() { return true; } /** * Is it available , Disabled users cannot authenticate * * @return */ @JSONField(serialize = false) @Override public boolean isEnabled() { return true; } @Override public Collection<!--? extends GrantedAuthority--> getAuthorities() { return null; }}There are some attributes I have omitted , You can download the source code at the end of the article .
Guys, see , This LoginUser Realized UserDetails Interface , But and vhr There is a big difference in , There is no treatment here getAuthorities Method , That is to say, when the system wants to obtain user permissions , Without saying a word, you can return to one null. What's the matter ?
Because in this scaffold , When performing permission verification in the future , It is based on the following :
@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('system:menu:add')")@PostMappingpublic AjaxResult add(@Validated @RequestBody SysMenu menu) { // Omit }@PreAuthorize In the annotations @ss.hasPermi('system:menu:add') expression , Represents a call to Spring One of the containers is named ss Of Bean Of hasPermi Method , To determine whether the current user has a system:menu:add Authority . A group called ss Of Bean Of hasPermi The method is as follows :
@Service("ss")public class PermissionService { /** * All permission identifiers */ private static final String ALL_PERMISSION = "*:*:*"; /** * Administrator role permission id */ private static final String SUPER_ADMIN = "admin"; private static final String ROLE_DELIMETER = ","; private static final String PERMISSION_DELIMETER = ","; /** * Verify that the user has certain permissions * * @param permission Permission string * @return Whether the user has certain permissions */ public boolean hasPermi(String permission) { if (StringUtils.isEmpty(permission)) { return false; } LoginUser loginUser = SecurityUtils.getLoginUser(); if (StringUtils.isNull(loginUser) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(loginUser.getPermissions())) { return false; } return hasPermissions(loginUser.getPermissions(), permission); } /** * Determine whether permission is included * * @param permissions Permission list * @param permission Permission string * @return Whether the user has certain permissions */ private boolean hasPermissions(Set<string> permissions, String permission) { return permissions.contains(ALL_PERMISSION) || permissions.contains(StringUtils.trim(permission)); }}Because this is a purely manual operation , In comparison , Get the current login user object directly LoginUser, Then call his... Manually hasPermissions Method to determine whether the permission is satisfied , Because they are all custom operations , So whether to realize UserDetails#getAuthorities Methods are no longer important , But according to the comparison scheme here , Wildcard comparison is not supported .
For example, the user has all the operation permissions for the dictionary table , Expressed as system:dict:*, But when and system:dict:list When comparing , It is found that the comparison result is false, It is also possible to compare success , For example, you can operate through regular expressions or other methods , It's all string comparison anyway , I believe everyone can handle it by themselves .
Now? , The front end provides the operation page , You can also configure the role of each user , You can also configure the permissions that each role can operate , This is a little bit easier , Not much to say .
All right. , This is it. TienChin In the project RBAC Permission implementation scheme , SongGe will also record relevant video tutorials later , Friends interested in videos poke here :TienChin Here comes the supporting video of the project .</string></string></string>
边栏推荐
- Express, route, request object, response object, middleware, EJS template
- Problèmes rencontrés lors de l'utilisation de redistemplate
- 股票在哪个平台买比较安全呢?
- What financial product does the new bond belong to?
- 软件构造课程ADT与OOP理解
- Fibonacci sequence set
- 【GO】Go Modules入門
- Analysis on the wallet system architecture of Baidu trading platform
- ECMAScript6新特性
- Is it reliable to get new debts? Is it safe?
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
How to set the power-off auto start of easycvr hardware box
13. Roman numeral to integer
Ecmascript6 new features
Kunlundb query optimization (II) project and filter push down
Typecho仿盧松松博客主題模板/科技資訊博客主題模板
Hello, is the securities account presented by the Business School of qiniu business school safe? How can I open a safe stock account to speculate in stocks
[go] go array and slice (dynamic array)
OpenCvSharp (C# OpenCV) 微信QRCode解码功能使用介绍(附源码)
KunlunDB 查询优化(一)
flowable 全局监听 监听流程的启动和流程的结束
昆仑分布式数据库技术优势
Fibonacci sequence set
Package management tools --npm, -cnpm, -yan, -cyarn
声网多人视频录制与合成支持掉线再录制 | 掘金技术征文
Es5 object extension methods //call, apply and bind
Database daily question - day 20: selling products by date
Is Ruida futures safe? What are the procedures for opening futures accounts? How to reduce the futures commission?
事物系统的几种异常场景
事务系统的隔离级别
2022 TIANTI match - National Finals rematch