当前位置:网站首页>[ES6 breakthrough] promise is comparable to native custom encapsulation (10000 words)
[ES6 breakthrough] promise is comparable to native custom encapsulation (10000 words)
2022-06-24 09:05:00 【codeMak1r.】
In this article , You can learn :
Promise The underlying implementation principle of object
Promise Object implementation custom encapsulation
Synchronous and asynchronous
Callback function
In function scope this Point to the problem
trycatch Capture the error
JavaScript Bottom implementation ideas🤩 If you can follow the ideas of the article and type the code together , I believe you can also encapsulate your own promise
Packaged promise Source code at the end of the article
Insist on creating ️, Learning together , Code out the future !
List of articles
- Preface
- 1、promise Custom encapsulation -- Initial structure construction
- 2、promise Custom encapsulation --resolve And reject Structure building
- 3、promise Custom encapsulation --resolve and reject Code implementation
- 4、promise Custom encapsulation --throw Throw an exception to change the State
- 5、promise Custom encapsulation --Promise Object state can only be modified once
- 6、promise Custom encapsulation --then Method to execute the callback
- 7、promise Custom encapsulation -- Execution of asynchronous task callback
- 8、promise Custom encapsulation -- Specify multiple callbacks
- 9、promise Custom encapsulation -- Sync then method
- 10、promise Custom encapsulation -- asynchronous then method
- 11、promise Custom encapsulation --then Method perfection and optimization
- 12、promise Custom encapsulation --catch Method -- Exception penetration and value passing
- 🥤Promise——API
- 13、promise Custom encapsulation --resolve Method encapsulation
- 14、promise Custom encapsulation --reject Method encapsulation
- 15、promise Custom encapsulation --all Method encapsulation
- 16、promise Custom encapsulation --race Method encapsulation
- 17、promise Custom encapsulation --then Asynchronous execution of method callback
- 18、promise Custom encapsulation --class Implementation of version
- At the end
Preface
We've been working on it before Promise The object has a certain understanding
JavaScript–ES6【Promise】 Object details
JavaScript–【Promise】 Detailed explanation Promise_API
What about this article , I will take you through the customs , A custom implementation of one's own 【promise】
That is to say 【 Tear your hands Promise–Promise Custom encapsulation of 】
Let's have a look ~
Your support will be the greatest motivation for my creation
Follow the likes collection
1、promise Custom encapsulation – Initial structure construction
html:
<head>
<title>Promise-- Custom encapsulation </title>
<!-- Import custom promise.js file -->
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script> let p = new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
resolve('OK') }) p.then(value => {
console.log(value) }, reason => {
console.log(reason) }) </script>
</body>
stay
prmoise.jsTo create a function calledfunction Promise();stay html Introduce this in promise.js file , In this case , When we are using new Promise() when , The created instance object is our customized one function Promise() Instance object of . instead of js The original one Promise object .
as a result of , We created our own Promise function , covers js The original one Promise object .
promise.js:
// Declaration constructor
function Promise() {
}
// add to then Method
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
}
2、promise Custom encapsulation –resolve And reject Structure building
promise.js:
// Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor) {
// Statement resolve and reject function
function resolve(resolveResult) {
}
function reject(rejectResult) {
}
// Actuator functions executor Internally, it is called synchronously
executor(resolve, reject);
}
// add to then Method
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
}
3、promise Custom encapsulation –resolve and reject Code implementation
analysis :resolve() What effect does function execution have ? Yes Promise What impact does the object have ?
【= Split line =】
In the last article we learned ,promise Object has two properties :
【PromiseState】 and 【PromiseResult】
obtain :
resolve() Execution of a function ,
- Can make promise Object state 【PromiseState】 Change ,【pending => resolved/fulfilled】( On behalf of success )
- You can also set promise The result of object success 【PromiseResult】=> resolve(‘OK’) The result of success is .
Let's make a preset promise Properties on the object instance :
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
resolve Function implementation :
// Statement resolve function
resolve = (data) => {
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
}
️ Be careful :
Here we need to use the arrow function to solve this Pointed question .
