当前位置:网站首页>C language from entry to soil function
C language from entry to soil function
2022-07-24 07:07:00 【Bubble milk】
🥳🥳🥳 Hello, everyone , I love bubble milk for dessert , It must be almost a holiday at this time , You can take this time to learn something new , Or consolidate what you have learned ,
As the saying goes “ I'd rather kill myself than others ”today , Xiaobian brings you ——C What are functions in language , And how to use it
Let's not talk more nonsense , Start today's content now

1. C Classification of functions in language
- Library function
- Custom function
1.1 Library function
give an example :
When we want to print a number, we will use printf This function , This function belongs to <stdio.h> Library functions in
When we want to copy strings , have access to strcpy , This belongs to <string.h> Library function
There are many library functions , When we want to include library functions, we need to use < > ( Angle brackets ) To reference the header file ,< > Will first search in the header file library .
I know so much , We should be How to learn library functions Well ?
Xiaobian is here to recommend a website cplusplus,
There are many introductions about functions .
Of course , As a programmer, I have certain English ability , It is more convenient to read library functions written by others
1.1.1 C Library functions are commonly used in languages
- IO function
- String manipulation functions
- Memory manipulation function
- Time / Date function
- Mathematical functions
- Other functions

notes : When using library functions , Must contain #include Corresponding header file
1.2 Custom function
Although there are library functions , But not everything can be done , So more importantly Custom function .
Custom functions need to have the following components :
- Function name
- Return type
- The parameters of the function
ret_type fname(paral pname)
{
// Content
;
}
ret_type Return type
fname Function name
paral Function parameter
for example :
Write a function to exchange two numbers
#include <stdio.h>
//swap Function design
// Error model
void swap1(int x, int y)
{
int tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
// Correct version
void swap2(int* p1, int* p2)
{
int tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
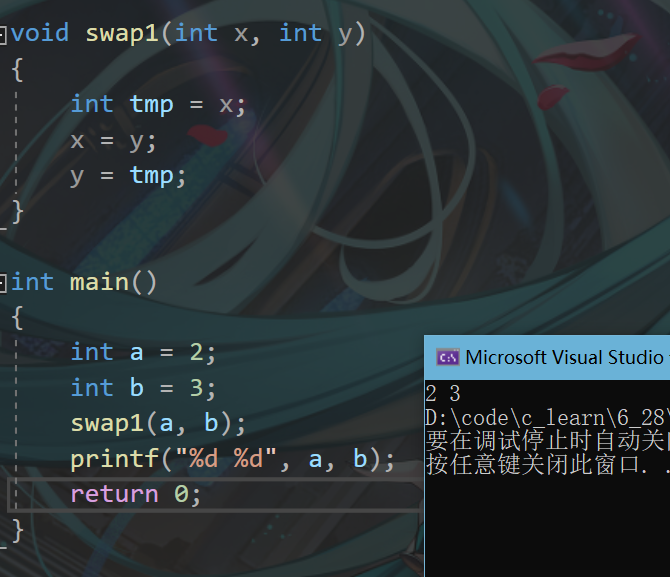
swap1(a, b);
printf("%d %d\n", a, b);
swap2(&a, &b);
printf("%d %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
2. The parameters of the function
The parameters of functions can be roughly divided into two categories
- Actual parameters
- Shape parameter
2.1 What are the actual parameters of a function ( Actual parameters )?
Truly pass the past cross arguments
The argument can be : Constant 、( The pointer ) Variable 、 expression 、 Functions, etc
No matter what the return type of the argument is , When a function is called , Parameters must have definite values , In order to pass these values to the arguments
Arguments are usually accessed through pointers , above swap2 Functions operate on arguments through pointers

