当前位置:网站首页>Custom type
Custom type
2022-07-25 01:01:00 【Kkkkvvvvvxxx】
Catalog
Preface
When analyzing the storage of data , I mentioned custom types , Including structure 、 Consortium, etc , This blog introduces basic user-defined types and various types of features ;
1. Structure
1.1 Declaration of a structure
Structure : A combined data structure composed of different data
The general declaration method is :
struct Structure name
{
List of members
};
among , Structure name is also called “ Structural markings ”, Inside the curly brackets are the sub items contained in the structure , The member table column is also called “ Domain table ”, Each structure member is each domain in the structure .
1.2 Define and initialize structure type variables
There are three ways to define structural variables , Let's take a look at one by one :
1.2.1 Declare the structure type before initializing
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
struct Student
{
int num;
char name[20];
char sex;
int age;
char addr[30];
};
int main()
{
struct Student Stu1 = {
10,"kkk",'n',20,"11111" };
return 0;
}
1.2.2 Declare the structure type and define variables
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
struct Student
{
int num;
char name[20];
char sex;
int age;
char addr[30];
}Stu2 = {
30,"zzz",'n',40,"kkkkkkkkk" };
1.2.3 Define struct type variables directly without specifying type names
struct
{
int num;
char name[20];
char sex;
int age;
char addr[30];
}Stu2 = {
30,"zzz",'n',40,"kkkkkkkkk" };
At this time, an anonymous structure type is specified , Obviously, you cannot define other variables in this structure type area .
1.3 Array of structs
When multiple data of the same structure type is required , Now we can introduce the structure array ; Each of these elements is of structural type .
It is defined as follows :
1️⃣
struct Structure name
{
List of members
} Array name [ The length of the array ];
2️⃣
struct Structure name
{
List of members
};
Type of structure Array name [ The length of the array ];
1.4 Structure pointer
It is defined as (struct Type name *p); here p Is a pointer variable that points to the structure type .
1.4.1 Pointer to struct variable
struct Student
{
int num;
char name[20];
char sex;
int age;
char addr[30];
};
int main()
{
struct Student* pt;
struct Student Stu;
pt = &Stu;
Stu.num = 1;
Stu.age = 20;
Stu.sex = 'M';
strcpy(Stu.name, "zhangsan");
strcpy(Stu.addr, "kkkkkkkk");
printf("%-5d %-5d %-5c %-10s %-10s\n", Stu.num,
Stu.age,
Stu.sex,
Stu.name,
Stu.addr);
printf("%-5d %-5d %-5c %-10s %-10s\n", pt->num,
pt->age,
pt->sex,
pt->name,
pt->addr);
printf("%-5d %-5d %-5c %-10s %-10s\n", (*pt).num,
(*pt).age,
(*pt).sex,
(*pt).name,
(*pt).addr);
return 0;
}
It is easy to know from the above code ,pt The pointer points to the structure , When assigning a value to the structure , We have 3 In the way , They are structure references ,(*p) quote , And the pointing operator -> quote .
1.4.2 A pointer to an array of structs
struct Student
{
char name[20];
int age;
};
int main()
{
struct Student stu[3] = {
{
"zhangsan",20},{
"lisi",17},{
"wangwu",22} };
struct Student* pt;
pt = stu;
for (; pt < stu + 3; pt++)
{
printf("%-10s %-5d\n", pt->name, pt->age);
}
return 0;
}
here , The pointer points to the structure array , send pt First point to the address of the first element of the array , So as to keep printing , The use method is consistent with the pointer pointing to an ordinary array .
1.4.3 Use structural variables and pointers of structural variables as parameters
- Use structural variable members as parameters , The usage is consistent with ordinary variables , Belong to " Value passed ", But the types of formal and actual parameters need to be consistent
- Use structural variables as arguments , It also uses " Value passed ", On function call , Formal parameters also need to occupy memory units ; This method costs a lot of space and time , And after changing the formal parameters , Cannot return the calling function , Often used infrequently .
- Use a pointer to a structure variable as an argument , Pass the address of the structure variable as an argument .
1.5 Structure memory alignment
1.5.1 Structure memory calculation
In profiling data storage , I mentioned that each type has size , So next, we will introduce the size of the structure in memory .
Let's look at examples :
1️⃣
struct s1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
printf("%d", sizeof(struct s1));

2️⃣
struct s1
{
char c1;
char c2;
int i;
};
printf("%d", sizeof(struct s1));

In the first two cases , We can see that when designing the structure, the members that occupy less space are gathered together to save space .
3️⃣
struct s2
{
double d;
char c;
int i;
};
printf("%d", sizeof(struct s1));

4️⃣
struct s1
{
double d;
char c;
int i;
};
struct s2
{
char c1;
struct s1 s1;
double d;
};
int main()
{
printf("%d", sizeof(struct s2));
}