Or we can put this preserved :
const self = this;
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';This method is also possible .
reject() Function and resolve() The function is the same :
// Statement reject function
reject = (data) => {
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
}
4、promise Custom encapsulation –throw Throw an exception to change the State
promise There are only three ways to change the state of an object :
resolve(),reject() as well as throw Throw an exception .
among throw After throwing an exception , state (PromiseState)【penging => rejected】
Let's preset a promise example :
<script> let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Throw an exception throw "error"; }) console.log(p) </script>
stay promise.js Use in 【 t r y c a t c h trycatch trycatch】 Method to handle throwing an exception :
// Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor) {
// Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
// Statement resolve and reject function
resolve = (data) => {
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
}
reject = (data) => {
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
}
try {
// Actuator functions executor Internally, it is called synchronously
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
// modify promise The state of the object is failed
reject(error)
}
}
// add to then Method
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
}
5、promise Custom encapsulation –Promise Object state can only be modified once
All we need to do is reject() Function and reject() Before the function changes state , For the current 【PromiseState】 Just judge ;
if PromiseState by 【pending】, The status has not been modified ;
if PromiseState Not for 【pending】, The status has been modified , Modification is no longer allowed .
// Statement resolve and reject function
resolve = (data) => {
// Determine whether the status has been changed
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
}
reject = (data) => {
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
}
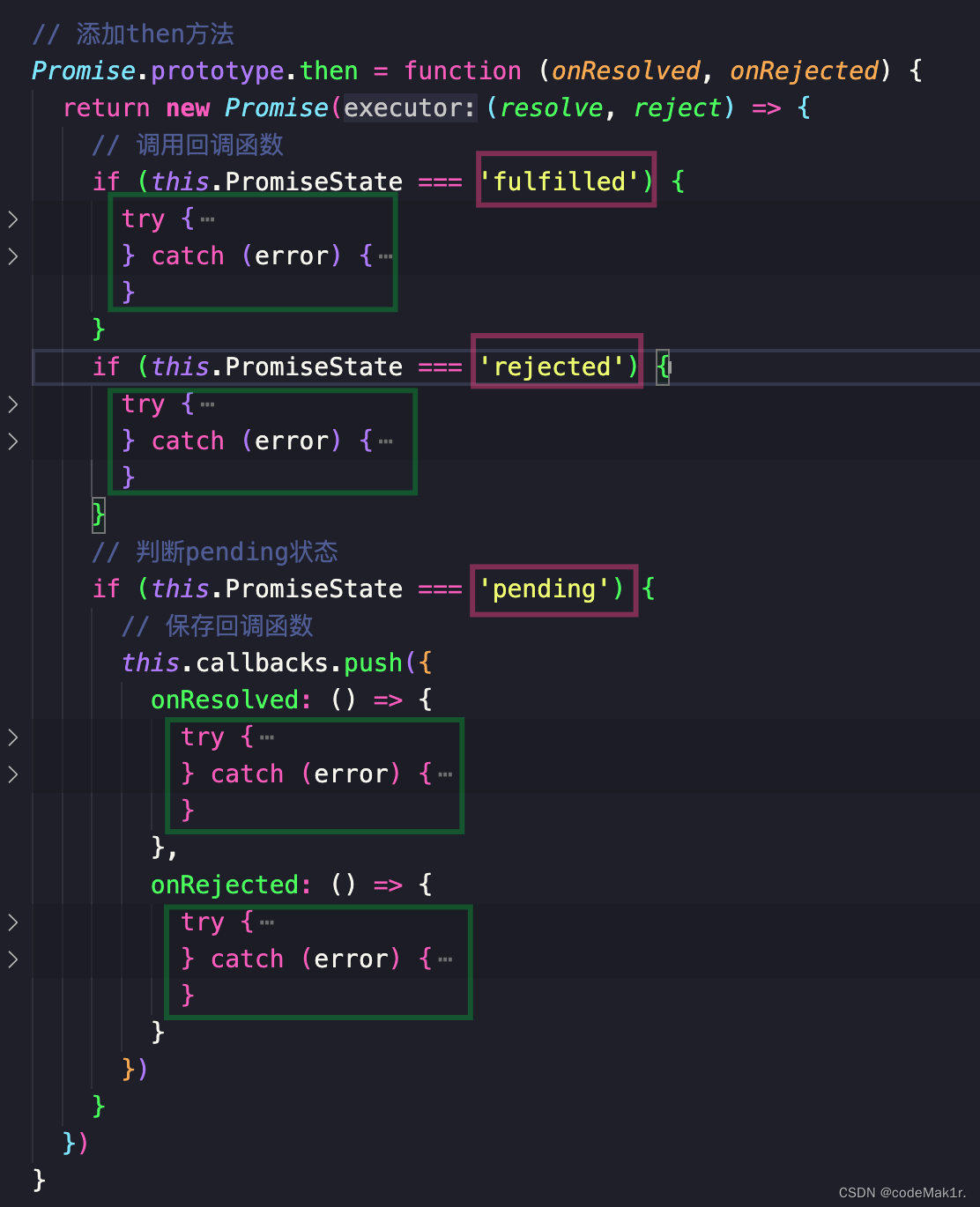
6、promise Custom encapsulation –then Method to execute the callback
promise.js Realization then Method
// add to then Method
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
// Call callback function
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
onResolved(this.PromiseResult)
}
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}
}
html
<script> let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('OK') }) console.log(p) p.then(value => {
console.log(value) }, reason => {
console.warn(reason) }) </script>
We know then The first argument to the method is promise Callback on success , The second argument is the callback on failure ;
onResolved As then Method first row parameter , Called when the status is success ;
onRejected As then Method second row parameter , Called when the status is failed .
