当前位置:网站首页>爱可可AI前沿推介(6.26)
爱可可AI前沿推介(6.26)
2022-06-26 13:07:00 【智源社区】
转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
摘要:皮层-皮质网络单相深度学习、基于单色事件相机的神经辐射场、图神经网络梯度流框架、基于半监督多任务训练改善药物-靶点亲和力预测、实时3D人体特征点与姿态估计、多模态多视Transformer集成、用自动生成轮廓替代标记真实图像数据集、用艺术作品对生成模型进行基准测试、低精度随机梯度Langevin动力学
1、[LG] Single-phase deep learning in cortico-cortical networks
W Greedy, H W Zhu, J Pemberton, J Mellor, R P Costa
[University of Bristol]
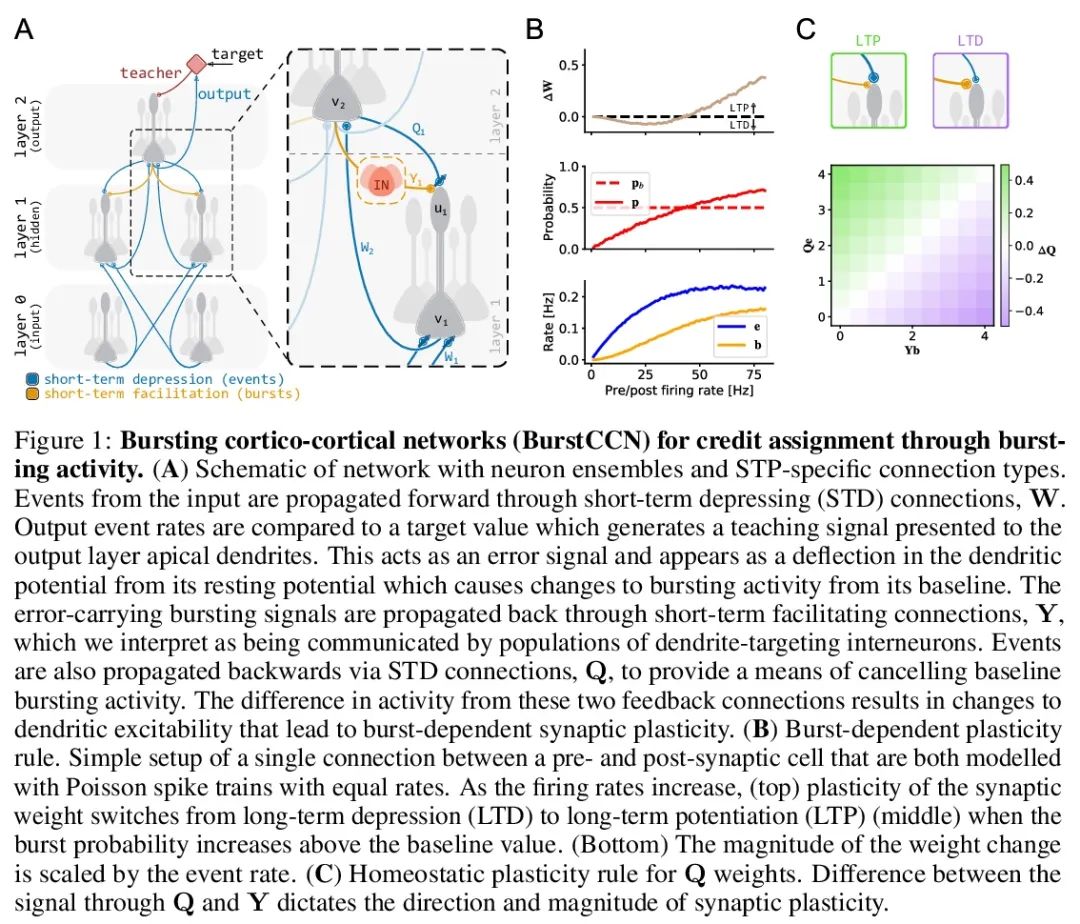
皮层-皮质网络单相深度学习。误差反向传播(backprop)算法仍然是人工神经网络中最常用的信用分配算法。在神经科学中,大脑是否可以采用类似的策略来正确地修改其突触尚不清楚。最近的模型试图弥补这一差距,同时与一系列的实验观察相一致。然而,这些模型要么不能有效地跨多层反向传播错误信号,要么需要一个多相学习过程,这两者都不能让人联想到大脑中的学习。在此,本文提出一种新模型——bursting cortico-cortical networks (BurstCCN),通过整合皮质网络的已知特性,即bursting活动、短期可塑性(STP)和树突靶向中间神经元来解决这些问题。BurstCCN依赖于通过连接类型特定的STP的burst多路复用,在深度皮层网络中传播类似背反向传播的误差信号。这些误差信号在远端树突编码,并诱导burst依赖的可塑性作为兴奋-抑制自上而下输入的结果。本文证明了所提出模型可有效地反向传播误差通过多层使用单相学习过程。以经验和分析的方式展示了在该模型中学习近似反向传播导出的梯度。证明了该模型能学习复杂的图像分类任务(MNIST和CIFAR-10)。实验结果表明,亚细胞、细胞、微电路和系统水平的皮层特征共同构成了大脑中单相高效深度学习的基础。
The error-backpropagation (backprop) algorithm remains the most common solution to the credit assignment problem in artificial neural networks. In neuroscience, it is unclear whether the brain could adopt a similar strategy to correctly modify its synapses. Recent models have attempted to bridge this gap while being consistent with a range of experimental observations. However, these models are either unable to effectively backpropagate error signals across multiple layers or require a multiphase learning process, neither of which are reminiscent of learning in the brain. Here, we introduce a new model, bursting cortico-cortical networks (BurstCCN), which solves these issues by integrating known properties of cortical networks namely bursting activity, short-term plasticity (STP) and dendrite-targeting interneurons. BurstCCN relies on burst multiplexing via connection-type-specific STP to propagate backprop-like error signals within deep cortical networks. These error signals are encoded at distal dendrites and induce burst-dependent plasticity as a result of excitatory-inhibitory topdown inputs. First, we demonstrate that our model can effectively backpropagate errors through multiple layers using a single-phase learning process. Next, we show both empirically and analytically that learning in our model approximates backprop-derived gradients. Finally, we demonstrate that our model is capable of learning complex image classification tasks (MNIST and CIFAR-10). Overall, our results suggest that cortical features across sub-cellular, cellular, microcircuit and systems levels jointly underlie single-phase efficient deep learning in the brain.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.11769