Access address through pointer , We can modify the original value directly

2.2 What are the formal parameters of a function ( Shape parameter )?
Formal parameters refer to , stay Function name After the brackets Of Temporary variable
Because it can only be used when the function is called ( Open up memory units ), So it's called formal parameter .
Formal parameters are only valid in functions , When the function call is complete , Automatically destroy .
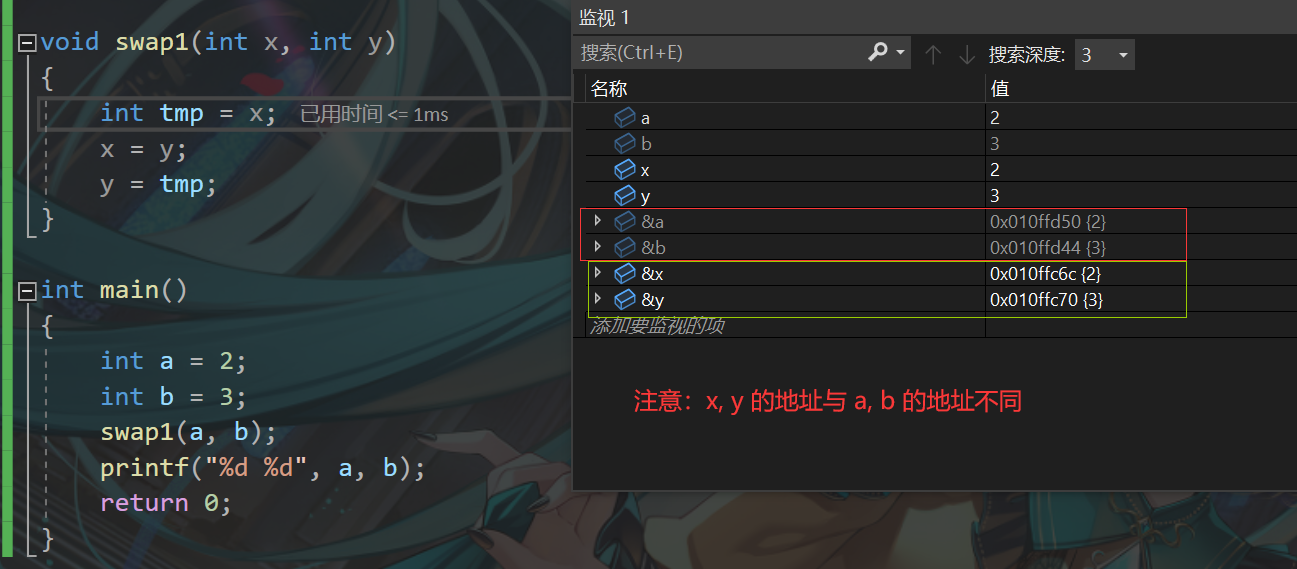
When you pass in a value , Copy the value to x and y , Out of swap1 Function ,x and y Automatically destroy , and a and b The original value has not changed .
Through the above example , We can simply think that —— A formal parameter is a temporary copy of an argument
3. Function call
3.1 Value transfer call
Value passing call is to transfer parameters Shape parameter A call method passed to a function .
The formal and actual parameters of the function occupy different memory units respectively , The modification of formal parameters will not affect the arguments
At the top of the swap1 It's called by value
3.2 Address call
- Address calls are external to the function Memory address A call method passed to a function parameter .
- In this way, functions can be used Directly change the original parameters .
4. Nested calls and chained access to functions
*4.1 Nested calls
Functions can be combined and called according to actual needs , for example
seek 1~10 The prime between
analysis :
Primes are numbers that can only be 1 Or the number divided by itself , We can think in reverse , When there are other numbers that can divide it completely , This number is not prime , We just need to find the number in the square root of a number , If there is a number
iDivisibilityn, thatnIt's not prime
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int is_prime(int n)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); ++i)// function sqrt Need to use math.h The library of
{
if (n % i == 0)// Express n Can be i to be divisible by
{
return 0;// If there is a satisfaction, it is not a prime number
}
}
return 1;// Otherwise, it is prime
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i < 10; ++i)
{
if (is_prime(i))
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
return 0;
}

Among them, we have customized a function , In custom functions , We also call a sqrt function ( This function needs to cooperate with math.h Library function of )
Be careful : Functions can be called nested , But you can't nest definitions
*4.2 Chained access
Put a number of Return value As an argument to another function
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char ch[] = "abcdef";
printf("%u", strlen(ch));//%u Print unsigned integers
return 0;
}
The output is :

Let's take a look first strlen function

One of them
size_t, We can select this function in the compiler , Right click mouse -> choice Go to definition


Choose
size_t, Continue selecting go to definition

You can see ,
size_tIt's essentiallyunsigned int, bestrlenThe return value ofunsigned int
5. Function declaration and definition
5.1 Declaration of functions
- Function declaration can only be declared after the function exists , A function that does not exist cannot be declared
- The function declaration should be made before the function is used , Satisfy Declare before use
- Function declarations are usually placed in header files