reflection ️:
Why can I then Method is directly used internally this.PromiseState Do judgment ?
Because of this then The method is Promise example
pCalled (p.then),So this then Method this Implicit pointing p The instance .
Who called ,this Just point to who .
【this.PromiseState】 Refers to p The instance itself PromiseState attribute .
7、promise Custom encapsulation – Execution of asynchronous task callback
Let's start by new One promise example :
<script> let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('OK') }, 1000) }) p.then(value => {
console.log(value) }, reason => {
console.warn(reason) }) </script>
Open console , Wait for one second to print out .
Now let's introduce our own custom promise.js:
<head>
<script src="./promise.js"></script>
</head>
promise.js :
// Declaration constructor
function Promise(executor) {
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
resolve = (data) => {
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved
this.PromiseResult = data
}
reject = (data) => {
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
this.PromiseResult = data
}
try {
// Actuator functions executor Internally, it is called synchronously
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
// modify promise The state of the object is failed
reject(error)
}
}
// add to then Method
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
onResolved(this.PromiseResult)
}
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}
}
I found that the printing desk was not as I expected , Print out .
analysis :
stay p When the instance is created , Get into 【setTimeout】 function ,resolve() Enter asynchronous queue ;
But at this time , The synchronization queue does not wait for this ;
The synchronization queue is executed downward until then Method (p.then)
here promise The state has not changed , Is still pending;
And we declare ourselves then Method has no internal control over state pending Make any judgment ;
( Self defined then Only if the status is fulfilled as well as rejected Response from time to time .)
Specify an attribute variable first , Essence is an object :
this.callback = {
}
stay then In the method pending State to judge :
// Judge pending state
if (this.PromiseState === 'pending') {
// Save callback function
this.callback = {
onResolved: onResolved,
onRejected: onRejected
}
}
If the state is pending, Save the callback function first , Wait until the asynchronous task is completed , That is, call after the state changes then Method .
// Statement resolve and reject function
resolve = (data) => {
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved
this.PromiseResult = data
// Call successful callback
if (this.callback.onResolved) {
this.callback.onResolved(data)
}
}
reject = (data) => {
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
this.PromiseResult = data
// Call failed callback
if (this.callback.onRejected) {
this.callback.onRejected(data)
}
}
If
this.callbackOn this object existsonResolvedattribute , explain resolve() Function entered the asynchronous queue , call then When the method is used promise The object is still in 【pending】 state .So we call
this.callback.onResolved(data), Call again after the state changes then MethodsonResolved.
【onRejected】 Empathy .