2、[CV] EventNeRF: Neural Radiance Fields from a Single Colour Event Camera
V Rudnev, M Elgharib, C Theobalt, V Golyanik
[Max Planck Institute for Informatics]
EventNeRF:基于单色事件相机的神经辐射场。到目前为止,学习基于坐标的立体3D场景表示,如神经辐射场(NeRF),一直在假设RGB或RGB-D图像作为输入进行研究。同时,从神经科学文献中得知,人类视觉系统(HVS)是定制化处理异步亮度变化而不是同步RGB图像,以建立和不断更新周围环境的心理3D表示,用于导航和生存。受HVS原理启发的视觉传感器是事件摄像机。因此,事件是稀疏和异步的逐像素亮度(或颜色通道)变化信号。相对于已有的神经3D场景表示学习的研究成果,本文从一种新角度来研究该问题。本文证明了从异步事件流中学习适合RGB空间中新视图合成的NeRF是可能的。所提出模型在RGB空间中实现了具有挑战性场景的新视图的高视觉精度,尽管使用更少的数据(即,来自围绕物体移动的单个事件相机的事件流)训练,而且比使用RGB图像训练的现有NeRF模型更有效(由于事件流固有的稀疏性)。
Learning coordinate-based volumetric 3D scene representations such as neural radiance fields (NeRF) has been so far studied assuming RGB or RGB-D images as inputs. At the same time, it is known from the neuroscience literature that human visual system (HVS) is tailored to process asynchronous brightness changes rather than synchronous RGB images, in order to build and continuously update mental 3D representations of the surroundings for navigation and survival. Visual sensors that were inspired by HVS principles are event cameras. Thus, events are sparse and asynchronous per-pixel brightness (or colour channel) change signals. In contrast to existing works on neural 3D scene representation learning, this paper approaches the problem from a new perspective. We demonstrate that it is possible to learn NeRF suitable for novel-view synthesis in the RGB space from asynchronous event streams. Our models achieve high visual accuracy of the rendered novel views of challenging scenes in the RGB space, even though they are trained with substantially fewer data (i.e., event streams from a single event camera moving around the object) and more efficiently (due to the inherent sparsity of event streams) than the existing NeRF models trained with RGB images. We will release our datasets and the source code, see https: //4dqv.mpi-inf.mpg.de/EventNeRF/.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.11896





