当前位置:网站首页>Collection collection framework
Collection collection framework
2022-07-24 13:14:00 【No fish in Haikou】
java The collection framework of
java.util.Collection Interface
Collection: It is the top-level interface of all collections , It specifies the relevant functions of the set operation elements. The method set is the same as the array , Used to store a set of elements , But there are many different implementation classes to implement different data structures
Collection Here are two common sub interfaces
1.1 java.util.List:** * The linear table , characteristic : It can store repeated elements in order , You can operate by subscript
List Common implementation classes :
java.util.ArraysList: Internal use of array implementation , Better query performance
java.util.LinkedList: Internal implementation with linked list , The performance of adding and deleting elements is better , The performance of adding and deleting elements at the beginning and end is the best
( The determination of repeated elements here depends on the element itself equals Method depends on the result of comparison )
1.2: java.util.Set: A collection that cannot be repeated , And disorder
Set Common implementation classes :
1.java.util.HashSet
HashSet The bottom is HashMap
HashMap Connect
Queue inheritance Collection So the queue itself is also a collection :
Queue link address
2.java.util.TreeSet( Binary tree )
Create set
Collection c = new ArrayList();
boolean add(E e): Add an element to the current collection , After adding successfully, return true Otherwise return to false
c.add("one");
int size(): Returns the number of elements in the current collection
int size = c.size();
boolean isEmpty(): Judge whether the set is empty , When you assemble size by 0 when ,isEmpty return true
boolean isEmpty = c.isEmpty();
c.clear(): Empty the set
boolean contains(Object o): Determine whether the current collection contains the given element
A collection of contains The basis for judging inclusion is : Whether the given element exists with the existing element in the collection equals Compared with true The situation of , Existence is considered to include
boolean contains = c.contains(p);
remove Method to delete an element is also deleted from the collection equals Compared with true Of , Element for List In terms of aggregation , Duplicate elements are deleted only once
c.remove(p);
A collection can only hold elements of reference type , And it stores the reference of the element ( Address )
Point p = new Point(1,2);
c.add(p);
p.setX(2); // modify p The first parameter of is 2:(2,2)
boolean addAll(Collection c): Add all elements in a given set to the current set
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("java");
c1.add("c++");
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add("android");
c2.add("ios");
c1.addAll(c2);
boolean containsAll(Collection e): Determine whether the current set contains all elements in a given set
Collection c3 = new ArrayList();
c3.add("java");
boolean contains = c1.containsAll(c3);
removerAll: Delete the common elements of the current set and the given set
c1.removeAll(c3);
Traversal of the set
- Collection Provides a way
- Iterator iterator()
- This method will return an iterator implementation class for traversing the current collection , It can be used to traverse the collection
java.util.Iterator Interface : iterator
- The iterator specifies the relevant methods required to traverse the collection elements , The principle of iterator traversal is : ask , take , Delete , Deleting elements is not a necessary operation in the traversal process
- notes : Different collection implementation classes provide an iterator implementation class for traversing itself , We don't need to know their names , Think of them as Iterator Just operate .
JDK5 A new feature was introduced : Generic
Generic types are also called parameter instantiation types , It allows us to specify the parameters and return value types of some properties or methods when using a type , This makes our use of this class more in line with our needs
Generics are widely used in collections , Used to specify the element type in the collection
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("one");
c.add("#");
c.add("two");
c.add("#");
c.add("three");
System.out.println(c);
// Iterators also support generics , When using, the specified type is consistent with the collection element type
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();
// boolean hasNext(): Determine whether there are elements in the set that can be iterated
while (it.hasNext()){
// E next(): Get the next element of the collection ( Get the first element on the first call , And so on )
String str = it.next();
System.out.println(str);
if ("#".equals(str)){
/* Iterators have a requirement , In the process of traversal, you cannot pass the method of collection Add or delete elements , Otherwise, there will be an exception */
/* Iterators provide remover Method can delete the elements traversed this time */
it.remove();
}
}
java.util.List Interface :
List list = new ArrayList<>();
E get(int index): Get the element corresponding to the specified subscript
E set(int index,E e): Sets the given element to the specified location , The return value is the original element in this position
void add(int index,E e): Add the given element to the specified location , The original position and the sequence of subsequent elements move backward
list.add(2,"3");
E remove(int index): Delete and return the element at the specified location
String old = list.remove(3);
List subList(int start,int end): Get the subset within the specified range of the current set
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
list.add(i);
}
System.out.println(list);
List<Integer> subList = list.subList(3,8);
System.out.println(subList);