8、promise Custom encapsulation – Specify multiple callbacks
We know , In a native JS Medium Prmoise Object instance , No matter how many 【then】 Callbacks are executable ;
But in our custom encapsulated Promise in , hinder 【then】 Will overwrite the previous 【then】
as a result of :
In the latter 【then】 Method Statement when ,Promise It's still 【pending】;
Save the callback again :
this.callback = { onResolved: onResolved, onRejected: onRejected; }here , All in front then The method is the last one then Method overrides , What is saved in the save callback is always the last then Method .
therefore :
We should save the callback in another way ;
// Judge pending state if (this.PromiseState === 'pending') { // Save callback function this.callbacks.push({ onResolved: onResolved, onRejected: onRejected }) }
take callback Replace objects with arrays , Every time then Method will be called back through the array push Method will each then Method push Into the callbacks In this array .
and callbacks After becoming an array , Calling a successful callback certainly requires a change :
// This is the callback successfully called before
if (this.callback.onResolved) {
this.callback.onResolved(data)
}
// This is the callback successfully invoked now
this.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved(data)
})
Callback on failure 【onRejected】 Empathy .
9、promise Custom encapsulation – Sync then method
Promise Synchronize task modification status - -> then Results returned by method
Let's review :
then The return result of the method is determined by then Method is determined by the internal return result of the callback specified by the ;
The callback in the figure does not specify a return value ( No, return);
Then the callback will return the default 【undefined】;
【undefined】 Not one promise Object of type ,
So this then Method returns :
Promise object , state 【PromiseState】 For success ;
value 【PromiseResult】 by undefined.
The return value of the callback then The return value of Not Promise type state : success ; value : Determined by the return value of the callback ; for example : return undefined state : success ; value :undefined Promise type state : Internal by callback Promise The state of... Determines ;
value : Internal by callback Promise Value determination offor example : Callback inside Promise Status is success , The value is Success state : success ; value :Success
But we customize this package Promise, So far, ,then The return result of the method is not a Promise object ;
It is undefined.
This is because , We are defining then When the method is used , Return value is not declared , So this then The return value of the undefined.
// then Method code
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
// Call callback function
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
onResolved(this.PromiseResult)
}
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}
// Judge pending state
if (this.PromiseState === 'pending') {
// Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: onResolved,
onRejected: onRejected
})
}
}
So we should modify this code , Give Way then Method returns a Promise Object of type :
// add to then Method
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Call callback function
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
// Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = onResolved(this.PromiseResult)
if (result instanceof Promise) {
// If then Inside the specified callback is a Promise Object of type
result.then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
} else {
// If then The callback specified is not internal Promise Object of type ,
// The status is success , The value is the execution result of the callback function , That is, the previously saved result
resolve(result)
}
}
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}
// Judge pending state
if (this.PromiseState === 'pending') {
// Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: onResolved,
onRejected: onRejected
})
}
})
}

10、promise Custom encapsulation – asynchronous then method
Pictured , If the state is modified asynchronously , We customize the encapsulated 【Promise】
then Method Promise Object state is pending;
With native JS Medium Promise Differences exist , So we have to make changes .
// Judge pending state
if (this.PromiseState === 'pending') {
// Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: () => {
// Successful callback function
let result = onResolved(this.PromiseResult)
if (result instanceof Promise) {
result.then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
} else {
resolve(result)
}
},
onRejected: () => {
let result = onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
if (result instanceof Promise) {
result.then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
} else {
resolve(result)
}
}
})
}
When executing asynchronously ,P This instance calls then When the method is used ,Promise The state of the object is still 【pending】;
that , Let's save the callback function in callbacks On this array ;
When the state changes ( such as setTimeout As soon as the time comes , Status becomes success )
setTimeout(() => { resolve('OK') }, 1000)When the state changes , Then recall then Method :
resolve = (data) => { // Determine whether the status has been changed if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return // 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState) this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved // 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult) this.PromiseResult = data // Call successful callback this.callbacks.forEach(item => { item.onResolved() }) }If an exception is thrown , It can be used try catch solve :
onRejected: () => { try { let result = onRejected(this.PromiseResult) if (result instanceof Promise) { result.then(value => { resolve(value) }, reason => { reject(reason) }) } else { resolve(result) } } catch (error) { reject(error) } }
11、promise Custom encapsulation –then Method perfection and optimization
We can see , When the state of 【fulfilled】 as well as 【pending】 when , We are all right about then Method Promise Object has a series of settings ;
But if P When the instance status is failed , We haven't changed then Method Promise Anything of an object ;
So we also need to set it when the status is failed :
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') { try { let result = onRejected(this.PromiseResult) if (result instanceof Promise) { result.then(value => { resolve(value) }, reason => { reject(reason) }) } else { resolve(result) } } catch (error) { reject(error) } }
We can also see that , The code similarity in different judgment bodies is very high , We can do some optimization to the code , To achieve the purpose of code reuse :
Packaging function
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved, onRejected) {
const self = this
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
function callback(type) {
try {
// Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult)
if (result instanceof Promise) {
// If then Inside the specified callback is a Promise Object of type
result.then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
} else {
// If then The callback specified is not internal Promise Object of type ,
// The status is success , The value is the execution result of the callback function , That is, the previously saved result
resolve(result)
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
// Call callback function
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
callback(onResolved)
}
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
callback(onRejected)
}
// Judge pending state
if (this.PromiseState === 'pending') {
// Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: () => {
callback(onResolved)
},
onRejected: () => {
callback(onRejected)
}
})
}
})
}
Encapsulate a function function callback(type)
Call... On success callback(onResolved); Call... On failure callback(onRejected);
12、promise Custom encapsulation –catch Method – Exception penetration and value passing
In the custom encapsulated Promise Object catch Method :
// add to catch Method Promise.prototype.catch = function (onRejected) { return this.then(undefined, onRejected) }catch Method directly calls the preset then Method , The first parameter passed is undefined, The second parameter is onRejected;
here ,then The first successful callback of the method will not execute ;
Directly accept parameters to execute onRejected The second failed callback .