1.5.2 Reasons for memory alignment
- Platform reasons : Not all hardware platforms can access any address data , Some platforms can only get specific data types at specific addresses , Otherwise, throw an exception , This is a little similar to MCU .
- Performance reasons : data structure ( Stack ) It should be aligned at the natural boundary as far as possible , Because for unaligned memory , It requires two memory accesses , For aligned memory , Only one memory access is required .
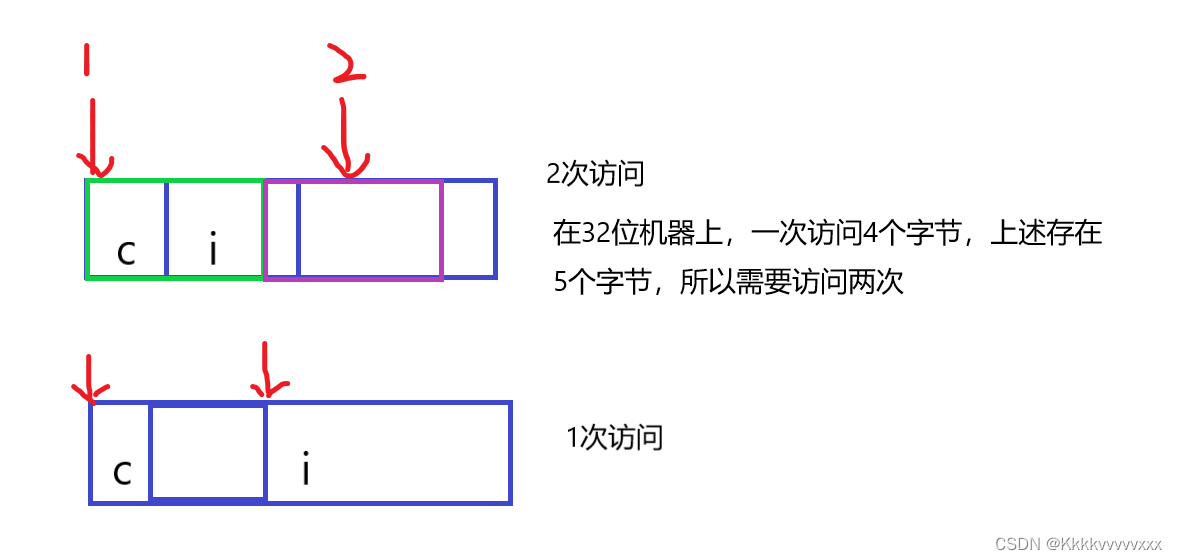
therefore : Memory alignment of structures is a space for time approach .
1.6 Change the default alignment number
#pragma pack(1)// Set the default alignment number to 1
struct s1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
#pragma pack()// Restore the default alignment number
struct s2
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s1));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s2));
return 0;
}
utilize #pragma Instruction to set the alignment number ;
#pragma pack() Restore the default alignment number .
stay VS The default alignment number in is 8, Of course , Some compilers do not have a default alignment number , So the alignment number is the size of its type !
2. Bit segment
2.1 Introduction of bit segment
The declaration and structure of bit segment are similar to that of structure ;
- The member of the segment must be int、unsigned int、char That is, integer .
- The member name of the bit field is followed by a colon and a number ( The number represents the size of the bit it occupies and cannot exceed the size of the bit of its type )
such as :
struct A
{
int _a:2;
int _b:5;
int _c:10;
int _d:30;
};
among _a Occupy 2 A bit ,_b Occupy 5 A bit , And so on .
2.2 Bit segment memory allocation
- Members of the bit segment can int、unsigned int 、char type ;
- The space of the bit segment is as needed 4 Bytes (int) perhaps 1 Bytes (char) To open up ;
- Bit segments involve many unstable factors , And the bit segment is not cross platform , Programs that focus on portability should avoid bit segments .
as follows , Let's look at how to store bit segments :
struct S
{
char a : 3;
char b : 4;
char c : 5;
char d : 4;
};
int main()
{
struct S s = {
0 };
s.a = 10;
s.b = 12;
s.c = 3;
s.d = 4;
return 0;
}