3、[LG] Graph Neural Networks as Gradient Flows
F D Giovanni, J Rowbottom, B P. Chamberlain, T Markovich, M M. Bronstein
[Twitter Inc]
图神经网络梯度流框架。能量最小化的动力学系统在几何和物理中是普遍存在的。本文提出一种GNN的梯度流框架,其中方程遵循可学习能量的最陡下降方向。这种方法允许从多粒子角度解释GNN的演化,通过对称的“信道混合”矩阵的正和负特征值学习特征空间中的吸引力和斥力。对解决方案进行谱分析,并得出结论,梯度流图卷积模型可以归纳由图高频主导的动力学,对异构数据集来说是理想的。本文还描述了通用GNN架构的结构约束,允许将它们解释为梯度流。通过彻底的消融研究,证实了所述理论分析,并展示了简单和轻量级模型在现实世界的同质性和异质性数据集上的竞争性能。
Dynamical systems minimizing an energy are ubiquitous in geometry and physics. We propose a gradient flow framework for GNNs where the equations follow the direction of steepest descent of a learnable energy. This approach allows to explain the GNN evolution from a multi-particle perspective as learning attractive and repulsive forces in feature space via the positive and negative eigenvalues of a symmetric ‘channel-mixing’ matrix. We perform spectral analysis of the solutions and conclude that gradient flow graph convolutional models can induce a dynamics dominated by the graph high frequencies which is desirable for heterophilic datasets. We also describe structural constraints on common GNN architectures allowing to interpret them as gradient flows. We perform thorough ablation studies corroborating our theoretical analysis and show competitive performance of simple and lightweight models on real-world homophilic and heterophilic datasets.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.10991





4、[LG] SMT-DTA: Improving Drug-Target Affinity Prediction with Semi-supervised Multi-task Training
Q Pei, L Wu, J Zhu, Y Xia, S Xie, T Qin, H Liu...
[University of Science and Technology of China & Microsoft Research Asia]
SMT-DTA:基于半监督多任务训练改善药物-靶点亲和力预测。药物-靶点亲和力(DTA)预测是药物发现和药物研究的重要内容。准确预测DTA对新药的设计有很大帮助。由于湿法实验成本高、耗时长,用于DTA预测的监督数据非常有限。这严重阻碍了基于深度学习的方法的应用,因为深度学习方法需要大量的监督数据。为应对这一挑战并提高DTA的预测精度,本文提出一种包含几种简单而有效策略的框架:(1)多任务训练策略,将DTA预测和掩码语言建模(MLM)任务用于配对药物目标数据集上;(2)一种半监督训练方法,通过在训练中利用大规模未配对分子和蛋白质来增强药物和靶标表示学习,这与之前预训练和微调方法只在训练前使用分子或蛋白质不同;(3)交叉注意力模块,增强药物和靶标表示之间的相互作用。在三个真实的基准数据集上进行了广泛的实验:BindingDB、DAVIS和KIBA。结果表明,所提出框架显著优于现有方法,实现了最先进的性能,针对特定药物靶标结合活性、药物特征可视化和现实应用的案例研究显示了本文工作的巨大潜力。
Drug-Target Affinity (DTA) prediction is an essential task for drug discovery and pharmaceutical research. Accurate predictions of DTA can greatly benefit the design of new drug. As wet experiments are costly and time consuming, the supervised data for DTA prediction is extremely limited. This seriously hinders the application of deep learning based methods, which require a large scale of supervised data. To address this challenge and improve the DTA prediction accuracy, we propose a framework with several simple yet effective strategies in this work: (1) a multi-task training strategy, which takes the DTA prediction and the masked language modeling (MLM) task on the paired drug-target dataset; (2) a semi-supervised training method to empower the drug and target representation learning by leveraging large-scale unpaired molecules and proteins in training, which differs from previous pre-training and fine-tuning methods that only utilize molecules or proteins in pre-training; and (3) a cross-attention module to enhance the interaction between drug and target representation. Extensive experiments are conducted on three real-world benchmark datasets: BindingDB, DAVIS and KIBA. The results show that our framework significantly outperforms existing methods and achieves state-of-the-art performances, e.g., 0.712 RMSE on BindingDB IC50 measurement with more than 5% improvement than previous best work. In addition, case studies on specific drug-target binding activities, drug feature visualizations, and real-world applications demonstrate the great potential of our work. The code and data are released at https://github.com/QizhiPei/SMT-DTA.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.09818