here , We can use it normally p.catch() as well as p.then() Method ,
however , In the use of p.then().catch() When the method is used , There's a problem :
p.then().catch() Method , In the original promise in , Support us then The second parameter of the method is not passed ;
for example :
p.then(value => { console.log(value) }).catch(reason => { console.warn(reason) })But in our custom promise On the body ,then If the second parameter is not passed, it will be recognized as yes 【undefined】;
This can lead to some errors *️;
So we need to be right about then The second argument to the method 【onRejected】 Judge :
// Determine the callback function parameters if (typeof onRejected !== 'function') { onRejected = reason => { throw reason; } }If the second parameter is not passed , will onRejected Defined as an arrow function , And throw an exception ;
That's right , The second parameter is not transmitted, which is set in advance ,
Do not pass the second parameter ==> Exception thrown by default
This is useful for exception penetration
extraordinary transmission
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject('888')
}, 1000)
})
p.then(value => {
// Do not pass the second parameter , Exception thrown by default
console.log('111')
}).then(value => {
// Do not pass the second parameter , Exception thrown by default
console.log('222')
}).then(value => {
// Do not pass the second parameter , Exception thrown by default
console.log('333')
}).catch(reason => {
console.warn(reason) // Handle exceptions thrown
})
Value passed
In the original promise On the body , Has the property of value passing ;
in other words ,then The first parameter of the method may not be passed :
p.then().then(value => { console.log('222') }).then(value => { console.log('333') }).catch(reason => { console.warn(reason) })The first one here then Both parameters of the method are not passed , But it still works ;
So in our custom encapsulated Promise On the body , There is no such feature .
We need to make some judgment on the first parameter :
if (typeof onResolved !== 'function') { onResolved = value => value }If then Method does not specify a parameter , Specify a parameter by default , To complete the value transfer .
This effect , Just like the original promise The effect is exactly the same ~
🥤Promise——API
Next, we will expand Promise「 API 」 Custom encapsulation of , About Promise【API】 Some of the Pre knowledge
You can browse JavaScript–【Promise】 Detailed explanation Promise_API
13、promise Custom encapsulation –resolve Method encapsulation
// add to resolve Method
Promise.resolve = function (value) {
// return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (value instanceof Promise) {
value.then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
} else {
resolve(value)
}
})
}
Be careful ️:resolve() The method is not Promise Object instance , But in Promise The object itself .
resolve() The purpose of the method is to quickly create a Promise object .
call :
const p = Promise.resolve('OK') console.log(p)there p It's just one. Promise Instance object .
14、promise Custom encapsulation –reject Method encapsulation
// add to reject Method
Promise.reject = function (reason) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(reason)
})
}
Be careful ️: And resolve() The same way ,reject() It's not in Promise Object instance , But in Promise The object itself .
reject() The purpose of the method is to quickly create a Promise object .
call :
const p = Promise.reject('Error') console.log(p)there p Is a failed Promise Instance object .