for instance
#include <stdio.h>
void test();// Function declaration
int main()
{
test();// call test function
return 0;
}
void test()// Implementation of function
{
printf("haha");
}
But in some places, we will encounter the following situations ( Usually in school will encounter )
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
void test(int x);// Declaration of functions
test(1);
return 0;
}
void test(int x)
{
printf("%d", x);
}
5.2 Definition of function
The definition of function refers to , The concrete realization of function
When declaring functions , As long as meet Statement or Definition stay Use the front Just go , So there is also such a way of writing
#include <stdio.h>
void test()//test The concrete realization of function
{
printf("haha");
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
This way of writing , Because the function definition is before use , At the same time of declaration, the function is also defined .
Usually , How should we standardize the writing method when writing a project ?( Reference resources 《 High quality C/C++ Programming 》)
test.h The content of
// Copyright and version notice
#ifndef TEST_H // prevent test.h Be repeatedly quoted
#define TEST_H // Use all capitals , Symbol . Change to _
// Include header file
#include <stdio.h>
...
#include <math.h>
...
#include "myhander.h"
...
// Function declaration
void Add(int x, int y);
void test2();
...
// Class structure declaration
struct Color
{
...
};
#endif
test.c The content of
#include <test.h>
// Implementation of function
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x+y;
}
...
This kind of writing is usually used to complete in modules , That is, we need to realize many functions , Let's take a look at the details Recursive implementation of minesweeping game
6. Recursion of a function
6.1 What is recursion ?
The program itself invokes its own programming technique, which is called recursion .
This method , It is mainly a large and complex problem Layer upon layer transformation Become a Similar to the original problem Of Smaller scale To solve the problem , This is the strategy of recursion .
The main way to think about recursion is : Make a big deal small
6.2 Two necessary conditions for recursion
- There is a limitation , It can stop recursion
- Each recursive call will be closer to the constraint
6.3 Recursion and iteration
We just learned what recursion is , Then let's meet next , The specific use of recursion
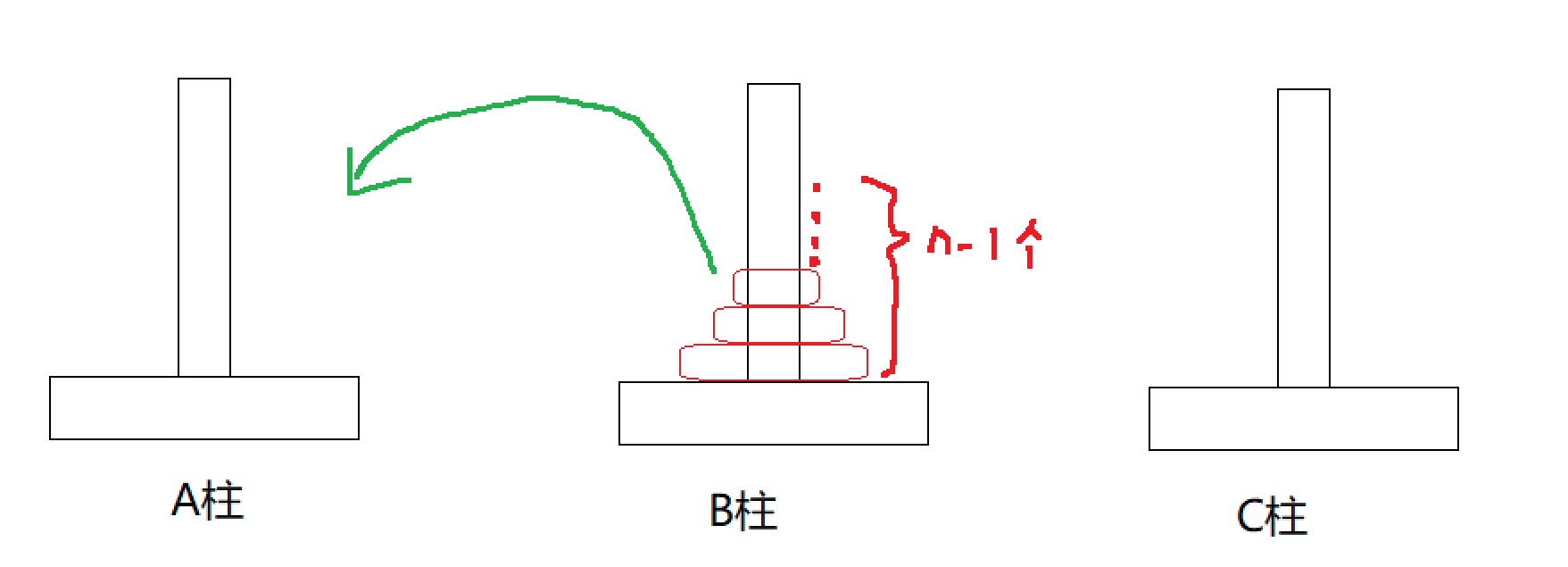
Q1 : solve n Second order Hanoi Tower problem
take A All the disks on the column move to C On the pillars , Only one can be moved at a time The disk , And the big disc cannot be above the small disc
#include <stdio.h>
void hanoi(int n, char a, char b, char c)
{
if (n == 1)
{
printf("%c -> %c\n", a, c);
}
else
{
hanoi(n - 1, a, c, b);
printf("%c -> %c\n", a, c);
hanoi(n-1, b, a, c);
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;// Express n Step Hanoi Tower
scanf("%d", &n);
hanoi(n, 'A', 'B', 'C');
return 0;
}
analysis :
According to recursive thinking , The original problem needs to be advanced layer by layer , Reduce it to the simplest problem similar to the original problem .
When A Only 1 When you have a disc , Move it directly to C On the post
When A There are... On the post n When you have a disc , In essence, it is to put the top n-1 All discs move to Tool post (B column ) On , Then move the lowest column to C column , Finally, put B The disc on the column Put it all back A column , Just repeat the above process
Q2 : Find the number of Fibonacci series n Number ( Don't think about spillovers )
Fibonacci series refers to such a series :1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89…
Start with the third item , The first of each term is equal to the sum of the first two terms
#include <stdio.h>
int Fibrec(int n)
{
if (n > 2)
return Fibrec(n - 1) + Fibrec(n - 2);
else
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", Fibrec(n));
return 0;
}