5、[CV] BlazePose GHUM Holistic: Real-time 3D Human Landmarks and Pose Estimation
I Grishchenko, V Bazarevsky, A Zanfir, E G Bazavan, M Zanfir, R Yee, K Raveendran, M Zhdanovich, M Grundmann, C Sminchisescu
[Google]
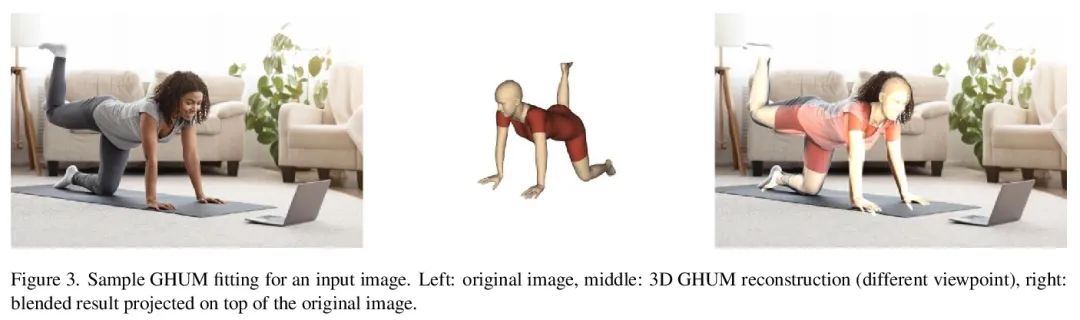
BlazePose GHUM Holistic:实时3D人体特征点与姿态估计。本文提出BlazePose GHUM Holistic,一种轻量神经网络管道,用于3D人体特征点和姿态估计,专门为实时设备推理而定制。BlazePose GHUM Holistic能从单一的RGB图像中进行动作捕捉,包括化身控制、健身追踪和AR/VR效果。本文的主要贡献包括:i)一种新的3D真实数据采集方法;ii)利用额外的手部特征点进行更新的3D人体追踪;iii)通过单目图像进行全身姿态估计。
We present BlazePose GHUM Holistic, a lightweight neural network pipeline for 3D human body landmarks and pose estimation, specifically tailored to real-time on-device inference. BlazePose GHUM Holistic enables motion capture from a single RGB image including avatar control, fitness tracking and AR/VR effects. Our main contributions include i) a novel method for 3D ground truth data acquisition, ii) updated 3D body tracking with additional hand landmarks and iii) full body pose estimation from a monocular image.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.11678




几篇论文实现代码:
[CV] M&M Mix: A Multimodal Multiview Transformer Ensemble
M&M Mix:多模态多视Transformer集成
X Xiong, A Arnab, A Nagrani, C Schmid
[Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.09852


[CV] Replacing Labeled Real-image Datasets with Auto-generated Contours
用自动生成轮廓替代标记真实图像数据集
H Kataoka, R Hayamizu, R Yamada, K Nakashima, S Takashima, X Zhang, E J Martinez-Noriega, N Inoue, R Yokota
[AIST]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.09132





[CV] The ArtBench Dataset: Benchmarking Generative Models with Artworks
ArtBench数据集:用艺术作品对生成模型进行基准测试
P Liao, X Li, X Liu, K Keutzer
[CMU & UC Berkeley]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.11404





[LG] Low-Precision Stochastic Gradient Langevin Dynamics
低精度随机梯度Langevin动力学
R Zhang, A G Wilson, C D Sa
[The University of Texas at Austin & New York University & Cornell University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.09909




边栏推荐
- Wechat applet -picker component is repackaged and the disabled attribute is added -- below
- Zero basics of C language lesson 7: break & continue
- 7-2 the cubic root of a number
- Lamp compilation and installation
- Connection migration for DataGrid configuration
- H5视频自动播放和循环播放
- A collection of common tools for making we media videos
- MySQL数据库常见故障——遗忘数据库密码
- ES中索引别名(alias)的到底有什么用
- Mysql database explanation (IV)
猜你喜欢

Zero basics of C language lesson 7: break & continue

Mysql database explanation (III)

Input text to automatically generate images. It's fun!

Awk tools

Jenkins build prompt error: eacces: permission denied

Update and download of Beifu EtherCAT XML description file

Es snapshot based data backup and restore

使用 Performance 看看浏览器在做什么

Here document interaction free and expect automatic interaction

Bigint: handles large numbers (integers of any length)
随机推荐
[shell] generate strings between specified dates
Wechat applet magic bug - choose to replace the token instead of clearing the token, wx Getstoragesync will take the old token value instead of the new token value
There are many contents in the widget, so it is a good scheme to support scrolling
Jenkins build prompt error: eacces: permission denied
【系统分析师之路】第十五章 复盘数据库系统(数据库案例分析)
Beifu PLC based on NT_ Shutdown to realize automatic shutdown and restart of controller
古瑞瓦特冲刺港交所上市:创下“多个第一”,获IDG资本9亿元投资
遍历指定目录获取当前目录下指定后缀(如txt和ini)的文件名
Es snapshot based data backup and restore
LAMP编译安装
Exercise set 1
Wechat applet -picker component is repackaged and the disabled attribute is added -- above
【Proteus仿真】Arduino UNO按键启停 + PWM 调速控制直流电机转速
d的is表达式
Learn how to develop owl components by hand (7): practical use of owl projects
[how to connect the network] Chapter 2 (next): receiving a network packet
I have a good word to say, and I admire myself
KITTI Tracking dataset whose format is letf_ top_ right_ bottom to JDE normalied xc_ yc_ w_ h
Nlp-d60-nlp competition D29
Zero basics of C language lesson 8: Functions