15、promise Custom encapsulation –all Method encapsulation
// add to all Method
Promise.all = function (promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Declare variables
let count = 0;
// Save an array of successful results
let arr = [];
// Traverse
for (let i = 0; i < promises.length; i++) {
promises[i].then(value => {
// Knowing the state of the object is successful
count++;
// Will the current promise The successful result of the object is stored in the array
arr[i] = value;
if (count === promises.length) {
// Every promise All objects are successful
resolve(arr)
}
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
}
})
}
Be careful ️:
all() The characteristic of the method is :
All the incoming promise All objects are successful ,all Method promise Objects are successful ,
And the successful values are all passed in promise An array of successful values of the object .
=【 Split line 】=
As long as the incoming promise One of the objects is a failure , that all Method promise The result of the object is failure ;
And the failed value is the one passed in promise The value of the result of .
call all() Method :
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { resolve('OK') }) let p2 = Promise.resolve('Success') let p3 = Promise.resolve('Oh Yeah') let result = Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]) console.log(result)result The printing result is successful Promise object , The value is [‘OK’,‘Sueccess’,‘Oh yeah’] Array .
16、promise Custom encapsulation –race Method encapsulation
️
race() The characteristic of the method is :
Incoming promise An array of objects as parameters , All of the promise object ,
Who changes the state first ,race() Method promise The state of is who .
such as :Promise.race([p1, p2, p3]) among ,p1, p2, p3 Are all promise Object of type
if p1 This promise Change the state first , And the status is failed ;
that , This race() Method returns a result of promise object , The status is also failed ;
race() The method can be understood as 【 compete in speed 】, That is, the incoming multiple promise Race between objects , Who changes the state first , Who decides race() The one returned by the method promise.
// add to race Method
Promise.race = function (promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
for (let i = 0; i < promises.length; i++) {
promises[i].then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
}
})
}
Use Promise.race()
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('OK') }, 1000) }) let p2 = Promise.resolve('Success') let p3 = Promise.resolve('Oh Yeah') let result = Promise.race([p1, p2, p3]) console.log(result)result The result is : The success of promise object , The successful value is ’Success’
17、promise Custom encapsulation –then Asynchronous execution of method callback
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('OK')
console.log('111')
})
p1.then(value => {
console.log('222')
})
console.log('333')
Under normal circumstances , Native Promise Medium then Method is executed asynchronously ;
So the output order should be :
111
333
222
as a result of ,then Methods are executed asynchronously inside , Only after the synchronization code is executed , Asynchronous 222 Will be output .
however , Use our custom encapsulated promise after , The order of output is :
111
222
333
The reason is that we are not right then Method to set the callback asynchronously , So we need to make some improvements .
In the declared resolve And reject Function , Set up asynchrony for calling callbacks :
resolve = (data) => {
// Determine whether the status has been changed
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
// Call successful callback
setTimeout(() => {
this.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved()
})
})
}
reject = (data) => {
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
this.PromiseResult = data
// Call failed callback
setTimeout(() => {
this.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved()
})
})
}
In the custom then In the method , Call callback to set asynchronism :
// Call callback function
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onResolved)
})
}
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onRejected)
})
}
thus , We customized this then Methods are the same as native Promise Of then The method is the same in performance .
Console output :
111
333
222
18、promise Custom encapsulation –class Implementation of version
So here , We customize this package Promise Some related functions have been completed .
Next , This will make us Promise Encapsulate as a class class .