// Expand each element of the subset 10 times
for (int i=0;i<subList.size();i++){
int a = subList.get(i);
int b = a*10;
subList.set(i,b);
}
System.out.println(subList);
*//*
When we pass a List After the collection gets a subset , Any operation on this subset
It is the operation on the element of the original set
*//*
System.out.println(list);
Enhanced for loop JDK5 A new feature introduced at launch
- It is also known as : enhance for loop
- The new cycle does not replace the traditional for Cycle work , It just uses the same syntax to traverse a set or array using
- The new loop is recognized by the compiler , instead of java Virtual machine approval , When compiling the source code, the compiler finds that it uses a new loop to traverse the array , Will change the code to normal for Cycle are
- The new loop traversal set will be modified by the compiler to iterator traversal So in the process of traversing with the new loop , You still can't add or delete elements through the method of collection
Set to array :Collection Provides a way :toArray(), You can convert the current collection into an array
Converts the current collection to an array , This method requires passing in an array , If this array can be used ( The length of the array >= A collection of size when ) The current set elements will be stored in the array, and then the array will be returned
If it cannot be used, it will create a parameter array of the same type and length as size Consistent array and return after storing the elements
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>(); // aggregate
String[] array = c.toArray(new String[c.size()]); // Array
Array to set : Array tool class :Arrays Provides a static method :asList, You can convert an array into a List aggregate
A set converted from an array , The element operation of this set is the operation of the original array, which needs special attention !
Because the array is fixed length , Therefore, you cannot call from the set converted from the array. Adding or deleting elements will affect the length of the array , Otherwise, an exception will be thrown :UnsupportedOperationException
If you want to add or delete elements to the set , You need to create a set by yourself , Then import the original set elements into the set
All collection elements support a parameter type of Collection Construction method of , The function is to include all elements in a given set while creating the current set
String[] array = {
"one","two","three","four","five"}; // Array
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(array); // aggregate
Collection sorting
Random generation 19 individual 100 Sort by a number within
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Random random = new Random();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
list.add(random.nextInt(100));
}
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list); // Sort from small to large
System.out.println(list);
Collection.sort(List list) The method is right List Natural sorting of collections
namely : Sort from small to large , But this method requires another set , The element must implement the interface
Comparable, Otherwise, the compilation fails
There is an abstract method in this interface that requires class rewriting , Used to define the size relationship between such elements
java Many commonly used classes in have implemented it , such as String, Packaging
When we call a method , This method, in turn, requires us to modify the code elsewhere
( For example, here we ask us to modify Point Class to achieve Comparable Interface and override methods )
This phenomenon is called invasive , The more invasive ( The more code you change ) The more unfavorable , Writing programs should try to
Avoid intrusiveness
// Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>() {
// public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// return o2-o1;
// }
// });
/* Anonymous inner class sorting , This method can be used for ascending and descending */
Collections.sort(list,(o1,o2)->o2-o1);
System.out.println(list);
// Collections.reverse(list); // Inversion of sets , From big to small
// System.out.println(list);
Comparable and Comparator difference
Comparable, Comparator Can be used to compare elements in a collection 、 The interface for sorting
Comparable: In the bag java.lang Next , Is a method defined inside a collection , There is an abstract method in this interface that requires class rewriting , Define the size relationship between such elements ,java Many commonly used classes in have implemented it , such as String, Packaging
Comparator: It is the interface of comparator , In the bag java.util Next , Is a method defined outside the collection , Implementing it requires rewriting compare To define , Therefore, the classes that implement this interface are comparable , Here, it is directly created as ,
Collection and Collections The difference between
**Collection:** It is the top-level interface of all collections , It specifies the functions that all sets must have . Collections are like arrays , Used to save a set of elements , But there are many implementation classes ( There are many different data structures )
**Collections:** Is a tool class , Provides a series of static methods to assist container operations , These methods include searching for containers 、 Sort 、 Thread safety, etc .
边栏推荐
- 开山之作造假!Science大曝Nature重磅论文学术不端,恐误导全球16年
- 2022.07.21
- Number of palindromes in Li Kou question
- Redis(13)----浅谈Redis的主从复制
- 24. Merge K ascending linked lists
- Is it safe to open an account on Oriental Fortune online? Is there a threshold for opening an account?
- [datasheet] interpretation of phy lan8720 network chip
- 30. Rearrange the linked list
- 32. Maximum path sum in binary tree
- 汉字风格迁移篇---用于汉字多字体生成的多样性正则化StarGAN
猜你喜欢