reflection :
When we want to calculate the number 50 One or even the third 100 A Fibonacci number can be very time-consuming
Why did this happen ?
- We might as well modify the original function
#include <stdio.h>
int count = 0;// Define global variables
int Fibrec(int n)
{
++count;// Every call ,count+1
if (n > 2)
return Fibrec(n - 1) + Fibrec(n - 2);
else
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", Fibrec(n));
printf("%d\n", count);
return 0;
}

You can find , When calculated to the third 40 Fibonacci number , The function has called 204668309 Time .
as a result of :
When calculating a large Fibonacci number , There will be a lot of duplicate data in the middle , This also greatly reduces the speed of operation
Every time the function is called, it will apply for a piece of space from memory , When there are too many function calls , It may also cause Stack overflow The phenomenon of
stack overflow( The space allocated by the system is limited , For always opening up space in the stack area , The situation that eventually leads to space exhaustion , We call it stack overflow )
How to solve the above problems ?
- Write recursion in a non recursive form ( Most can be solved iteratively ( That's circulation ))
- Use
staticInstead ofnonstaticLocal objects , This can reduce the generation and release of each recursive call and returnnonstaticThe cost of local objects
We transform the above problem into a non recursive form
#include <stdio.h>
int Fibloop(int n)
{
int i = 1, j = 1, k = 0;
if (n > 2)
{
n -= 2;
while (n--)
{
k = i + j;
i = j;
j = k;
}
return k;
}
else
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", Fibloop(n));
return 0;
}

Obviously, the speed is much faster , Although the result may not be quite right ,( Mainly beyond int The scope of the
When we will int Change to unsigned int It's much more normal

remind :
- The advantage of recursion is to make things smaller , Simplify the problem , At the same time, it can also make the form of code clearer , Weakness is Probably It will cause slow running speed or stack overflow
- Recursion can be used to solve the very troublesome problems of loops , Things that are difficult to solve recursively can use loops
🥳 Summary
All right. !ヾ(^▽^*))) That's the end of this issue , Do you have a deeper understanding of functions ? Then hurry to challenge yourself ヾ(≧▽≦*)o
If you like Xiaobian , Please support , Your support is my biggest motivation

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

STM32外部中断(寄存器版本)

Can recursion still play like this? Recursive implementation of minesweeping game

Introduction to pyqt5 - student management system

Ge port: sgmii mode and SerDes mode

Redis 哨兵机制

《大厂面试》之JVM篇21问与答

UE4/5 无法打开文件“xxx.generated.h”(Cannot open file xxx.generated.h)的解决方法总结

Huawei experts' self statement: how to become an excellent engineer

变量和数据类型(04)完结

Redis master-slave mechanism
随机推荐
Cmake notes
【LeetCode】444. 序列重建
Redis distributed cache learning notes
Practice of online problem feedback module (12): realize image deletion function
第二部分—C语言提高篇_1. C语言概述
reflex
STM32H750VBT6驱动程控增益放大模块PGA113——基于CubeMX的Hal库
C language from entry to soil (II)
Tensorflow Einstein function
(note sorting is not completed) [graph theory: find the shortest path of single source]
9. Use grid technology to draw a Pentagon on the screen.
Can you increase muscle without exercise??? Just get an injection of hibernating black bear serum
【方向盘】IDEA的代码审查能力,来保证代码质量
sojson jsjiami.com. V6 crawler JS reverse
[waveform / signal generator] Based on stc1524k32s4 for C on Keil
Job search memo
第二部分—C语言提高篇_4. 二级指针
GIMP自定义截图
先爱自己,再爱别人。
不去和谁比较,只需做好自己