class Promise {
// Construction method
constructor(executor) {
// Add attribute
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = null;
// Declarative attribute
this.callbacks = [];
// To save an instance object this
const self = this;
// Statement resolve and reject function
function resolve(data) {
// Determine whether the status has been changed
if (self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled' // resolved
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data
// Call successful callback
setTimeout(() => {
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onResolved()
})
})
}
function reject(data) {
if (self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 1. Modify the state of the object (promiseState)
self.PromiseState = 'rejected'
// 2. Set the object result value (promiseResult)
self.PromiseResult = data
// Call failed callback
setTimeout(() => {
self.callbacks.forEach(item => {
item.onRejected()
})
})
}
try {
// Actuator functions executor Internally, it is called synchronously
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
// modify promise The state of the object is failed
reject(error)
}
}
// add to then Method
then(onResolved, onRejected) {
// Determine the callback function parameters
if (typeof onRejected !== 'function') {
onRejected = reason => {
throw reason;
}
}
if (typeof onResolved !== 'function') {
onResolved = value => value
}
const self = this
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
function callback(type) {
try {
// Get the execution result of the callback function
let result = type(self.PromiseResult)
if (result instanceof Promise) {
// If then Inside the specified callback is a Promise Object of type
result.then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
} else {
// If then The callback specified is not internal Promise Object of type ,
// The status is success , The value is the execution result of the callback function , That is, the previously saved result
resolve(result)
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
// Call callback function
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onResolved)
})
}
if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
setTimeout(() => {
callback(onRejected)
})
}
// Judge pending state
if (this.PromiseState === 'pending') {
// Save callback function
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: () => {
callback(onResolved)
},
onRejected: () => {
callback(onRejected)
}
})
}
})
}
// add to catch Method
catch(onRejected) {
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
// add to resolve Method
static resolve(value) {
// return promise object
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (value instanceof Promise) {
value.then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
} else {
resolve(value)
}
})
}
// add to reject Method
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(reason)
})
}
// add to all Method
static all(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Declare variables
let count = 0;
// Save an array of successful results
let arr = [];
// Traverse
for (let i = 0; i < promises.length; i++) {
promises[i].then(value => {
// Knowing the state of the object is successful
count++;
// Will the current promise The successful result of the object is stored in the array
arr[i] = value;
if (count === promises.length) {
// Every promise All objects are successful
resolve(arr)
}
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
}
})
}
// add to race Method
static race(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
for (let i = 0; i < promises.length; i++) {
promises[i].then(value => {
resolve(value)
}, reason => {
reject(reason)
})
}
})
}
}

At the end
Last , We have completed the encapsulation of a native Promise object ~
End of the flower
Full text of 18470 word ,1323 That's ok , It took days
Originality is not easy. , Your support will be the driving force of my creation
Follow the likes collection
Code out the future !
边栏推荐
- A tip to read on Medium for free
- threejs辉光通道01(UnrealBloomPass && layers)
- 4274. 后缀表达式
- GradScaler MaxClipGradScaler
- 数据中台:中台实践与总结
- 【牛客】把字符串转换成整数
- 1704. judge whether the two halves of a string are similar
- Database migration from PostgreSQL to MySQL
- Transplantation of xuantie e906 -- fanwai 0: Construction of xuantie c906 simulation environment
- 剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度-dfs法
猜你喜欢

Target detection series fast r-cnn

阿里资深软件测试工程师推荐测试人员必学——安全测试入门介绍

OpenCV每日函数 结构分析和形状描述符(7) 寻找多边形(轮廓)/旋转矩形交集

Leetcode -- wrong set
![[quantitative investment] discrete Fourier transform to calculate array period](/img/0d/aac02463ff403fb1ff871af5ff91fa.png)
[quantitative investment] discrete Fourier transform to calculate array period

The list of open source summer winners has been publicized, and the field of basic software has become a hot application this year

opencv最大值滤波(不局限于图像)

Prompt code when MySQL inserts Chinese data due to character set problems: 1366

Linux (centos7.9) installation and deployment of MySQL Cluster 7.6

Opencv maximum filtering (not limited to images)
随机推荐
[noi Simulation Competition] send (tree DP)
数据中台:数据治理概述
The form image uploaded in chorme cannot view the binary image information of the request body
Camera projection matrix calculation
金仓KFS replicator安装(Oracle-KES)
Remote connection of raspberry pie without display by VNC viewer
How to import MDF and LDF files into MySQL workbench
Linux (centos7.9) installation and deployment of MySQL Cluster 7.6
听说你还在花钱从网上买 PPT 模板?
Pytoch read data set (two modes: typical data set and user-defined data set)
Floating error waiting for changelog lock
Huawei Router: IPSec Technology
The list of open source summer winners has been publicized, and the field of basic software has become a hot application this year
Ordinary people have no education background. Can they earn more than 10000 yuan a month by Self-taught programming?
I heard that you are still spending money to buy ppt templates from the Internet?
4274. suffix expression
Analyze the meaning of Internet advertising terms CPM, CPC, CPA, CPS, CPL and CPR
Essay - Reflection
MySQL | 视图《康师傅MySQL从入门到高级》笔记
Determination of monocular and binocular 3D coordinates