Put the above 16 It's binary 62 03 04 Convert to 2 Base is consistent with our assumption !
2.3 The cross platform problem of bit segment
- int It's uncertain whether a bit segment is treated as a signed number or an unsigned number ;
- The maximum number of bits in a bit segment is uncertain (16 The largest bit on the machine is 16,32 The largest bit on the machine is 32);
- Whether to allocate bits from left to right or right to left in the bit segment is uncertain , Our above assumption is to allocate from low to high , That is, from right to left ;
- When there are multiple bit segments , The second bit segment is relatively large , After the allocation of the first bit segment , The remaining space is not enough to support the allocation of the second bit segment , Therefore, it is uncertain whether to use the remaining bits or not after opening up new bytes .
therefore , in general , Compared to the structure , Bit segment can save space well, but its cross platform problem can still not be ignored !
3. enumeration
3.1 Definition of enumeration
enum Day
{
Mon,
Tues,
Wed,
Whur,
Fri,
Sat,
Sun
};
The default is 0 At the beginning , Each increment 1, Of course, you can also redefine the initial value .
{} The contents in are possible values of enumeration types , Also known as enumeration constants .
enum Day
{
Mon,
Tues,
Wed,
Whur,
Fri,
Sat,
Sun
};
enum Day d=Mon;
// You can only assign values to enumeration variables with enumeration constants
3.2 Advantages of enumeration
- Increase the maintainability and readability of the code
- And #define More rigorous than
- Prevent named pollution
- Easy to debug
- Easy to use , You can define multiple constants at once
4. Consortium ( Shared body )
4.1 Definition of common body
Its feature is to store multiple variables in a memory unit , These variables use this part of the memory unit together , And the starting addresses of these variables are the same !
Similar to the definition of structure :
union Community name
{
List of members
} List of variables ;
4.2 Common body size calculation
The members of the union share a single piece of memory , So the size of such a joint variable should be at least the size of the largest member, that is, the memory length of the longest member !
- The size of the consortium is at least the size of the largest member !
- When the size of the largest member is not an integer multiple of the maximum alignment number , It's about aligning to an integer multiple of the maximum number of alignments !
union un1
{
char c[5];
int i;
};
union un2
{
short arr[7];
int i;
};
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof (union un1));
printf("%d\n", sizeof (union un2));
return 0;
}
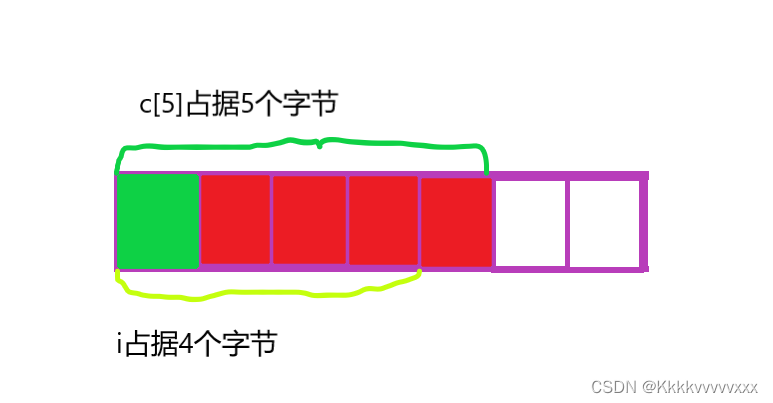
therefore , The first community occupies 8 Bytes , Empathy , Occupied by the second community 16 Bytes .
4.3 The characteristics of Commons
- Generally, only one variable is used in the community , Each variable will not be assigned at the same time , That is, there is only one content in the storage unit
- C99 standard , Common bodies of the same type can be assigned to each other
- C99 After the standard , You can use common body variables as function parameters ; Before , Only the pointer to the common body can be used as a function parameter
5.Ending
That's all for this custom type , The content is still relatively obscure , I hope this blog can help you , Okay , be it so *️*️

边栏推荐
- [mindspore] [mode] spontaneous_ The difference between mode and graph mode
- Pytorch structure reparameterization repvggblock
- torch.nn.SyncBatchNorm.convert_ sync_ Mindspore usage corresponding to batchnorm
- 7.24 party notice
- How to better use the touchpad of notebook
- The use of Multimeter in circuit analysis experiment of Shandong University
- Detailed explanation of the usage of vector, queue and stack
- Add the two numbers in the linked list of the second question of C language. Ergodic method
- Chapter IV drive subsystem development
- Login and payment arrangement in uniapp
猜你喜欢

Implementing DDD based on ABP -- domain logic and application logic

7.14 - daily question - 408

7.18 - daily question - 408

Kusionstack open source | exploration and practice of kusion model library and tool chain
![[Bert] QA, reading comprehension, information retrieval](/img/3b/f632271be813cd71a44b204f5060c4.png)
[Bert] QA, reading comprehension, information retrieval
![Why does [mindspore ascend] [custom operator] repeatedly assign values to one tensor affect another tensor?](/img/e3/135ac1e6eade70082c205d16ab8e34.jpg)
Why does [mindspore ascend] [custom operator] repeatedly assign values to one tensor affect another tensor?

How to implement the server anti blackmail virus system is a problem we have to consider

Financial RPA robot enables enterprises to open a new era of intelligence

Construction of Seata multilingual system
Example analysis of enum data type in MySQL
随机推荐
Wireshark packet capturing and rapid packet location skills
Basic functions of tea
Interview questions
Improve static loading dynamic loading
Mobile terminal touch event
jquer $(‘div li‘) $(‘div,li‘) $(‘div>li‘) $(‘div‘,‘li‘)
Install and configure php5-7 version under centos7.4
Free personal virtual machine - AWS free EC2 package
自动化测试系列-Selenium三种等待详解
Unity image control and rawimage
Financial RPA robot enables enterprises to open a new era of intelligence
Method properties of ASP adodb.stream object
The troubleshooting process of a segment error (disassembly address troubleshooting)
Login and payment arrangement in uniapp
Install scoop and lux (formerly Annie)
Some of my understanding about anti shake and throttling
The new version of Alibaba Seata finally solves the idempotence, suspension and empty rollback problems of TCC mode
Password input box and coupon and custom soft keyboard
Detailed explanation of the usage of vector, queue and stack
Uncaught typeerror: cannot read properties of null (reading 'append') solution