SSM在线租房售房平台多城市版本

Implement is by yourself_ default_ constructible

基于matlab的声音识别

36. Delete the penultimate node of the linked list

登临科技联合创始人王平:创新+自研“双核”驱动,GPU+赋能AI落地生根|量子位·视点分享回顾...

【论文阅读】Mean teachers are better role models

开山之作造假!Science大曝Nature重磅论文学术不端,恐误导全球16年
LEADTOOLS 22 套件 LEADTOOLS 超级套

The price of domestic flagship mobile phones is nearly 6000, but they can't even beat iphone12. It's clear who users choose
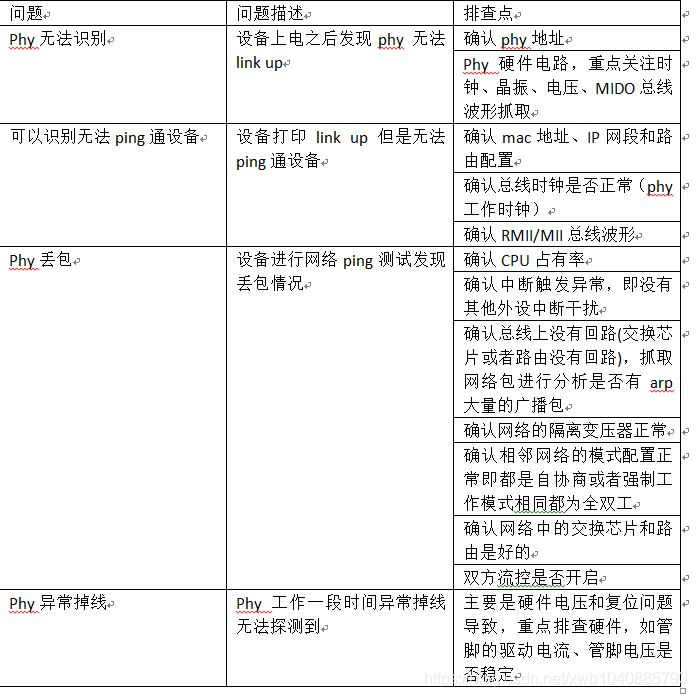
Summary of embedded network problems (packet loss of network card, unrecognized network card)
随机推荐
[datasheet] interpretation of phy lan8720 network chip
Square root of 33.x
2022.07.15 summer training personal qualifying (10)
SSM在线考试系统含文档
Is there any potential safety hazard for Xiaobai to open an account with Guotai Junan?
如何用WebGPU流畅渲染百万级2D物体?
mysql select延迟的场景对应的是所有数据库查询语句都会延迟吧,我这边场景注入后,执行了一条
26. Reverse linked list II
Deep and shallow copies of objects, extends
More functions and functions of the metauniverse lie in the deep transformation of the traditional way of life and production
sql的where+or的用法丢失条件
How to draw Bezier curve and spline curve?
No routines, no traps, no advertisements | are you sure you don't need this free instant messaging software?
Getting started with SQL join use examples to learn left connection, inner connection and self connection
Efficientformer: lightweight vit backbone
Finclip's "applet export app" function has been updated again by the company
The price of domestic flagship mobile phones is nearly 6000, but they can't even beat iphone12. It's clear who users choose
Implementation of dynamic columns in EAS BOS doc list
关于如何提升TTL(UART)通信抗干扰——心得
AtCoder Beginner Contest 261E // 按位思考 + dp